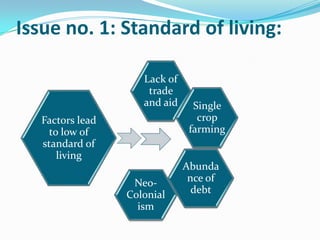
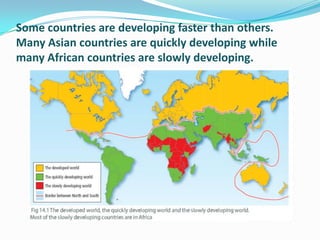
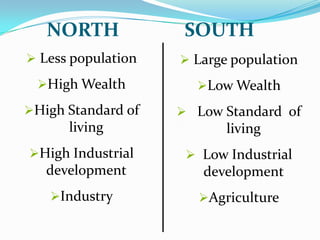
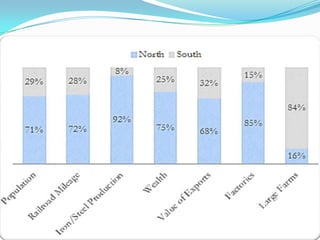
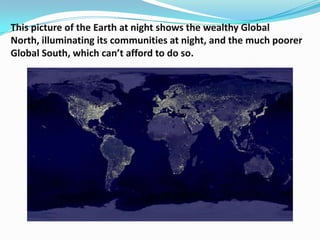
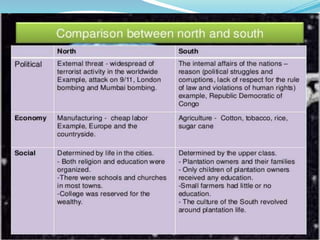
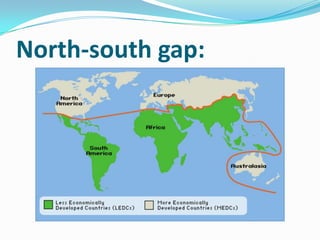
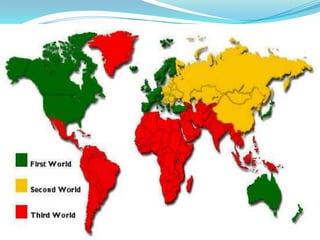
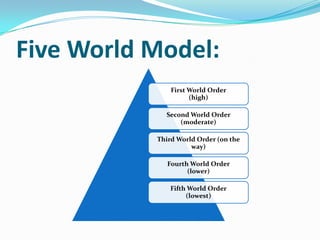
The document discusses the economic and social divide between the global North and South. It describes how the Northern economies were historically based on industries and manufacturing while the Southern economies relied on agriculture and cash crops. This led to disparities in standards of living and wealth distribution between the two regions over time. The document also examines some of the key issues associated with the North-South divide like economic competition and analyzes factors that have contributed to the development gap such as colonialism, unequal trade relations, and debt.