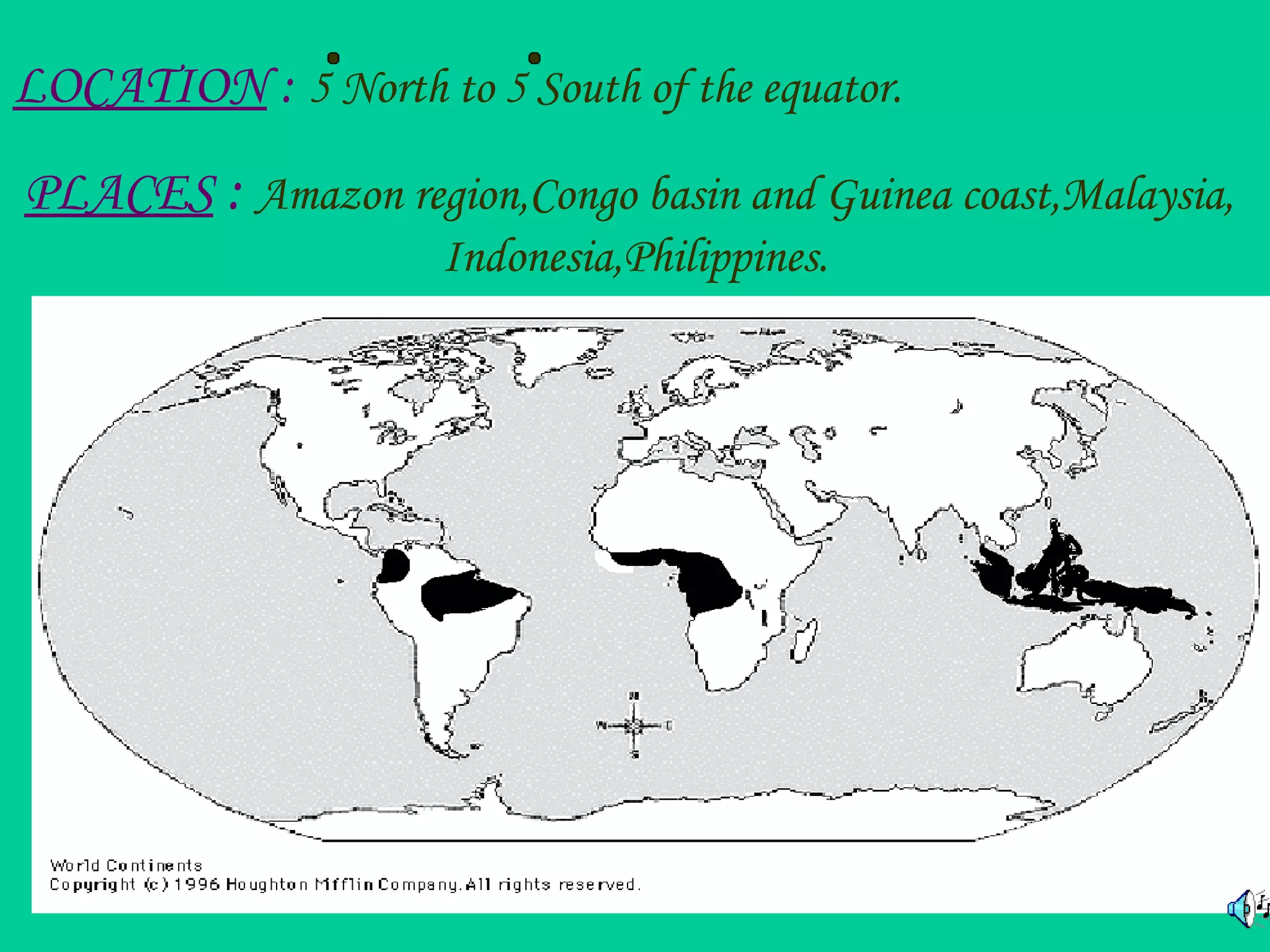
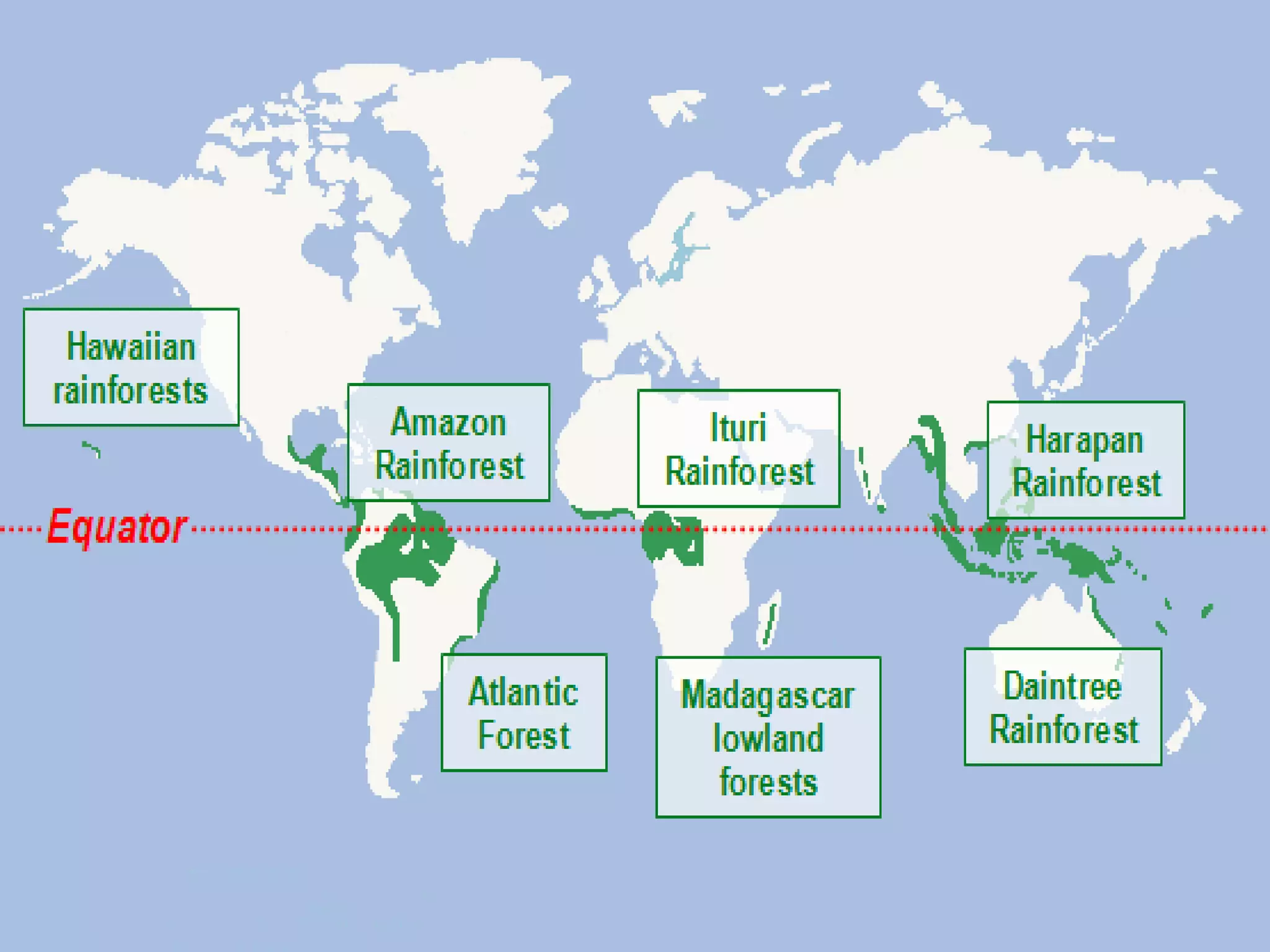
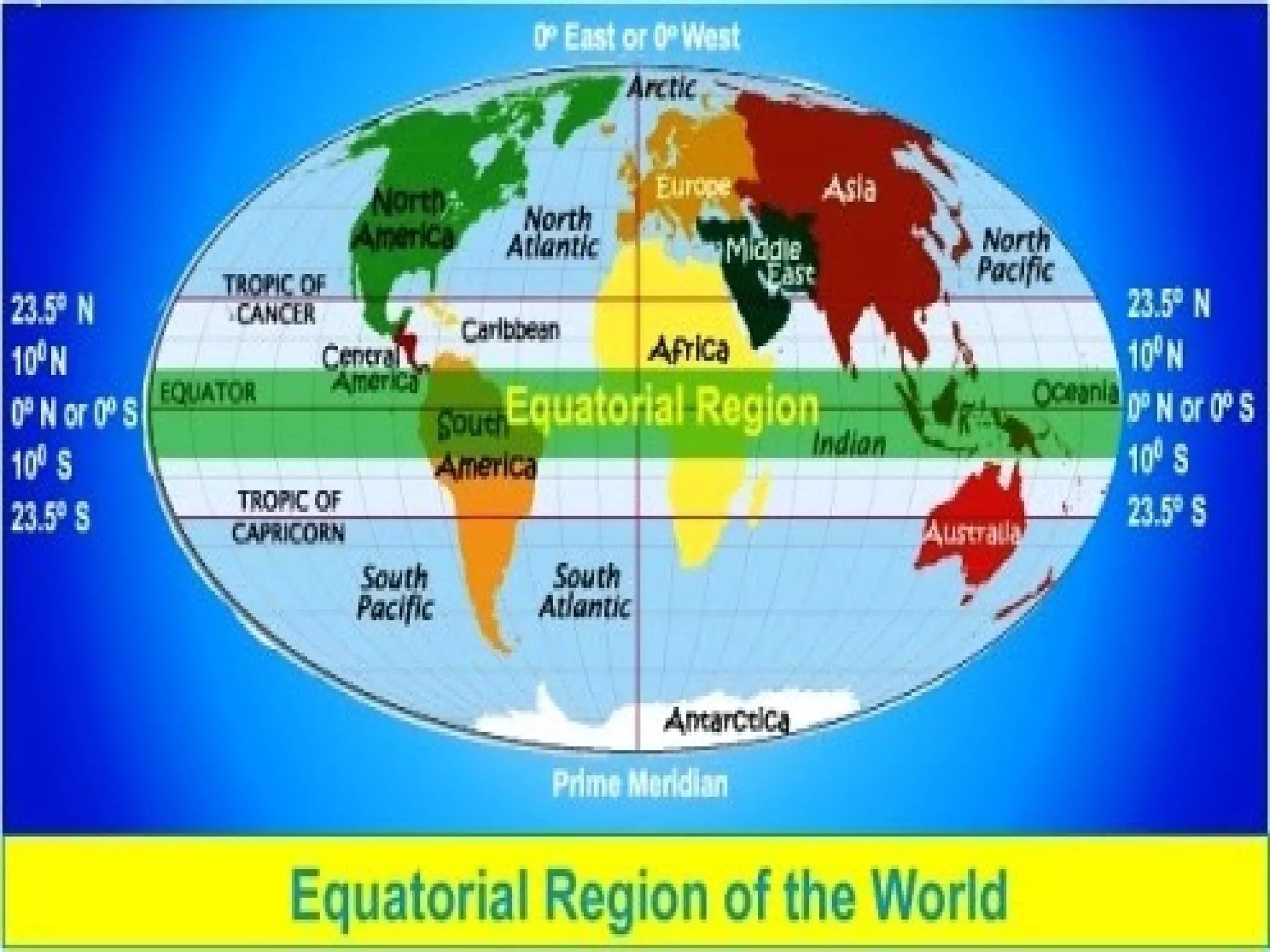
The document provides an overview of the equatorial region, located between 5° north and 5° south, characterized by its hot and wet climate, abundant natural vegetation, and diverse animal life. Key topics include its climate, types of vegetation like mahogany and rubber, and economic activities such as agriculture and lumbering. The region's development has progressed with the introduction of modern practices, moving from shifting cultivation to settled agriculture.