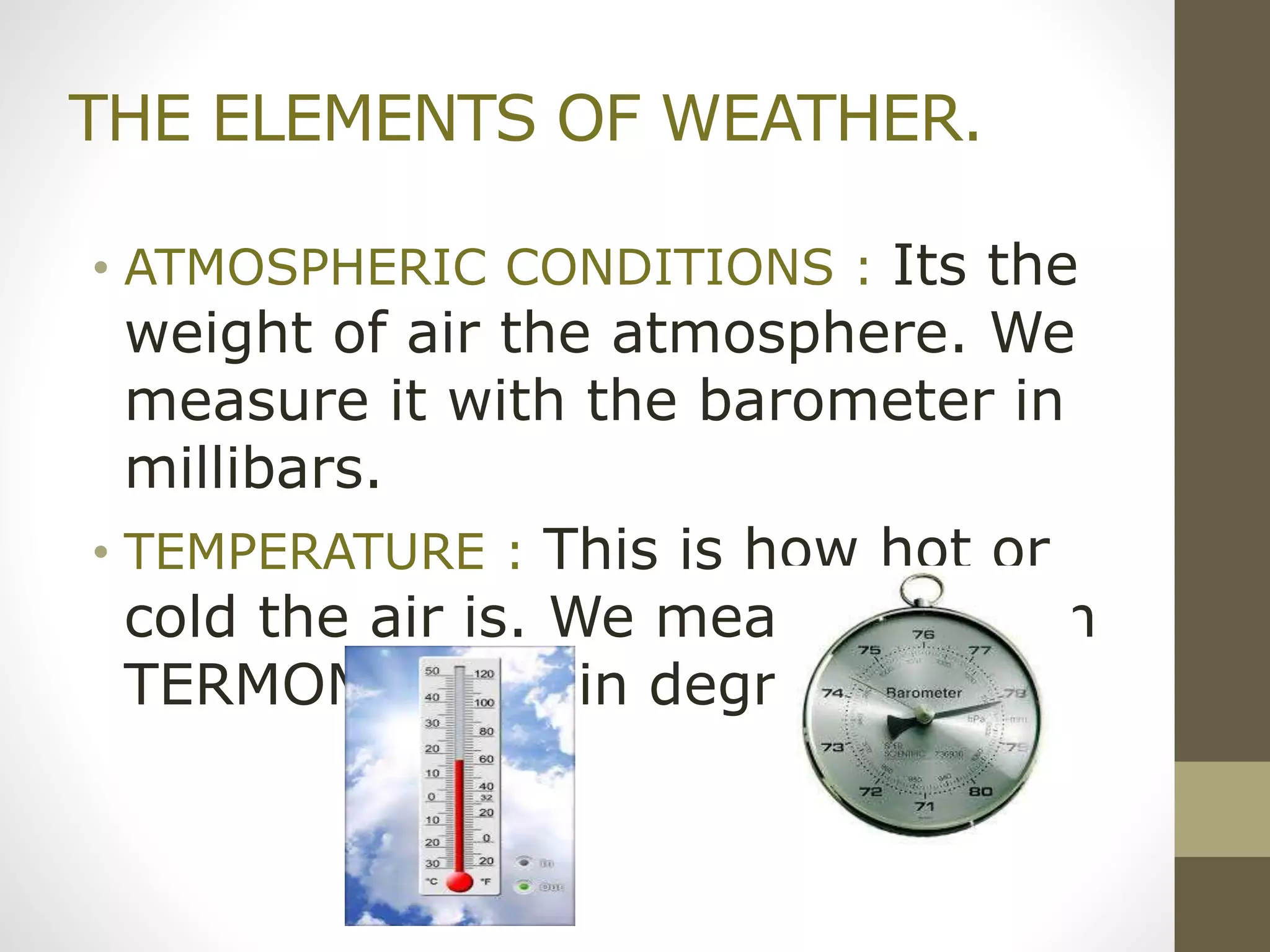
Weather refers to atmospheric conditions in a specific time and place, while climate describes typical weather in a region over many years. There are five elements of weather: wind, atmospheric conditions, temperature, precipitation, and humidity. Climate is influenced by climatic factors like latitude, altitude, and distance from bodies of water. There are three main climate zones - polar, tropical, and temperate. Climate change due to global warming is raising Earth's temperatures and causing sea levels to rise through melting ice, with potential consequences like drought and species extinction. Proposed solutions include reducing deforestation, pollution, and energy waste.