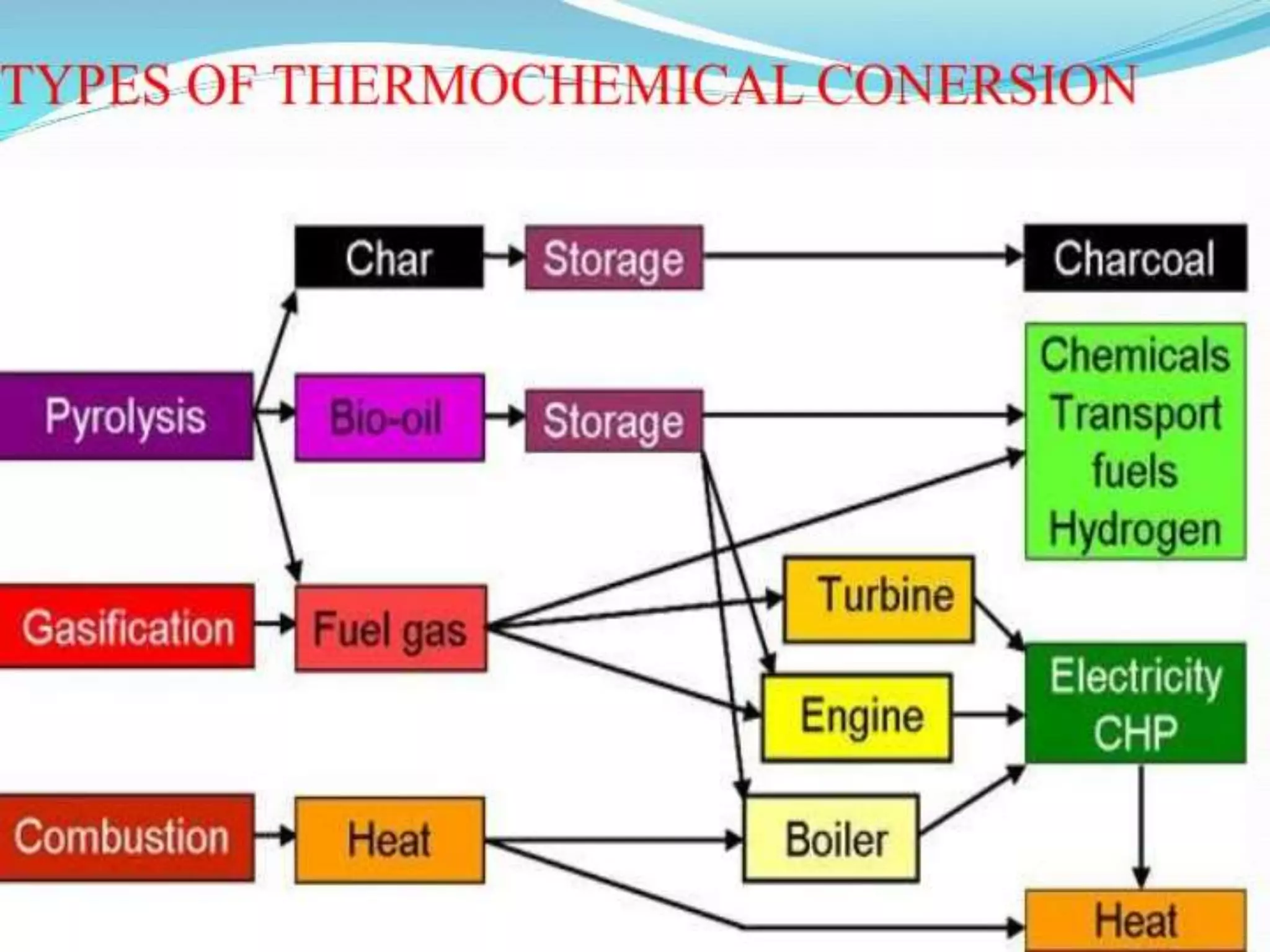
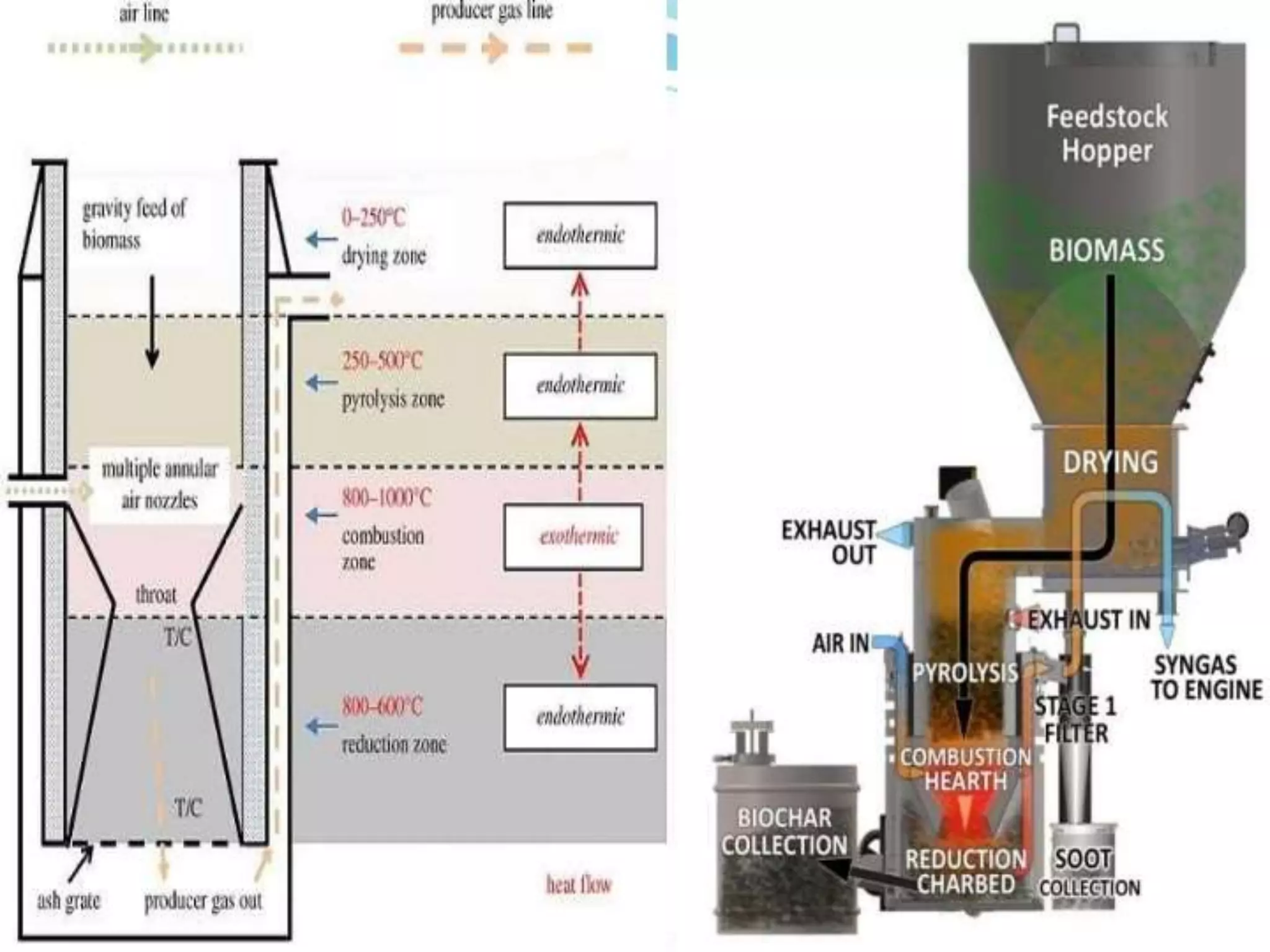
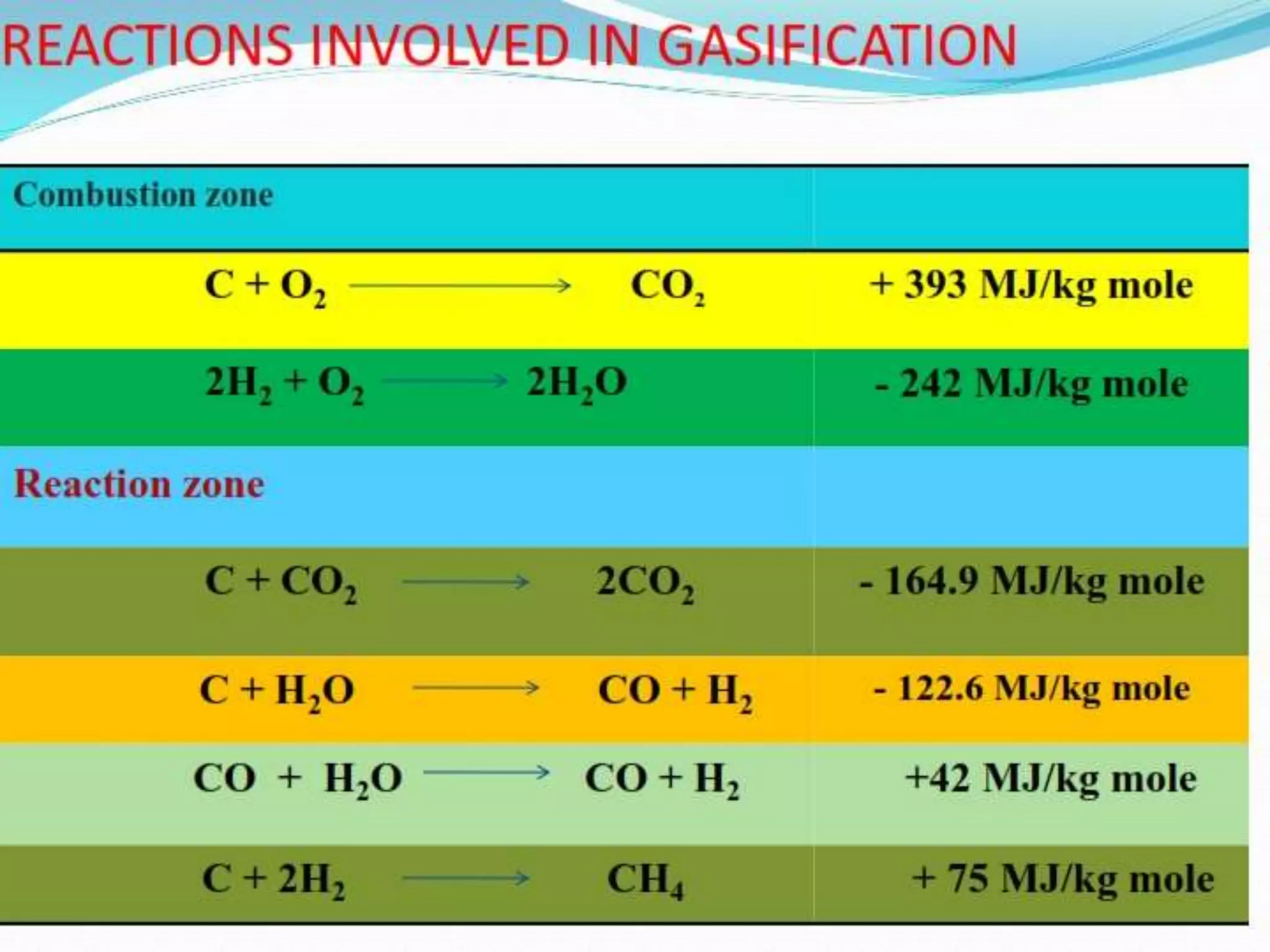
