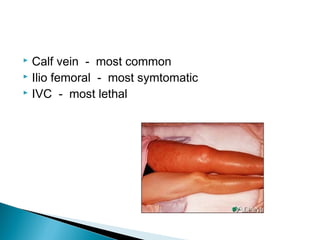
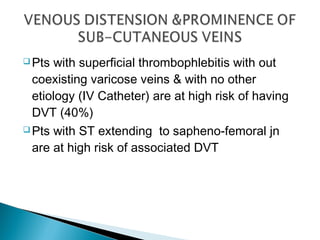
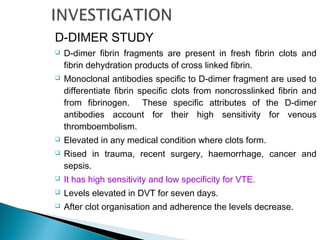
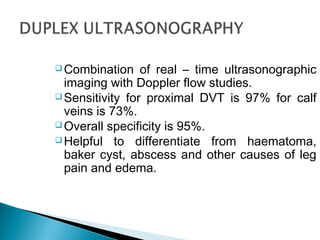
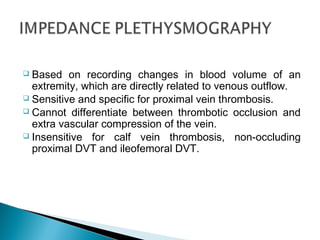
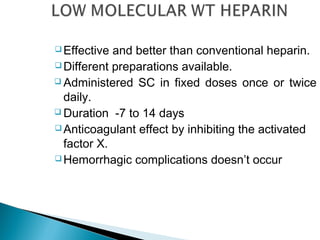
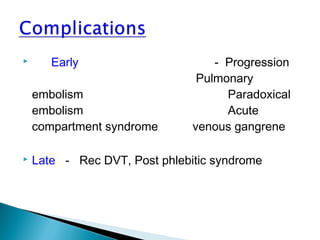
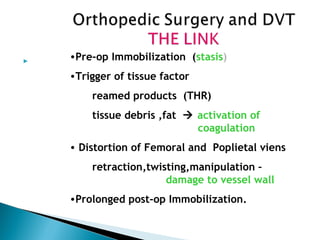
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) refers to deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). DVT occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs, and PE occurs when part of the clot breaks off and lodges in the lungs. Risk factors for VTE include older age, surgery, trauma, cancer, and prolonged immobility. Diagnosis involves blood tests like D-dimer and imaging tests like ultrasound, CT, or venography. Treatment consists of blood thinners like heparin or low molecular weight heparins to prevent clot growth and embolism while allowing the body to naturally break down the clots.







































![ THR, TKR
Hip fracture surgery
Spine surgery [ malignancy, neurological deficit]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deepveinthrombosis-130422050923-phpapp02/85/Deep-vein-thrombosis-55-320.jpg)
![ Although thromboprophylaxis is routinely given
to patients who undergo major orthopedic
surgery, it is usually stopped at discharge.
Coagulation cascade remains abnormal upto 4
weeks.
Risk of propagation of the DVT, and PE,
remains active during this period.
Patients undergoing THA TKA or HFS receive
Thromboprophylaxis with LMWH Fondaparinux
or VKA for a minimum of ten days. [can be cont.
for 4 – 5 wks]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deepveinthrombosis-130422050923-phpapp02/85/Deep-vein-thrombosis-56-320.jpg)
