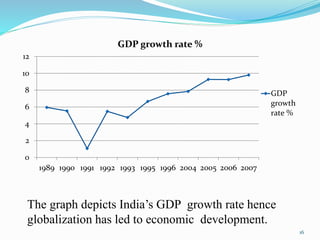
Globalization refers to the increasing integration of economies, cultures and political systems. It is driven by advances in technology and transportation as well as reductions in trade barriers. There are economic, social and political dimensions of globalization. While it provides benefits like cheaper goods, increased investment and cultural sharing, it also poses challenges such as unequal wealth distribution, exploitation of cheap labor and increased commodity prices. Companies can enter foreign markets through various strategies like exports, joint ventures, mergers and acquisitions. Pepsi's entry into India in the late 1980s demonstrated the challenges of navigating politics and regulations to establish operations in a new market.