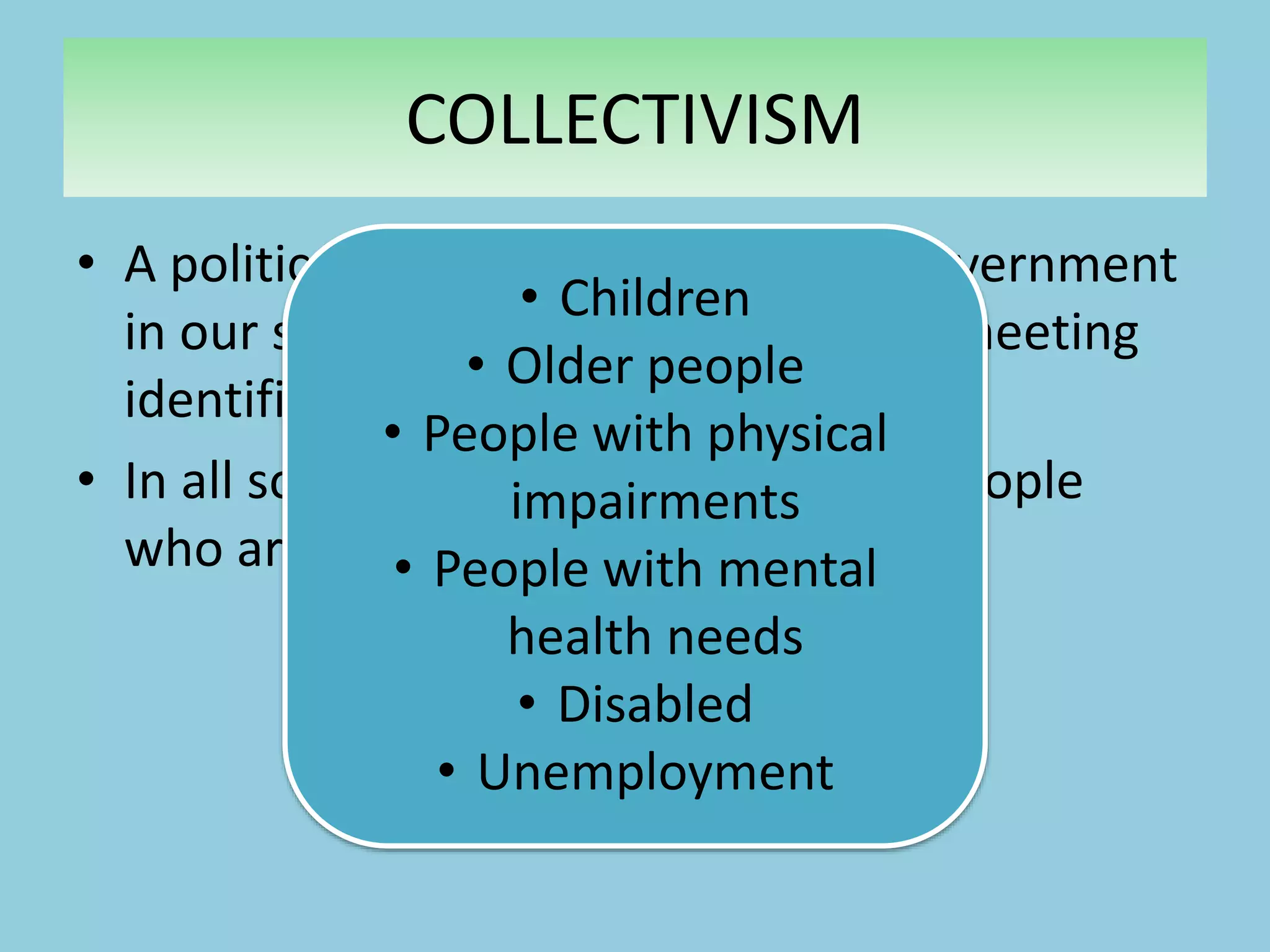
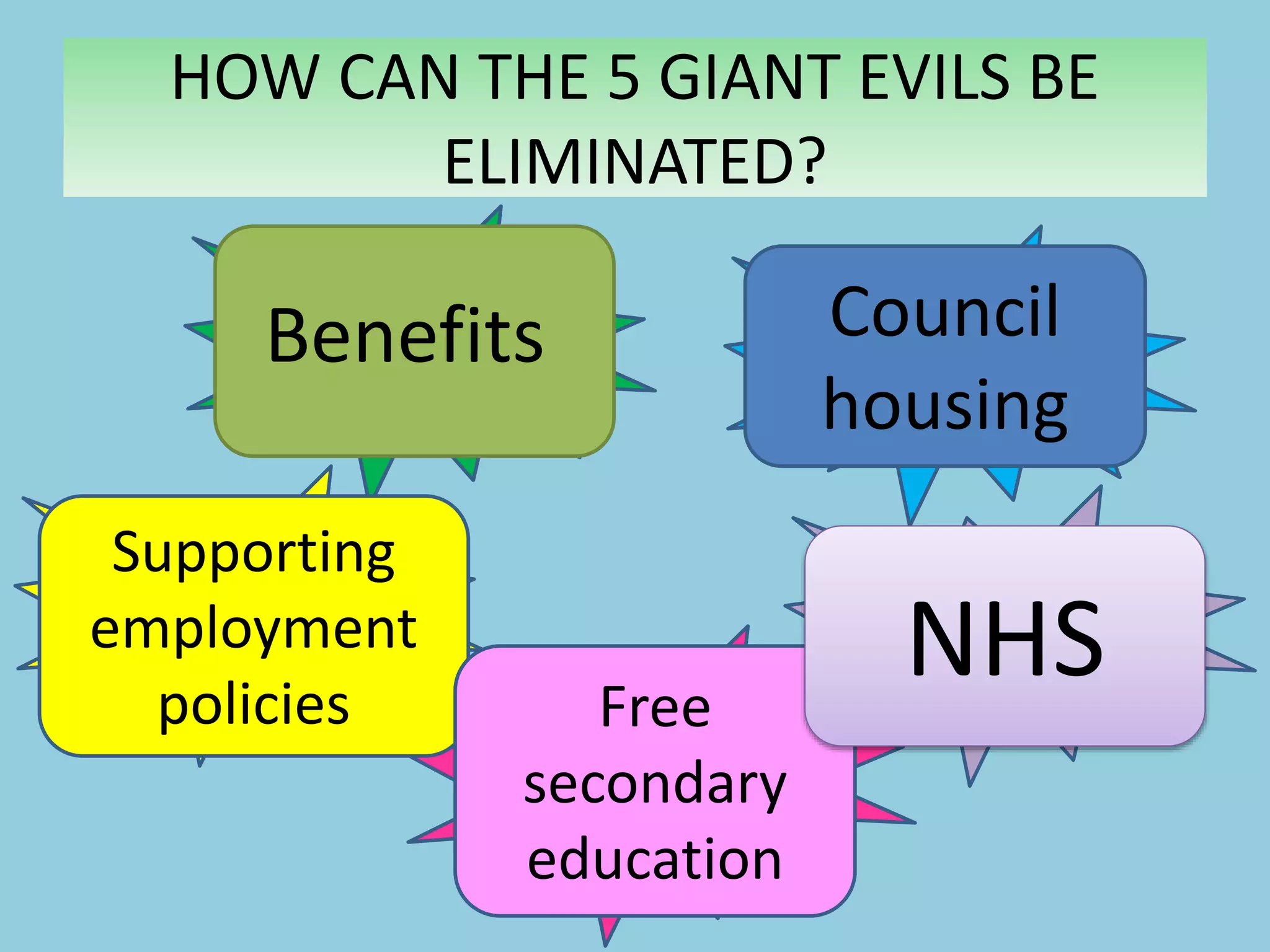
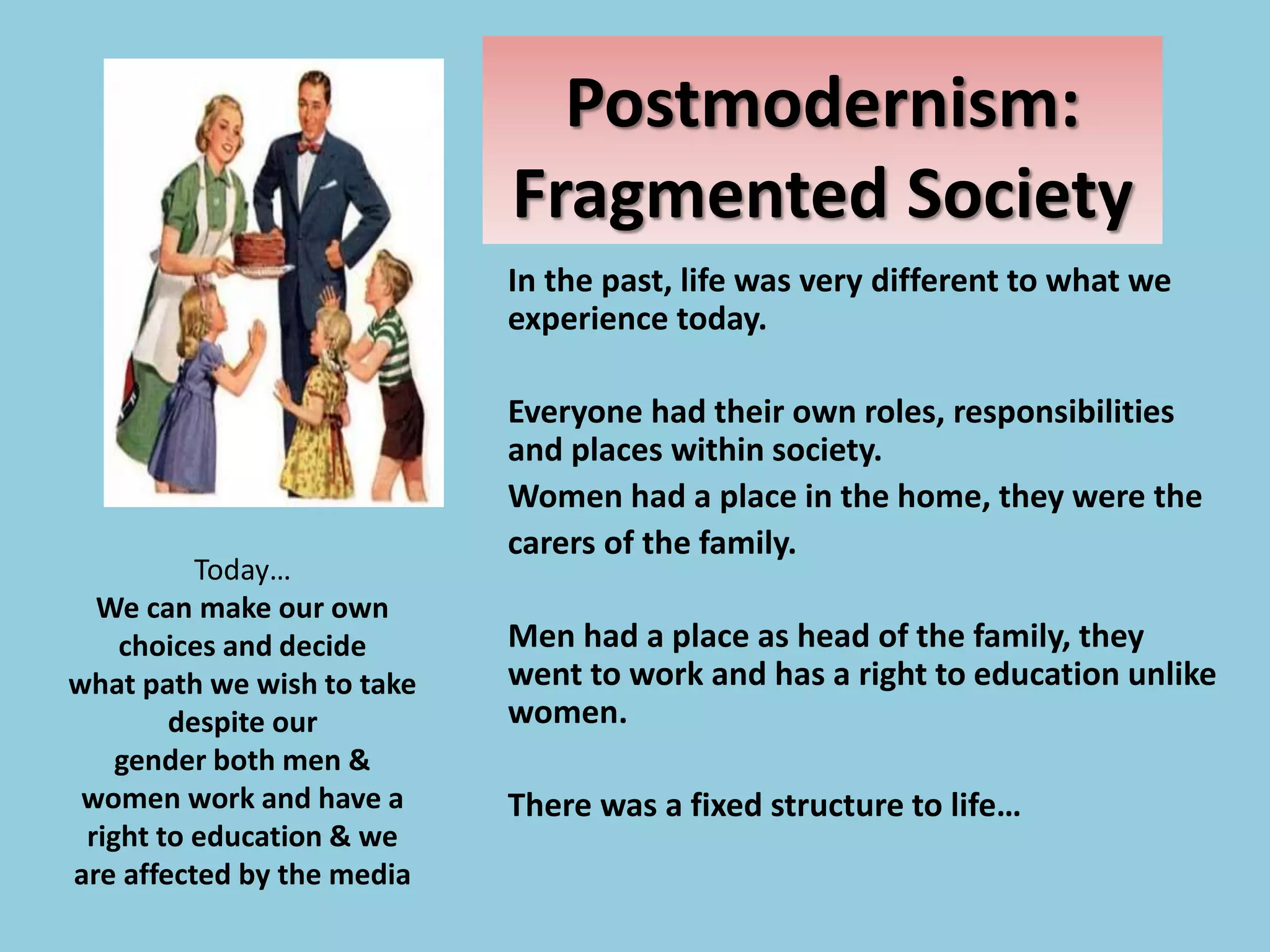
Collectivism views society as collectively responsible for meeting the needs of vulnerable groups through taxation and national insurance. It aims to eliminate poverty, idleness, disease, squalor, and ignorance. The New Right emerged in the 1980s advocating for smaller government and individual responsibility over welfare. Postmodernism sees society as uncertain and fragmented without stable institutions due to rapid change. It believes people construct their own identities and make independent choices from a range of options rather than conforming to social roles.