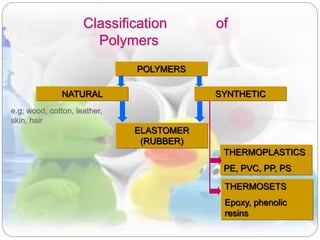
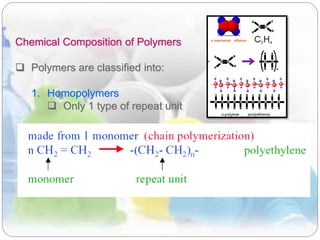
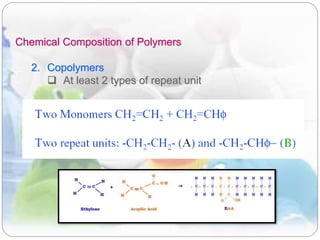
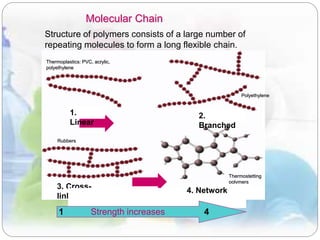
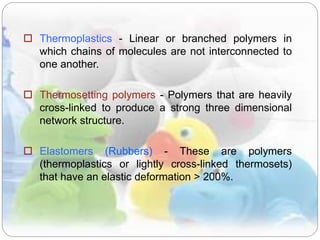
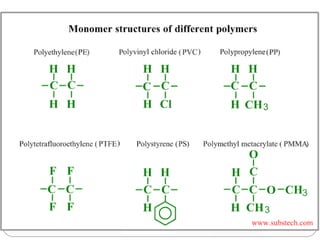
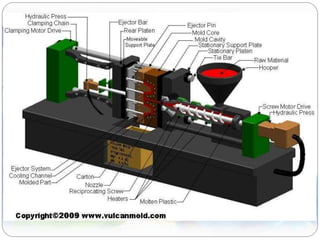
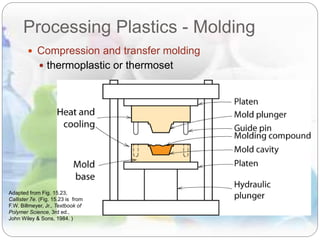
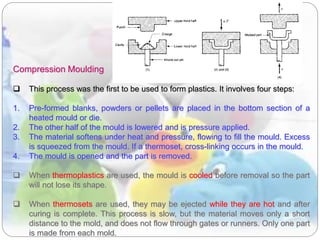
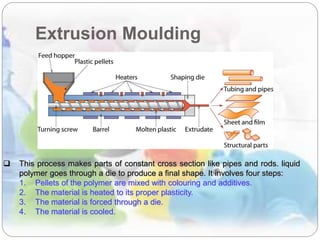
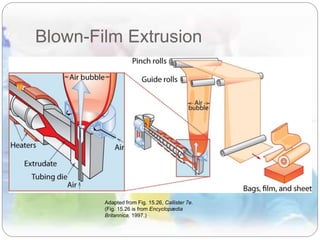
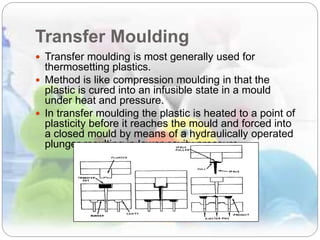
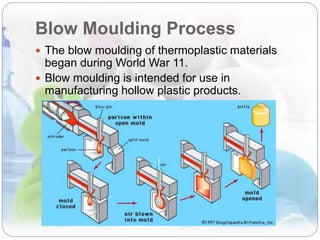
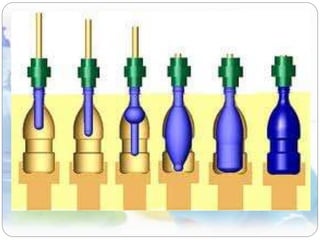
This document discusses plastics and polymers. It begins by defining polymers as large organic molecules made of repeating units linked in chains. It then classifies polymers as thermoplastics, thermosets, or elastomers. The document describes common thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers and their applications. It also summarizes several common plastic processing methods like injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, and compression molding.