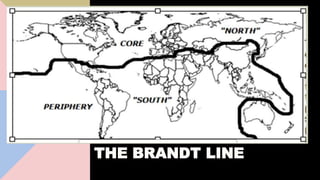
The document discusses the Brandt Line, which was developed in the 1980s as a way to show the geographic divide between relatively richer and poorer nations. It places most richer countries in the northern hemisphere and poorer countries in the southern hemisphere. It then discusses some key differences between the "Global North" (developed societies in Europe and North America) and the "Global South" (developing agrarian societies in Africa, India, China, and Latin America), including differences in levels of wealth, standards of living, industrial development, populations, and economic industries.