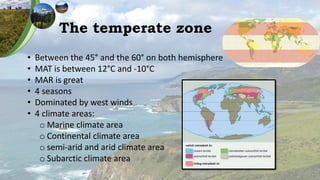
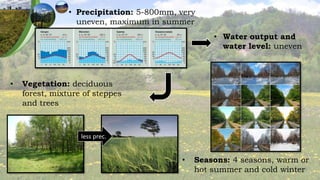
The document describes the various climate areas within the temperate zone, including the marine climate area, continental climate area, semi-arid and arid climate areas, and subarctic climate area. It discusses key features of each area such as typical temperature and precipitation levels, dominant winds, seasonal patterns, vegetation types, landforms, and soil types. The temperate zone encompasses areas between 45 and 60 degrees latitude in both hemispheres and is characterized by four distinct seasons and a variety of climate influences including proximity to oceans and prevailing wind patterns.