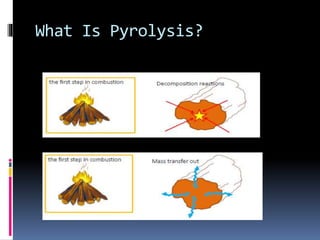
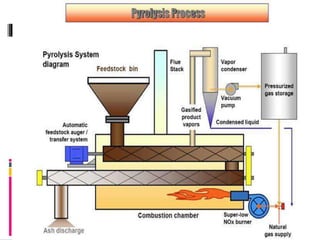
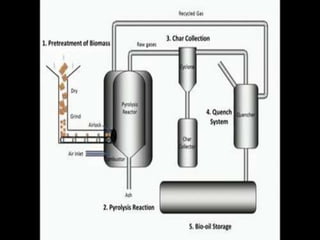
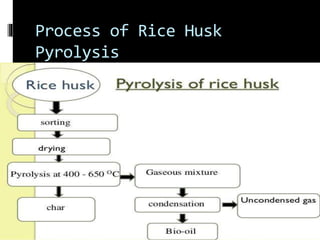
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that decomposes organic materials into bio-oil, bio-char, and syngas at high temperatures in the absence of oxygen. It encompasses slow and fast pyrolysis methods, with the latter producing a higher yield of bio-oil in a shorter time. This technology offers environmental benefits, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions and waste, although it faces challenges related to market development for its products.