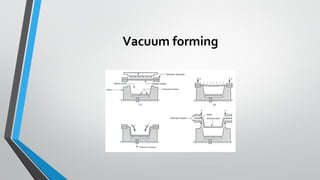
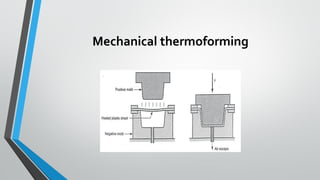
Thermoforming is a manufacturing process where sheets of thermoplastic are heated until soft, formed into shapes using molds, and trimmed. There are three main types - vacuum forming uses suction to draw the plastic against molds, pressure forming uses compressed air, and mechanical forming uses movable molds. Common materials are ABS, polyethylene, and PVC. Applications include food packaging, automotive parts, aircraft windows, and more.