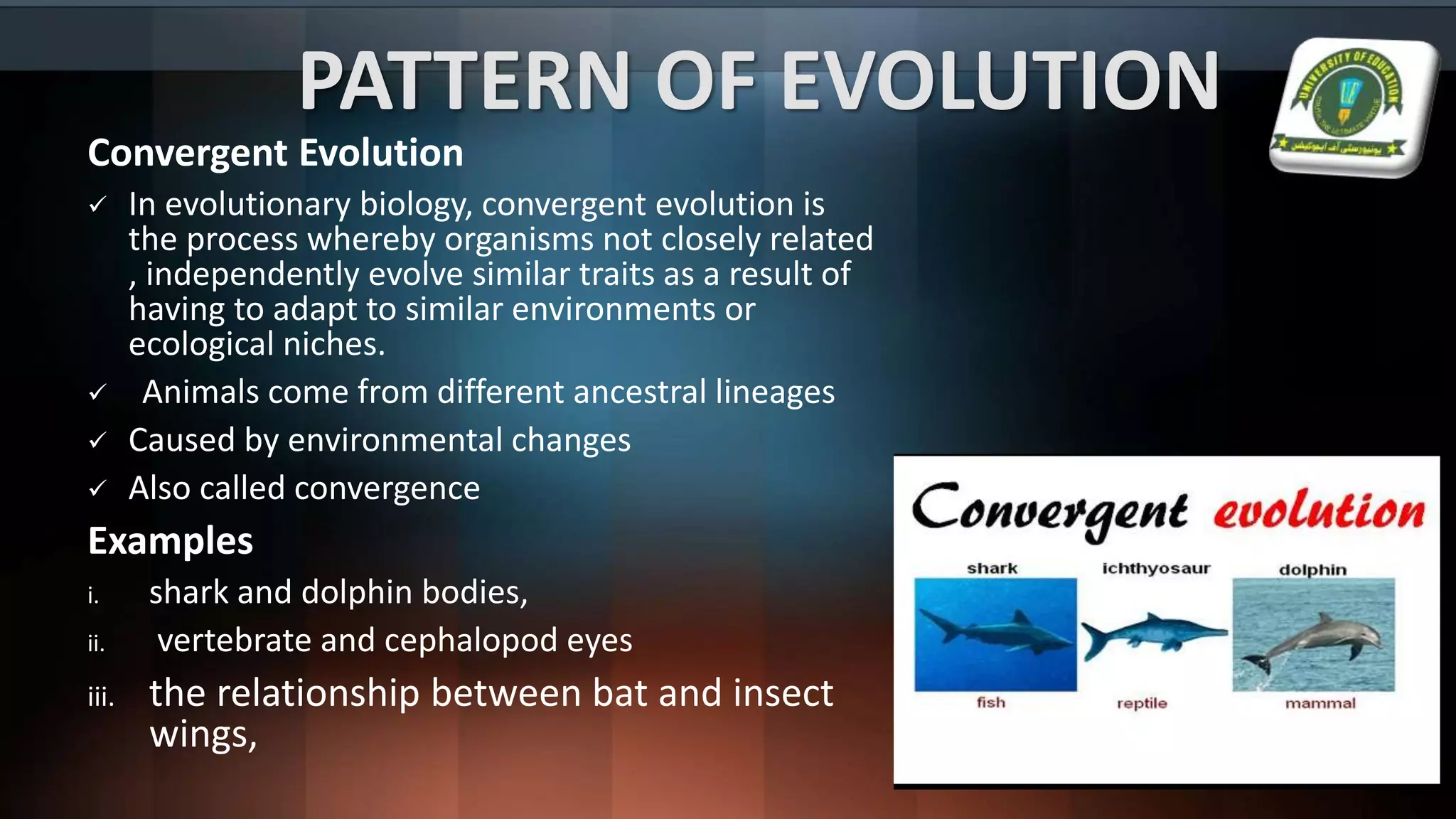
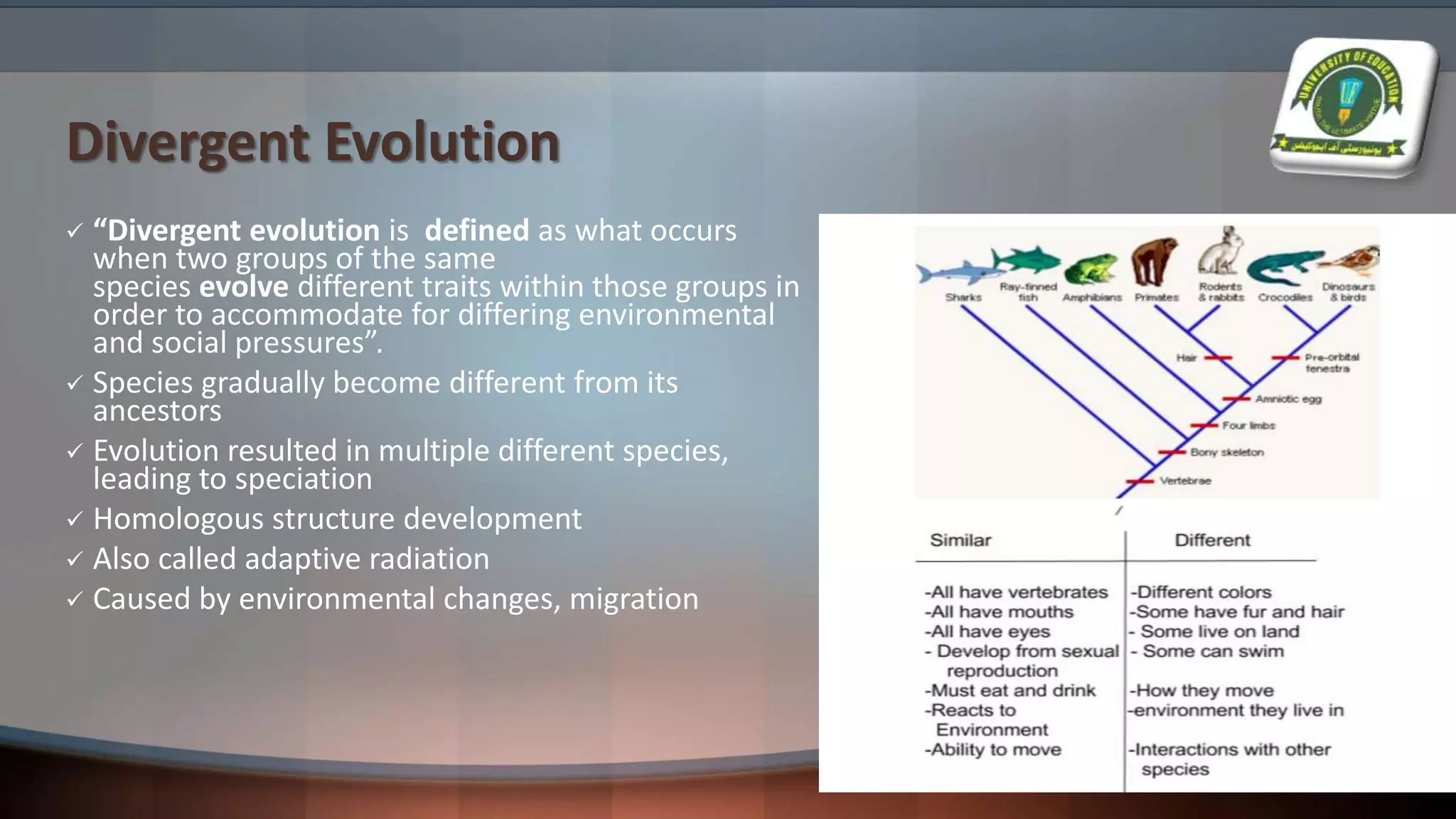
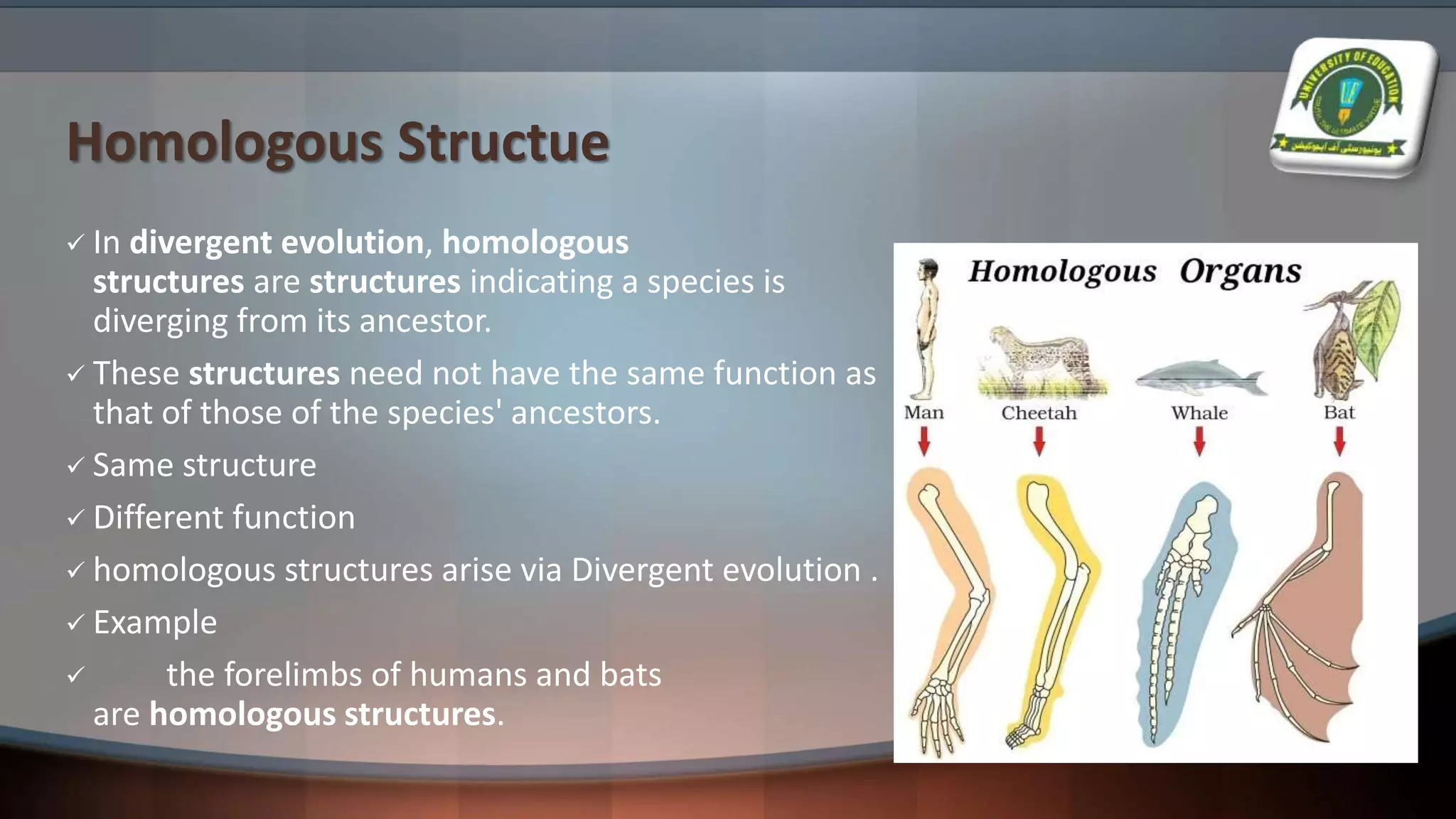