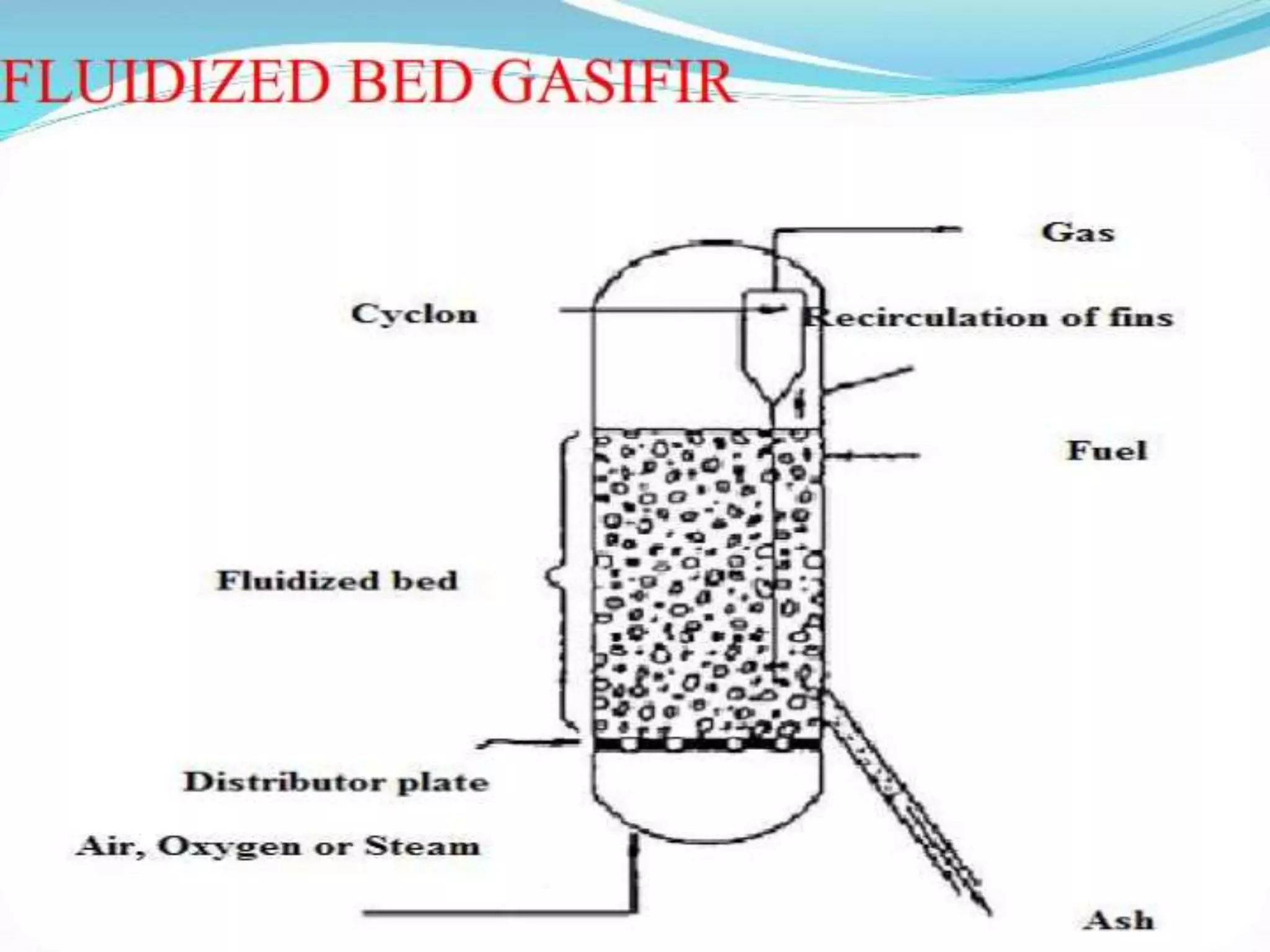
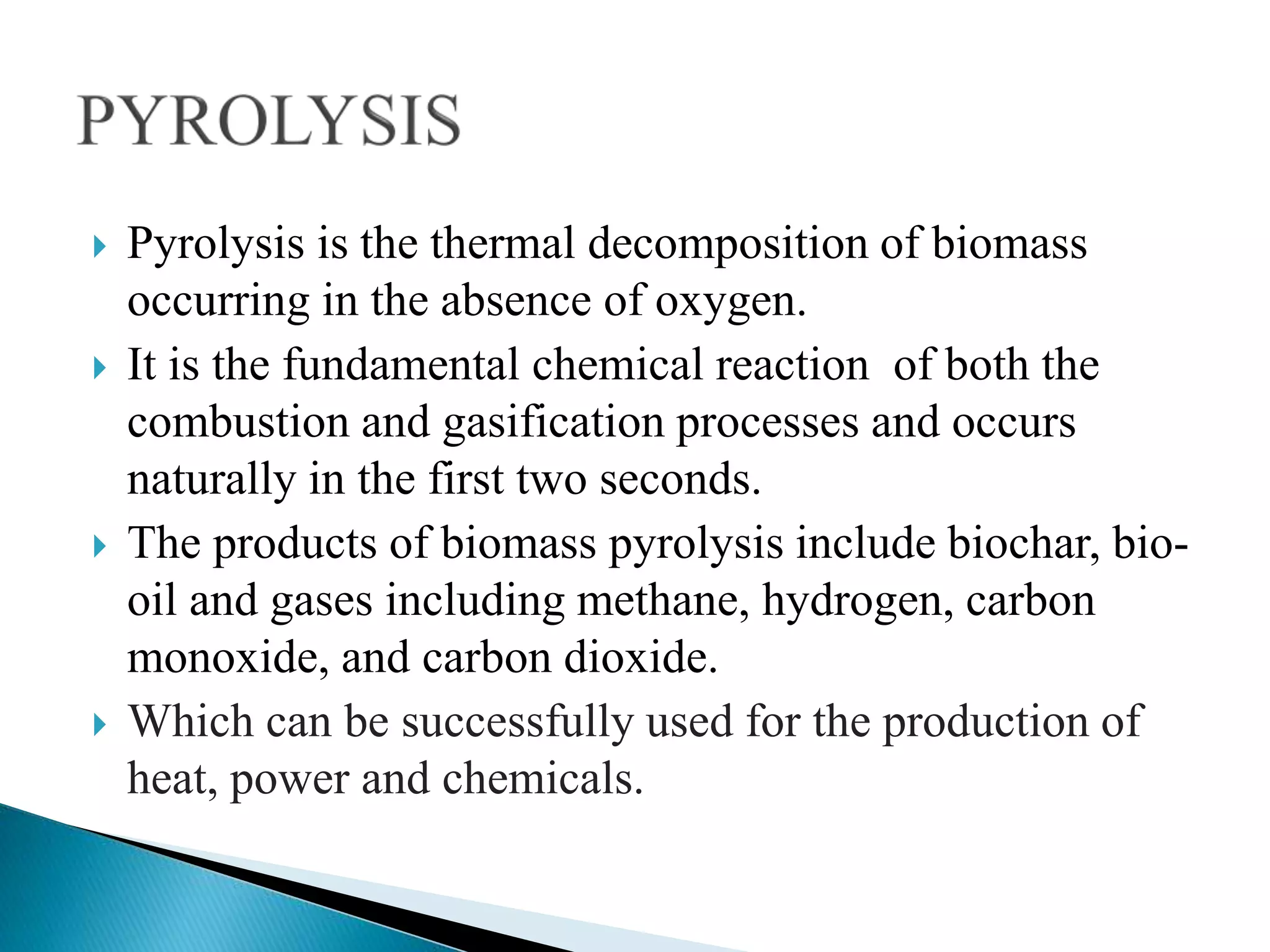
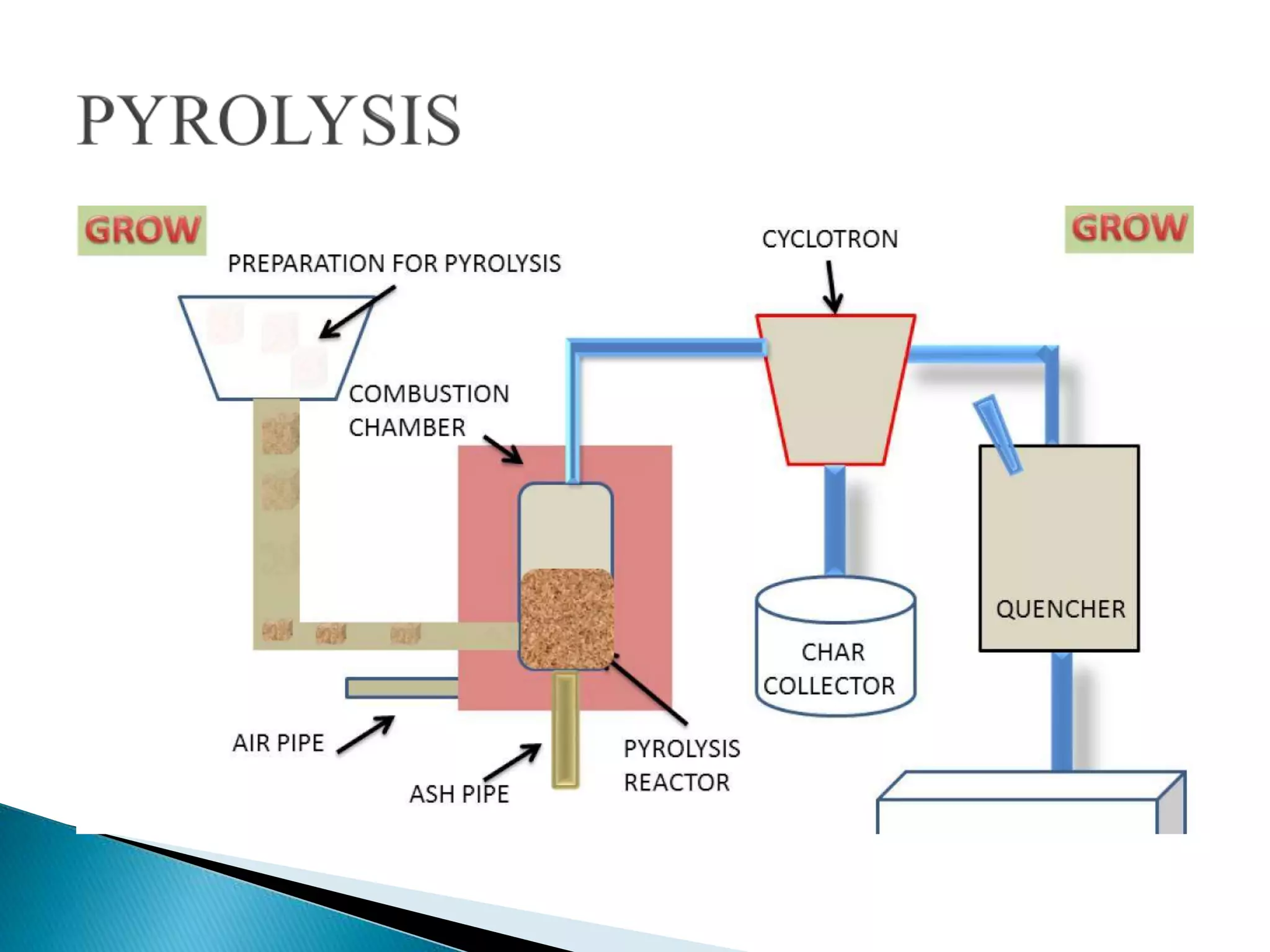
Thermo chemical conversion involves the biological, chemical, and thermal breakdown of biomass. Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of biomass through heating in the absence of oxygen, producing biochar, bio-oil, and gases. Pyrolysis can occur through slow or fast processes, with fast pyrolysis taking seconds and yielding mainly bio-oil, while slow pyrolysis takes hours and produces primarily biochar. Pyrolysis is dependent on temperature and particle size, and can convert biomass into easily stored and transported liquid fuels or soil amendments like biochar.