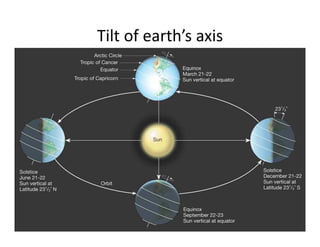
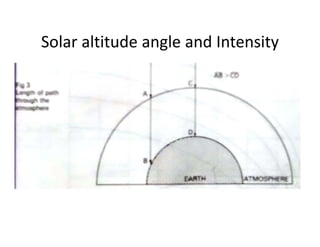
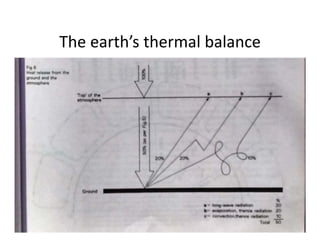
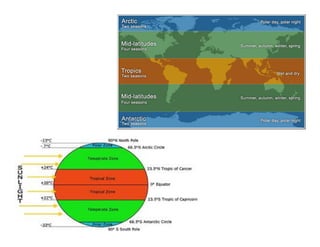
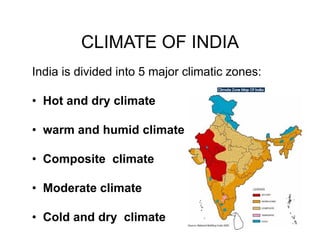
The document discusses climatology, defining climate and the factors that affect it such as solar radiation, the tilt of the Earth's axis, and atmospheric composition. It explains how solar radiation impacts temperature and weather patterns, detailing the Earth's thermal balance and the influence of winds and topography on climate. Additionally, it categorizes the world's major climatic zones and outlines the climate specifics of India.