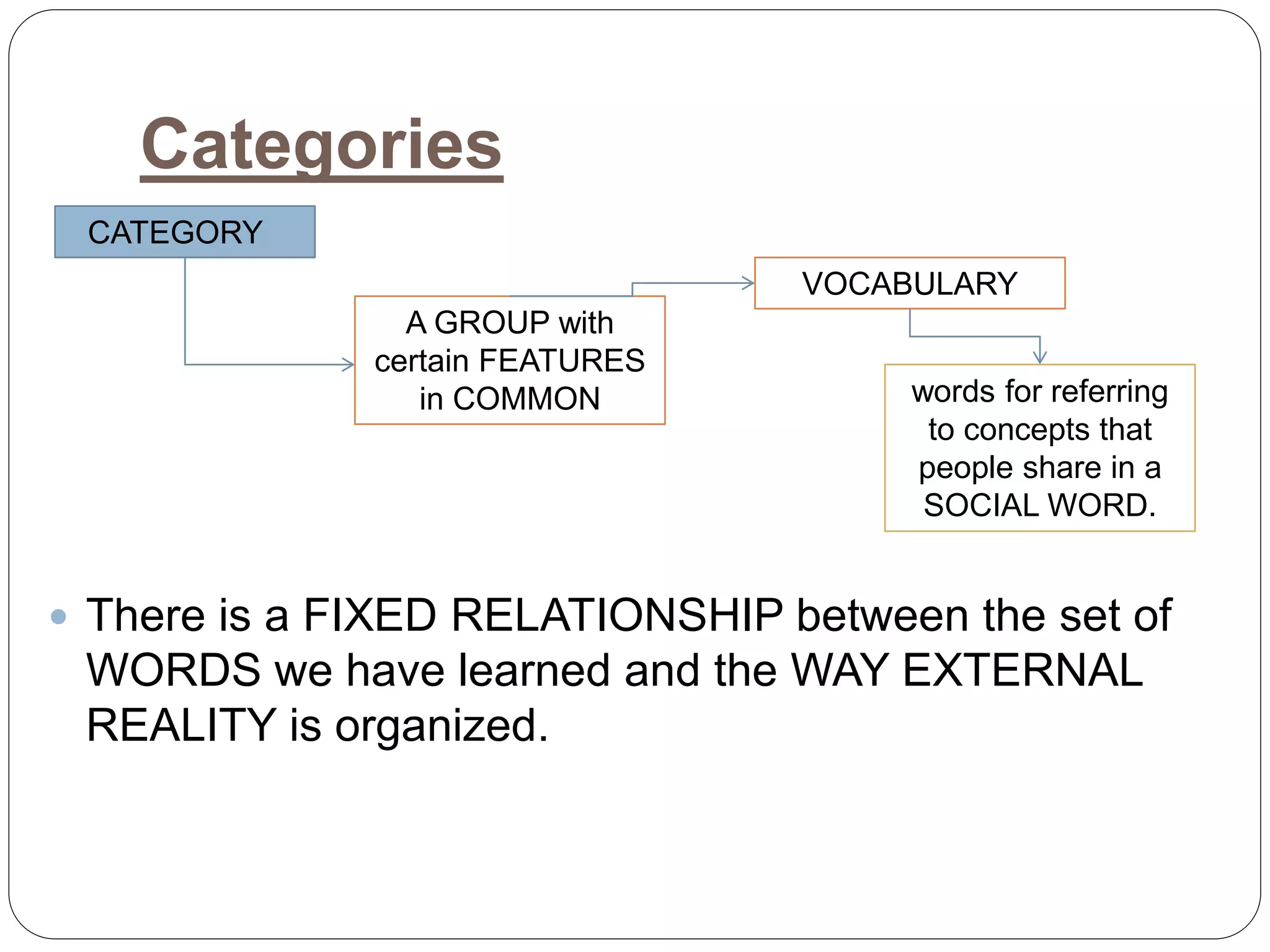
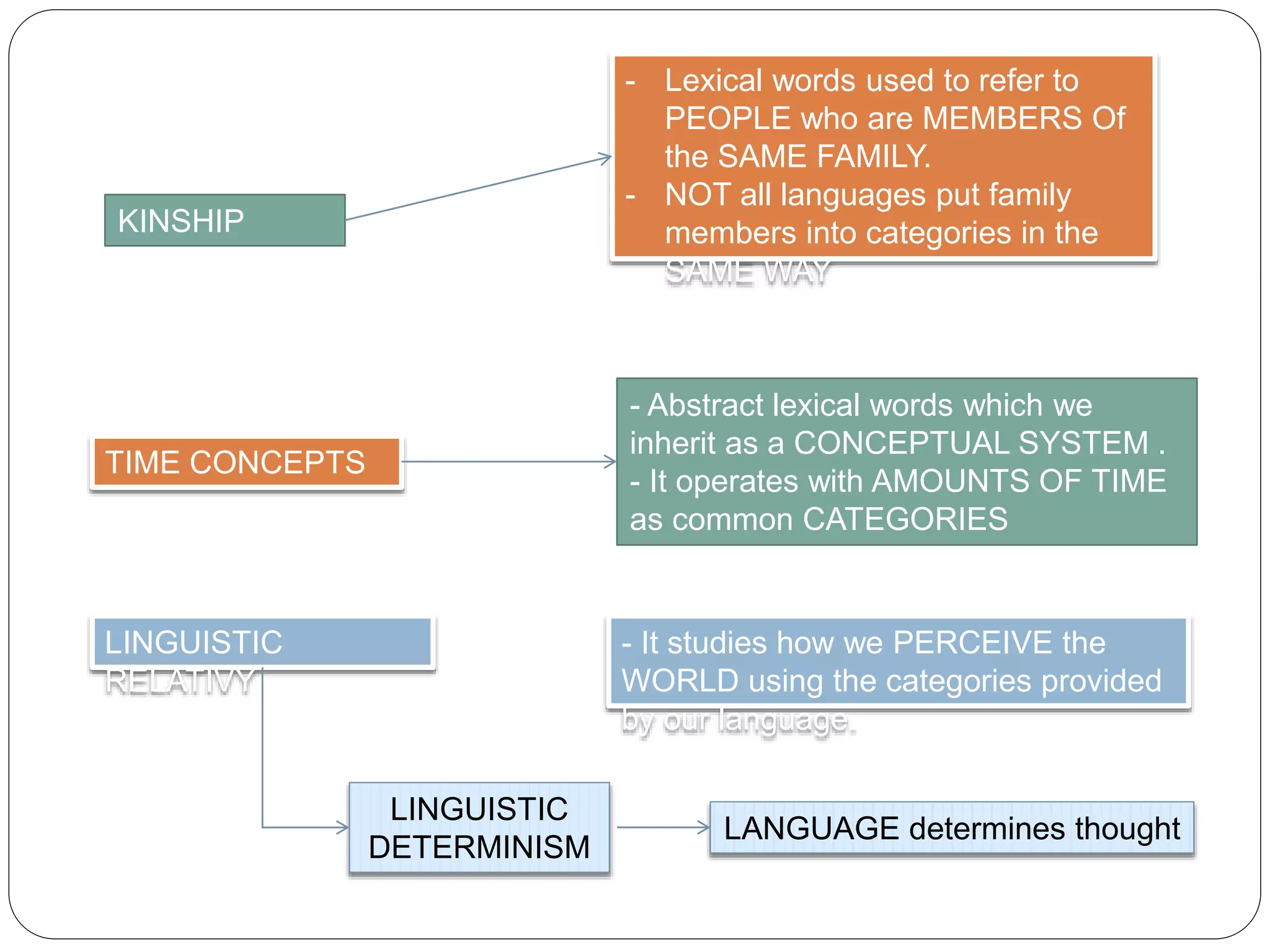
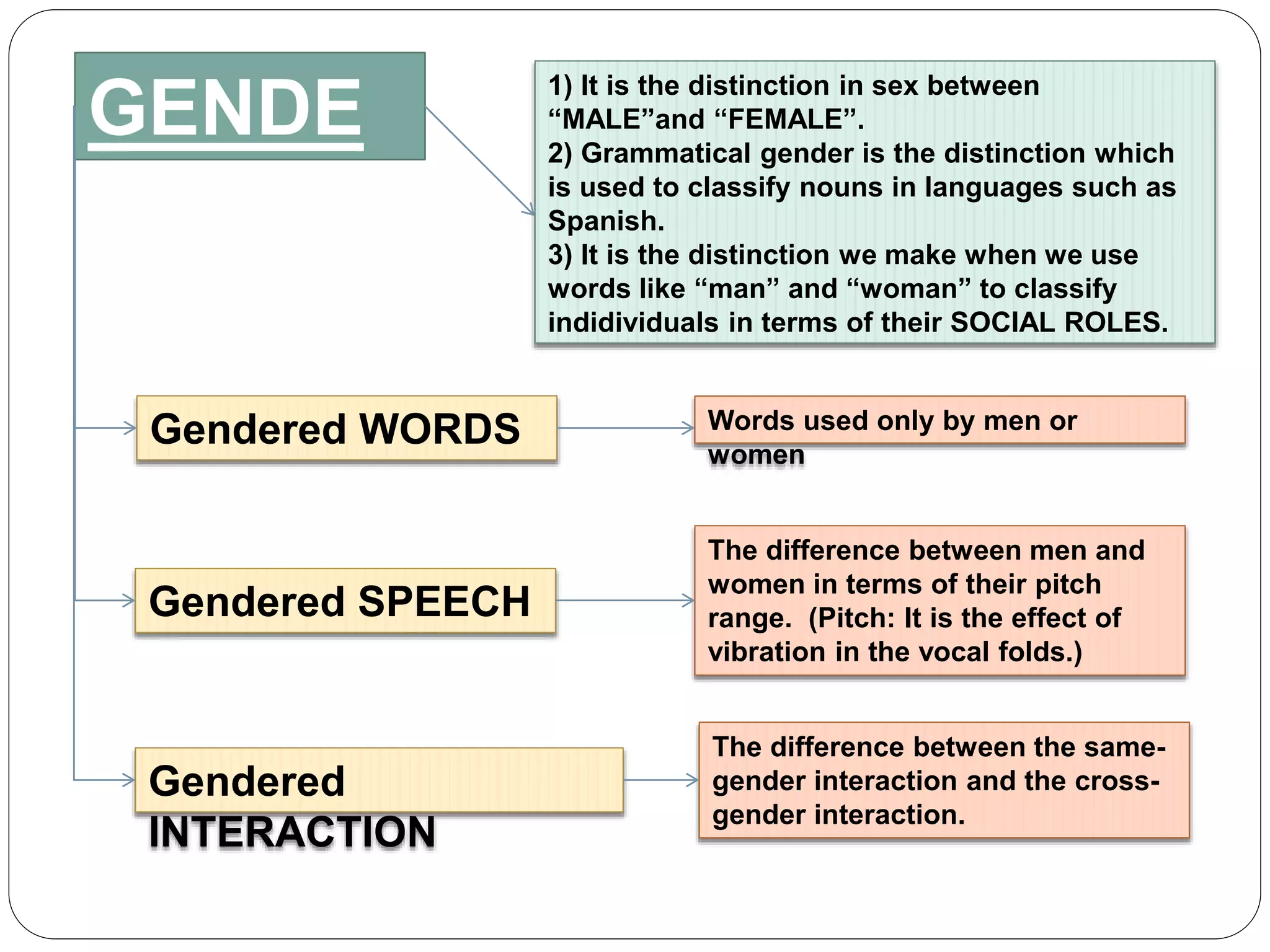
This document discusses language and culture from a linguistic perspective. It explains that culture refers to the ideas and assumptions we learn as members of social groups, including our particular language. Our language provides a system for categorizing the world that is acquired without conscious awareness. Some key linguistic categories discussed are kinship terms, time concepts, and grammatical markers. Social categories refer to how we are connected to others, demonstrated through pronouns. Gender is discussed as the distinction between male and female that is reflected linguistically in areas like grammatical gender, gendered words, interaction, and speech.