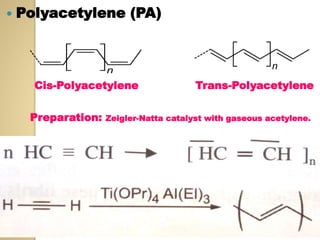
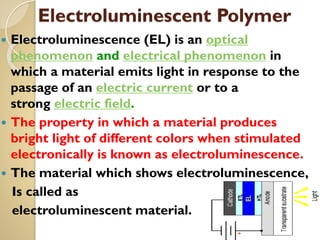
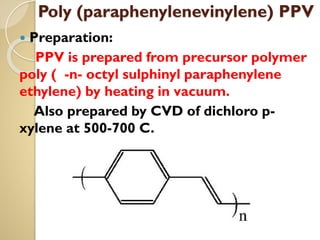
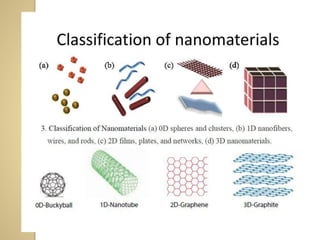
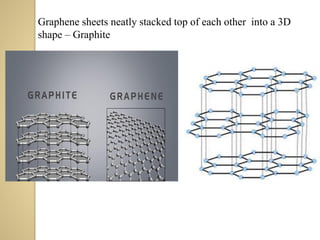
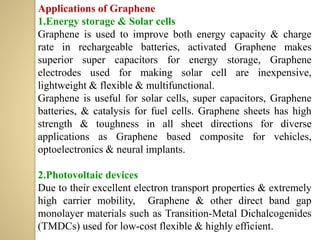
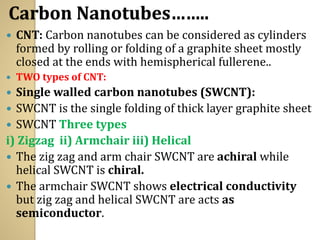
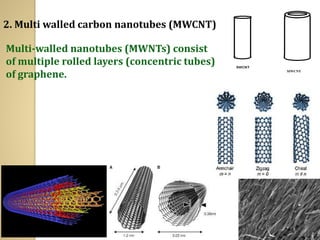
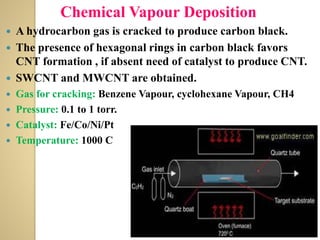
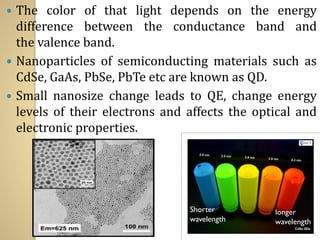
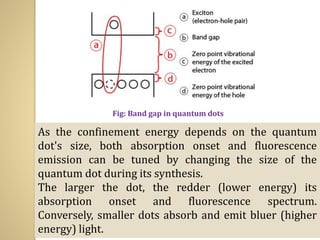
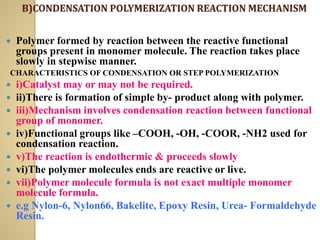
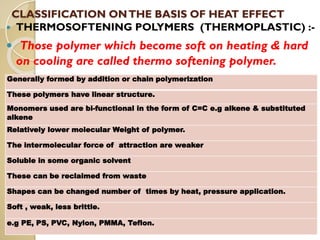
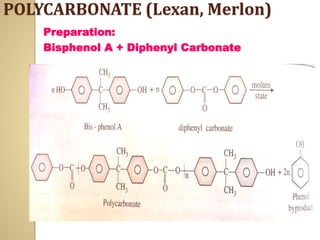
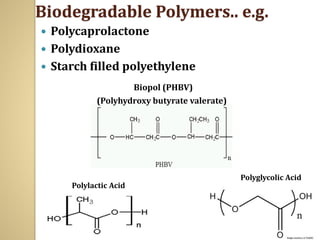
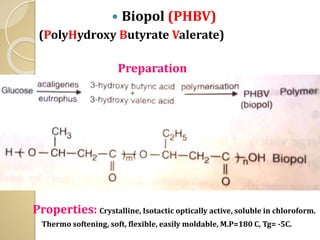
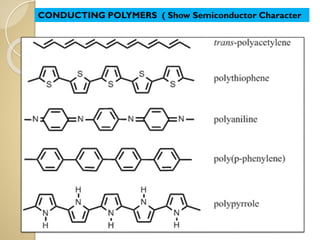
Synthetic polymers are widely used as substitutes for materials like metals, wood, cotton and glass. They have properties like low density, resistance to chemicals, flexibility and the ability to be molded into different shapes. Common synthetic polymers include polyethylene, polyester, nylon and polypropylene. Polymers can be thermoplastics, which soften when heated and harden when cooled, allowing reshaping, or thermosets, which remain rigid. Conductive polymers can transport electricity through conjugated pi electrons on their backbone, making them semiconductors when doped. Applications include medical devices, packaging and conductive fabrics.
























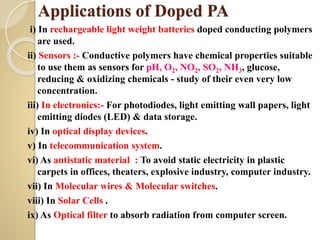
![ EXTRINSIC CONDUCTOR :-
If the polymers are made conducting by doping
it is called extrinsic conductors. There are two
types,
A]P-TYPE DOPING OR OXIDATIVE DOPING :-
i) Doping of suitable oxidizing agent to
conjugated polymer chains. (Lewis acid like I2,
Br2, FeCl2, PF6)
ii) The oxidizing agents extract a pair of π
electrons from chain & make it a positively
charged cation.
iii) Delocalization of positive charge (hole)
takes place over the whole polymer chain & it
becomes conducting.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-3engineeringmaterials-210415054659/85/Engineering-materials-Polymer-33-320.jpg)
![B] N-TYPE DOPING OR REDUCTIVE DOPING
i) A suitable reducing agent lewis base (Na, Li, K,
Metals, napthyl amines) are added to conjugated
polymer chain which donate a pair of electron to
polymer chain.
ii) This makes the polymer chain negatively
charged anion & it becomes conducting.
e.g. Polyacetylene + Na
iii) This is called reductive doping because polymer
chain has accepted electrons from the metal atom.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-3engineeringmaterials-210415054659/85/Engineering-materials-Polymer-34-320.jpg)