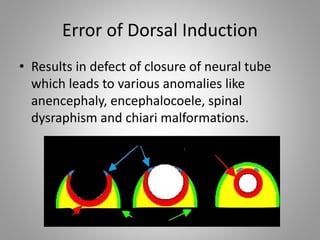
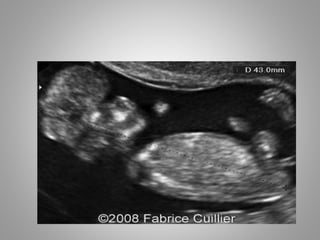
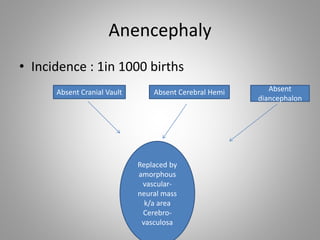
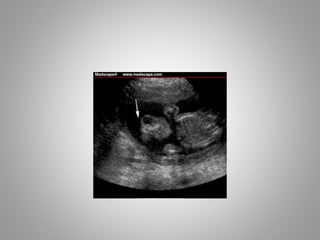
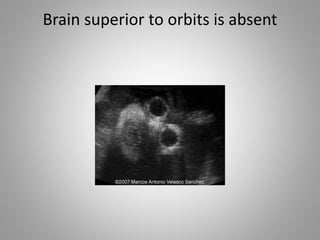
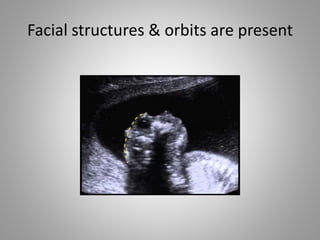
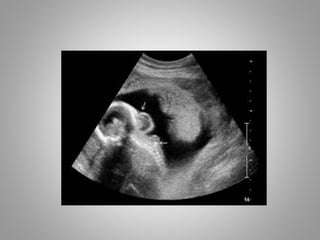
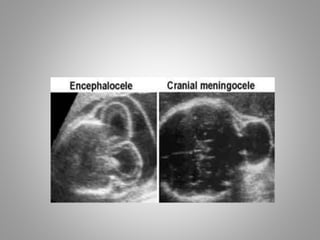
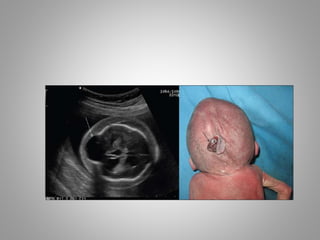
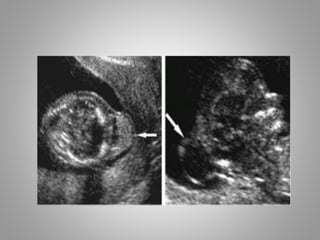
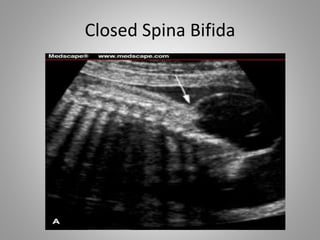
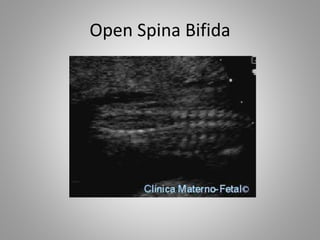
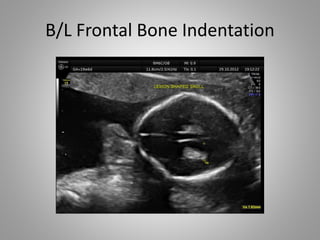
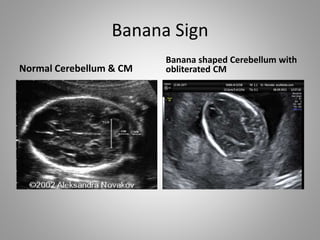
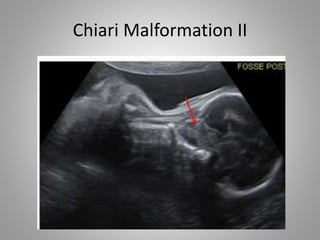
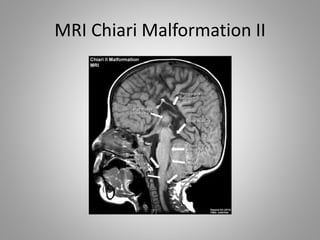
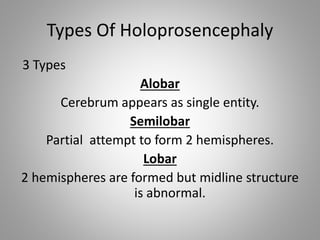
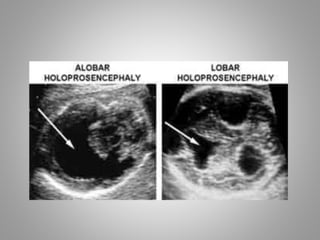
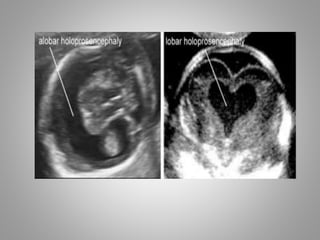
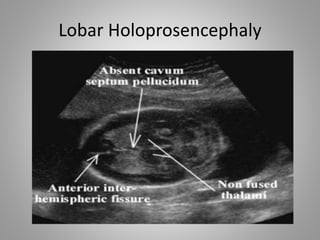
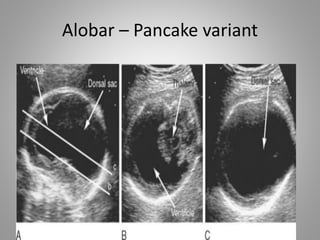
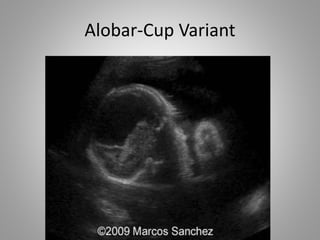
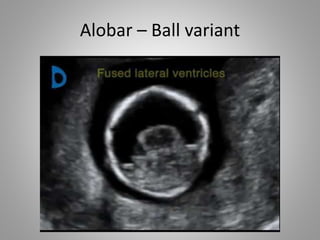
The document discusses various fetal brain anomalies, primarily focusing on errors of dorsal and ventral induction, including acrania, anencephaly, cephalocoele, encephalocoele, spina bifida, and holoprosencephaly. It covers definitions, classifications, associated prognoses, and ultrasound features for each condition, highlighting the critical outcomes and implications for pregnancy management. The information includes categorizations such as open and closed spina bifida, different types of holoprosencephaly, and associated syndromes, emphasizing the complexity of fetal brain development.