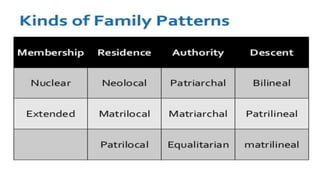
The document outlines characteristics and functions of social institutions, highlighting their purposive, permanent, structured, and value-laden nature. It identifies five essential tasks performed by these institutions: reproduction of members, teaching new members, production and consumption of goods, preservation of order, and providing a sense of purpose. Sociology examines institutions such as family, education, religion, economy, and government through interlocking social roles and the expectations tied to them.