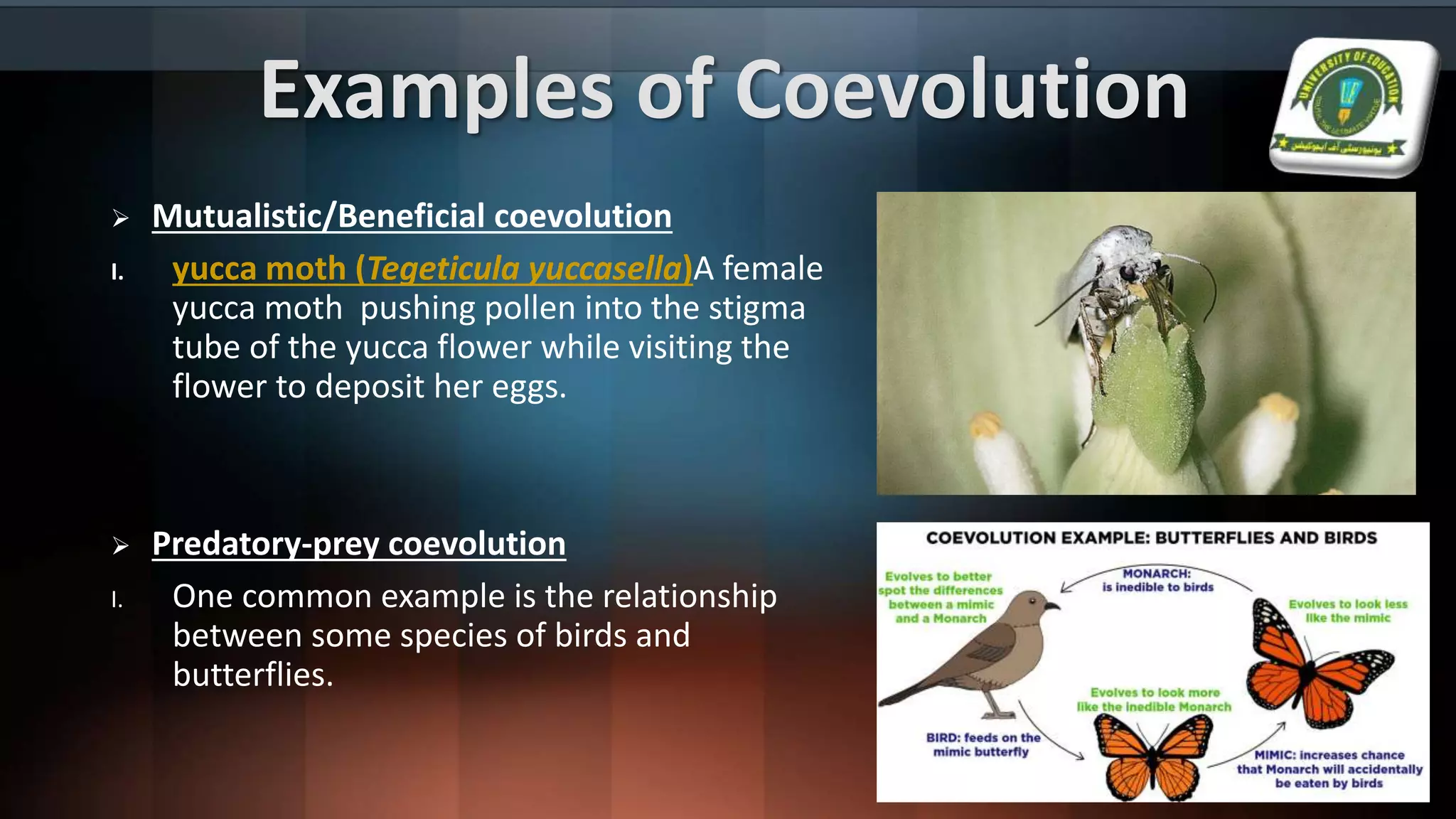
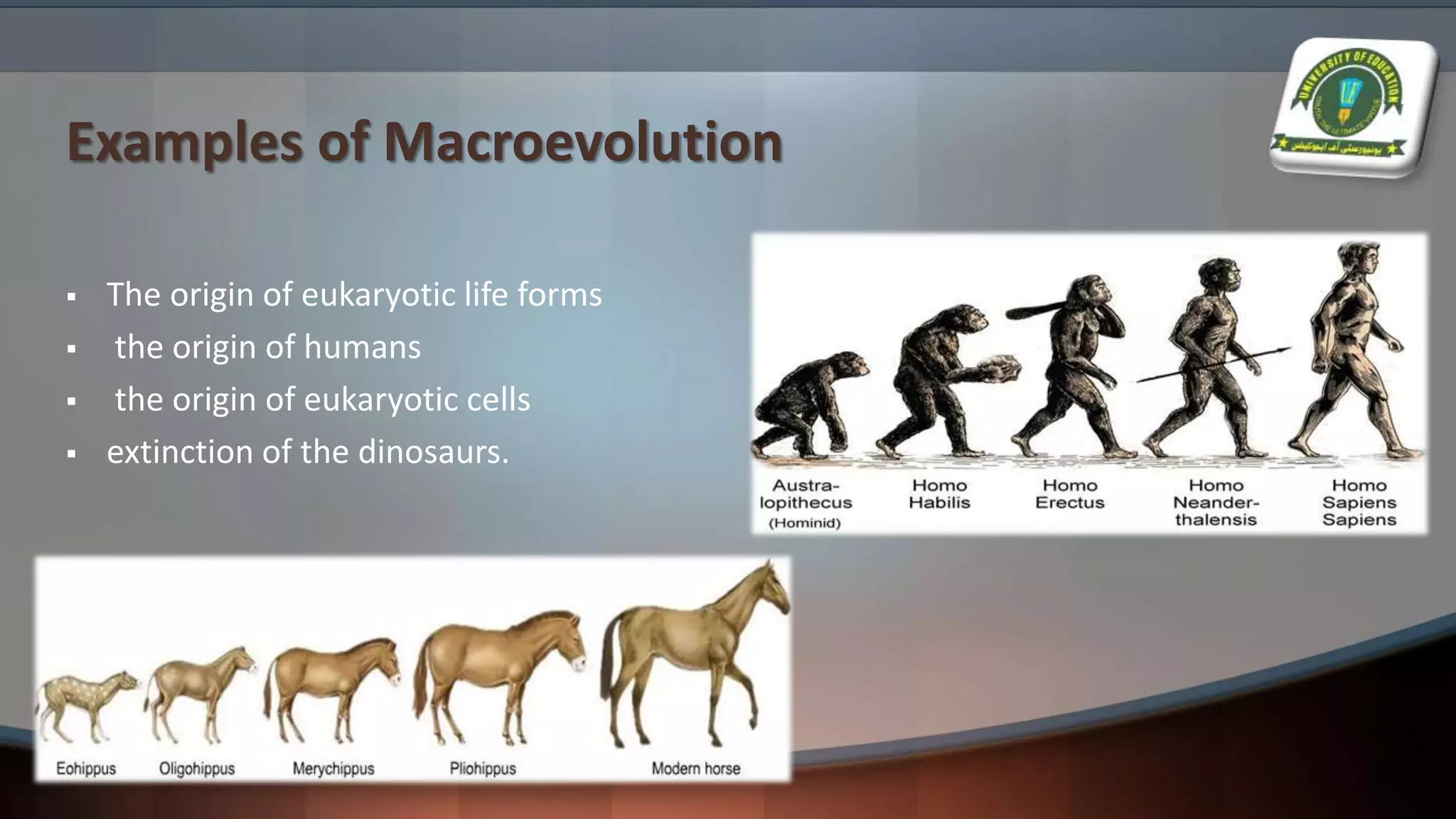
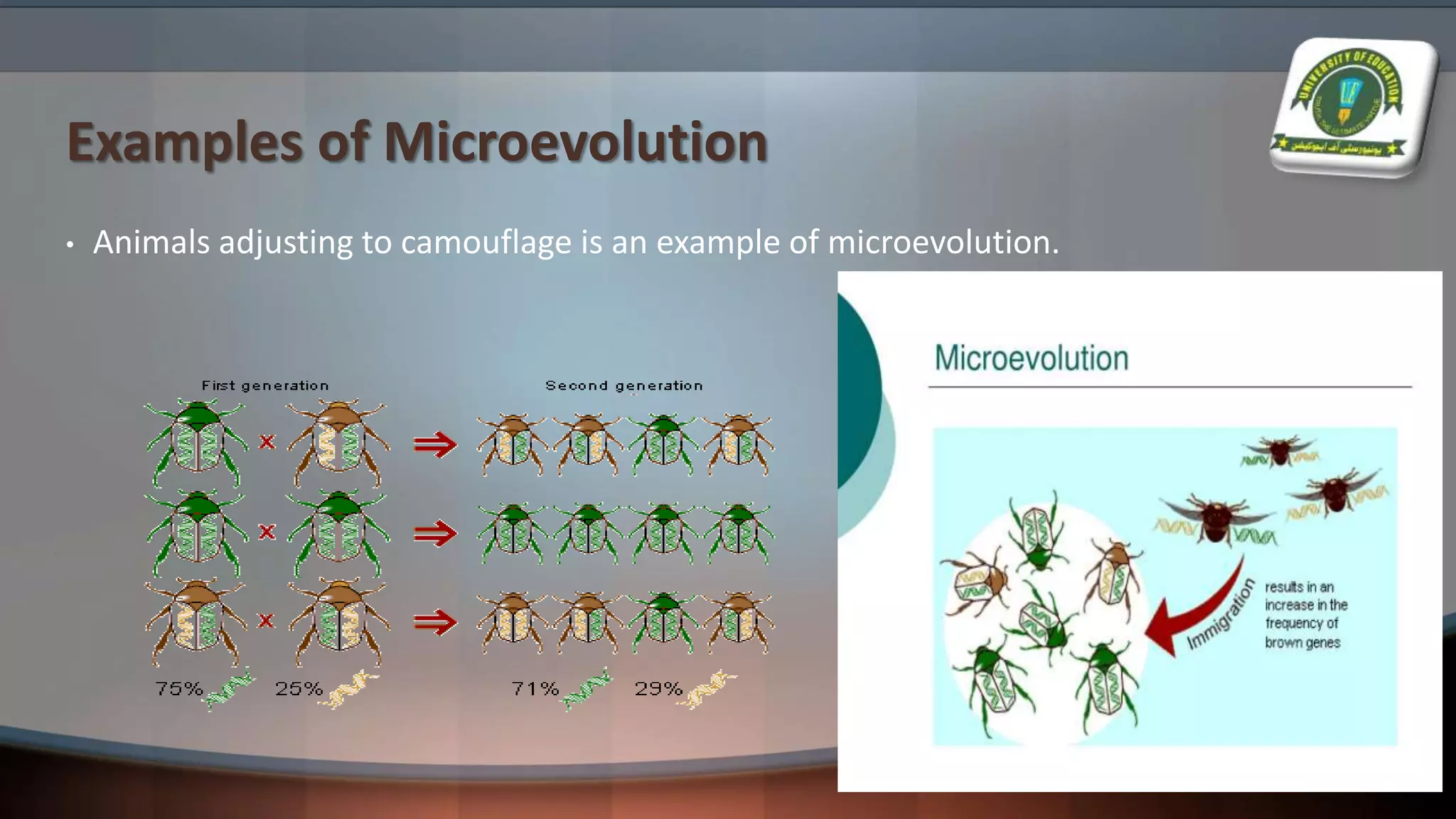
The document details various evolutionary patterns, including convergent, divergent, and parallel evolution, along with coevolution and their implications on species adaptation and diversity. It explains how organisms change over time, leading to speciation and the emergence of analogous and homologous structures. Additionally, it distinguishes between macroevolution and microevolution, highlighting their roles in the broader context of biological diversity and adaptation.