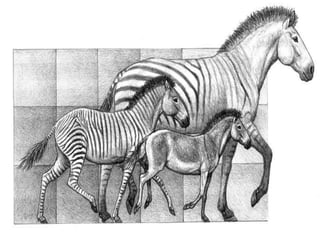
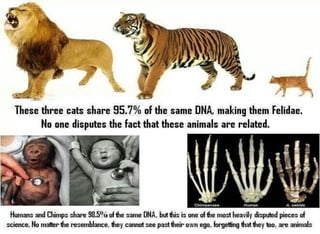
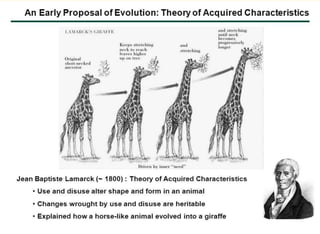
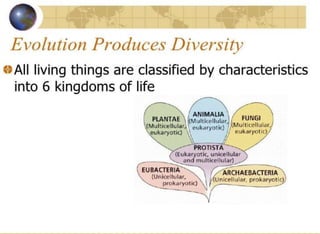
The document discusses the theory of evolution, highlighting key figures such as Pierre Louis Maupertuis, Karl Ernst von Baer, Thomas Malthus, Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, Charles Darwin, and Alfred Russel Wallace, who contributed to our understanding of adaptation and natural selection. It explains various mechanisms of evolution, including natural selection, genetic hitchhiking, and types of reproductive isolation, along with definitions of adaptations. The last universal common ancestor is also mentioned as the earliest ancestor of all current life on Earth.