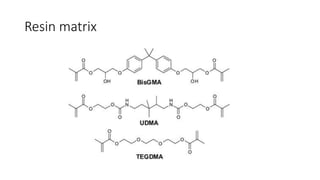
This document provides an introduction to polymer composites. It defines composites as materials made of two or more chemically and physically distinct phases separated by a distinct interface. Composites combine materials to achieve properties not attainable by the individual components alone. The matrix phase holds the dispersed reinforcing phase and shares the applied load. Polymer composites offer advantages like high strength and stiffness, as well as good impact and corrosion resistance. Properties depend on factors like interfacial adhesion between phases, shape and orientation of the dispersed phase, matrix properties, and size and concentration of the dispersed phase. Processing methods for polymer composites include hand lay-up, injection molding, and pultrusion. Dental composites contain resin