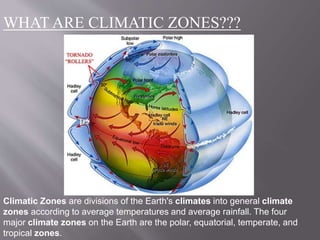
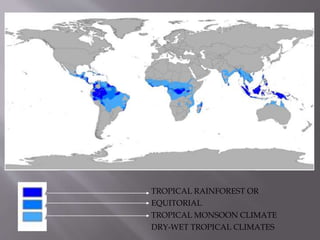
This document discusses three main climatic zones: tropical, equatorial, and temperate. It provides characteristics of each zone. The tropical zone extends from 0-23.5 degrees latitude and has very warm temperatures due to high solar radiation. The subtropics from 23.5-40 degrees receive less moisture and have deserts. The temperate zone from 40-60 degrees has cooler average temperatures and distinct seasons compared to the other zones.