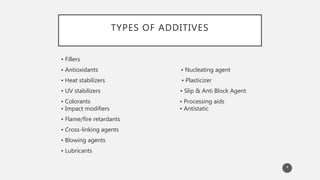
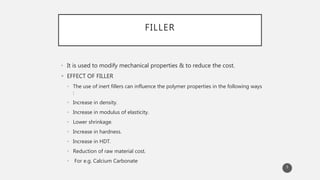
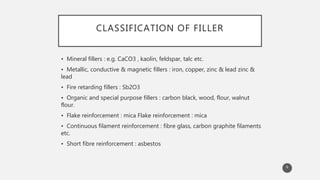
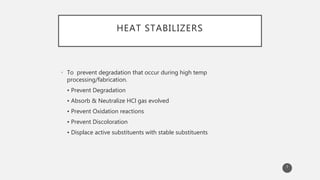
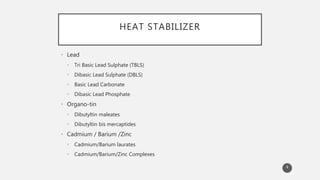
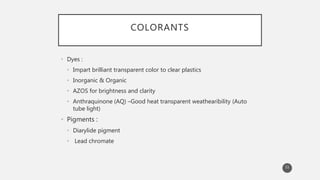
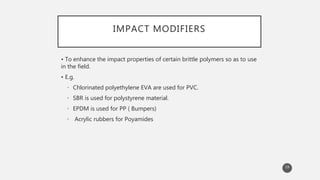
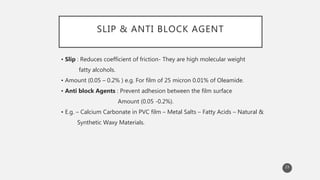
The document outlines the role and types of additives used in plastics, which are substances added to enhance properties, processing, and cost-effectiveness of resins. Key categories mentioned include fillers, heat stabilizers, UV stabilizers, colorants, antistatic agents, and flame retardants, each serving specific purposes such as improving mechanical strength, preventing degradation, and reducing electrostatic charges. The document also describes the working mechanisms and examples of various additives and their effects on plastic materials.