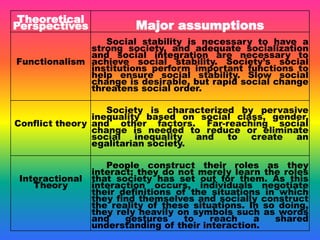
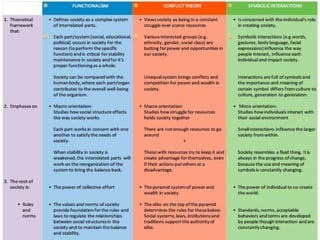
Conflict theory sees education as perpetuating social inequality by providing greater resources to schools in affluent districts, giving those students advantages. It argues that standardized tests exhibit cultural bias and are used to track students into different levels of education and careers. Critics say conflict theory takes too negative a view and does not acknowledge positive aspects of society. Functionalism sees education as socializing students and imparting skills and knowledge to benefit society. It argues education preserves culture but also changes it. Interactional theory focuses on day-to-day interactions in schools and how teacher expectations influence students, rather than larger social forces.