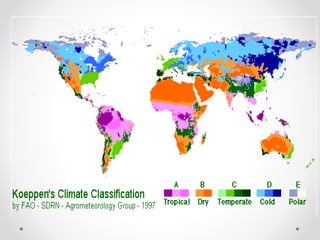
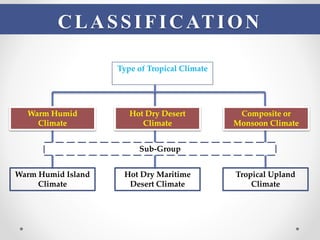
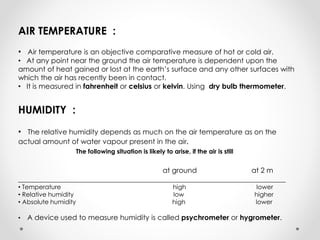
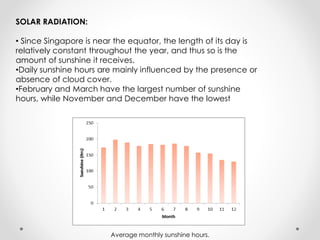
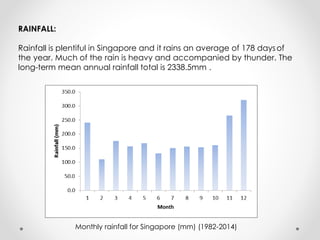
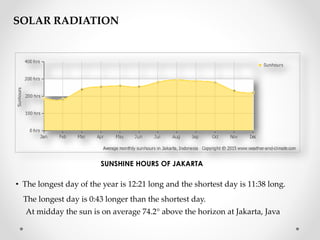
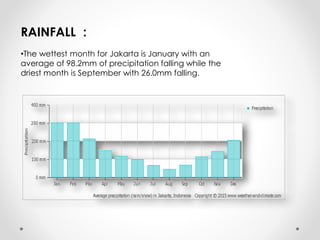
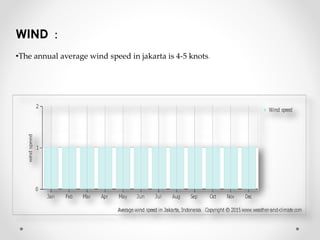
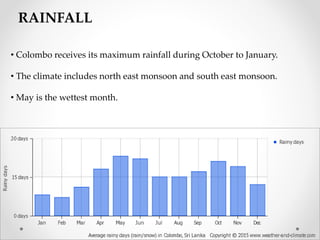
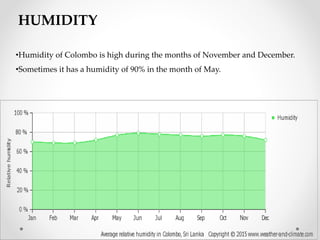
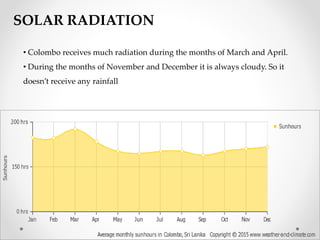
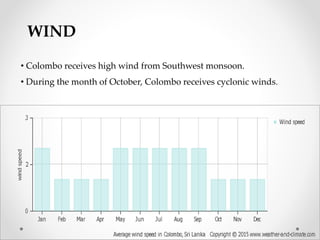
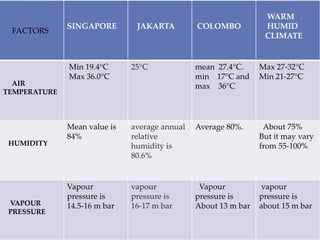
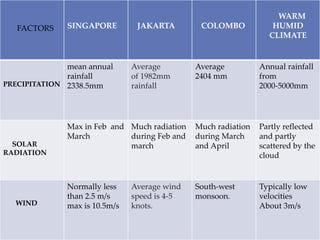
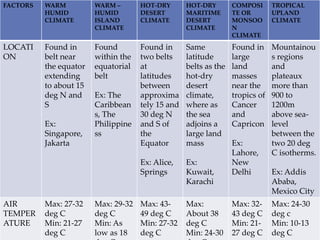
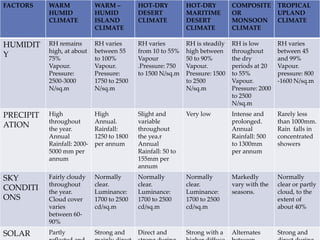
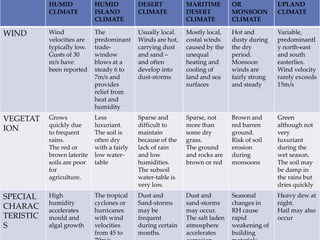
This document describes warm humid climates and compares examples in different locations. It discusses key climate elements for warm humid climates like Singapore, Jakarta, and Colombo including temperature, humidity, rainfall, and wind. Maximum temperatures typically range from 27-32°C while minimums are 21-27°C. Humidity remains high around 75-80% on average. Annual rainfall is usually over 2000mm. Building design recommendations in warm humid zones include maximizing ventilation, shading, and using reflective/ventilated roofs. The climate is suitable for vegetation but soils can be poor for agriculture.