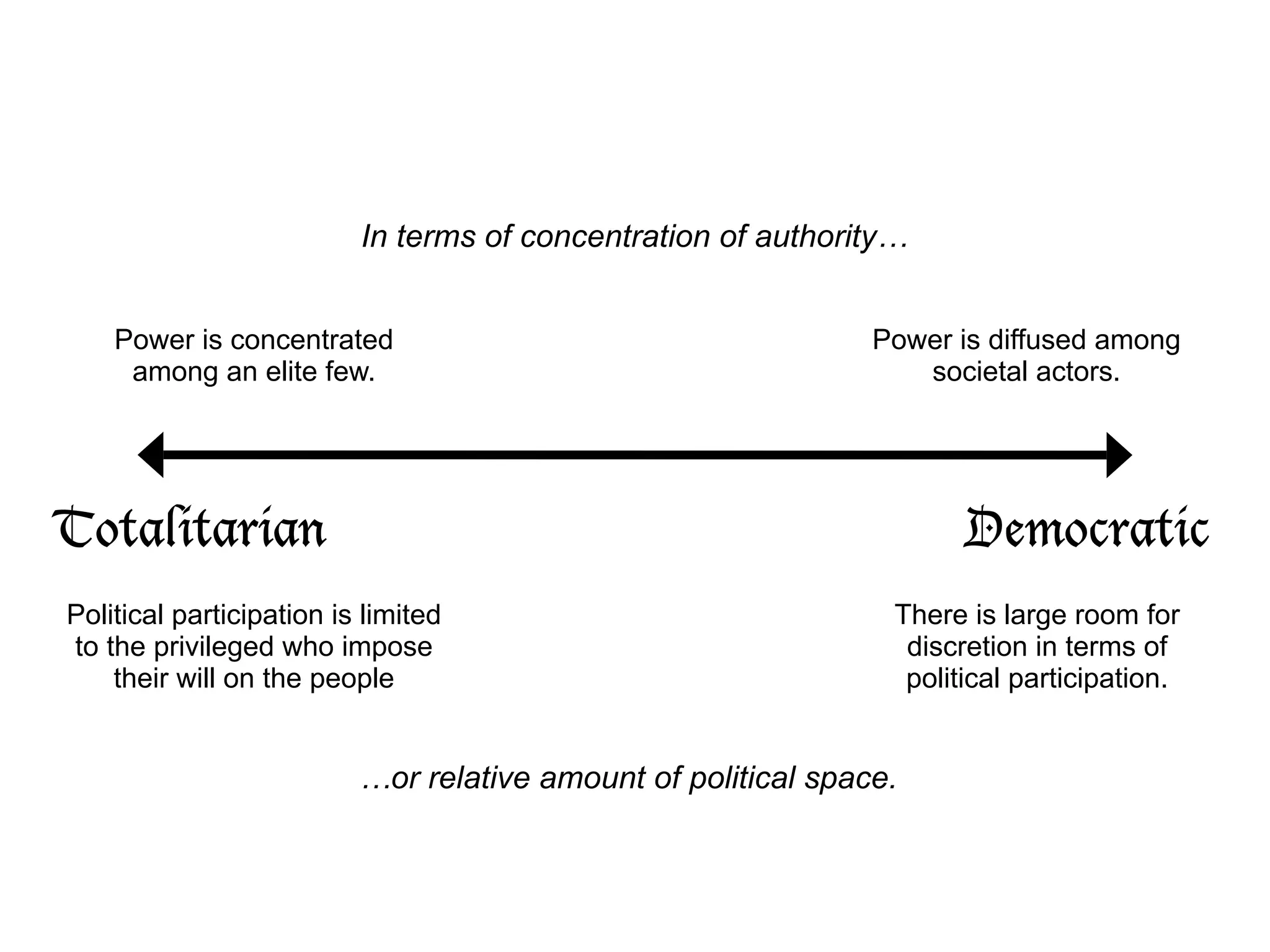
The document discusses the continuum of political systems ranging from totalitarianism to democracy, focusing on the concentration of power and the degree of political participation allowed. It compares different models of democracy, including Westminster and consensual approaches, and outlines various electoral systems such as plurality, majority, and proportional representation. Key features like party systems, government structure, and types of constitutions are also examined.


![“[Authoritarian regimes are] political systems with limited,
non-responsible political pluralism without an elaborated
and guiding ideology, but with distinctive mentalities,
without extensive or intensive political mobilization,
except at some points in their development, and in which
a leader to, occasionally, a small group exercises power
within formally ill-defined, but actually quite predictable
limits.”
(Morlino, 1981: 91)
Juan Linz’s (1964) Definition of Authoritarian Regimes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-political-systems-1230167408192281-2/75/Political-Systems-Handout-4-2048.jpg)



