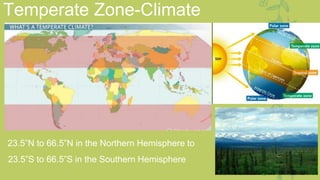
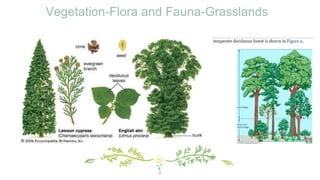
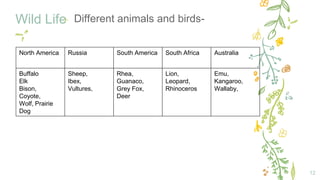
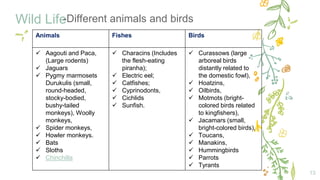
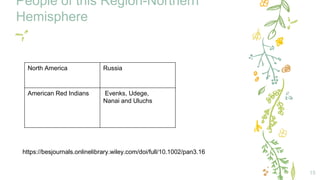
This document provides information about the temperate zone in a grade 5 social studies class. It includes a KWL chart about the temperate zone, a mind map of key aspects like climate, vegetation, and people. There are sections about the climate, vegetation/flora and fauna, and people in different regions of the temperate zone in both the northern and southern hemispheres. Examples of common trees, grasses, crops, and animals are listed for grasslands and deciduous forest regions.