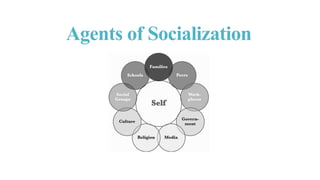
This presentation discusses agents of socialization, which are the social groups and institutions that influence how individuals learn social norms and behaviors. It defines key terms and identifies two main types of socialization - primary through families and secondary through other groups outside the family. The main agents discussed are families, peers, schools, social groups, workplaces, government, media, and religion. Each plays a distinctive role in transmitting culture and socializing individuals. The conclusion is that while socialization agents significantly shape people, individuals also have their own agency and can negotiate social influences based on their unique contexts.