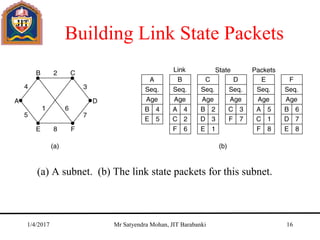
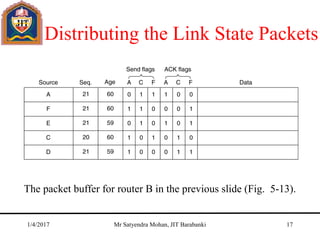
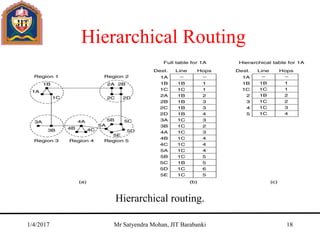
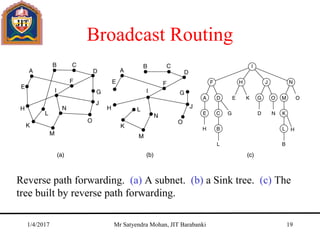
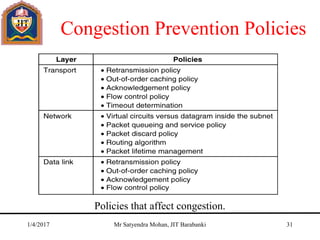
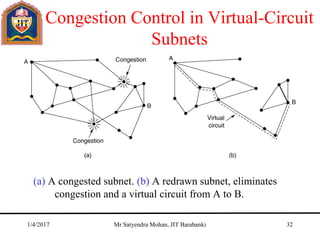
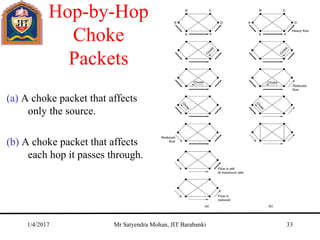
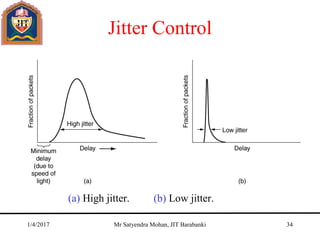
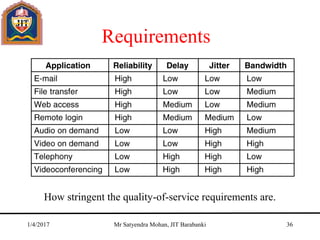
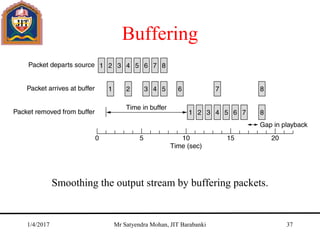
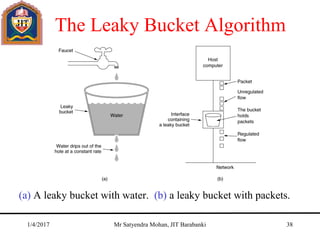
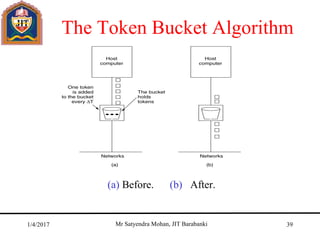
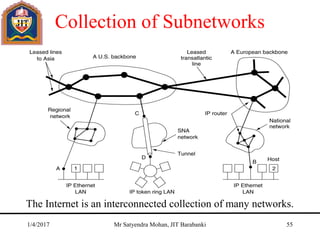
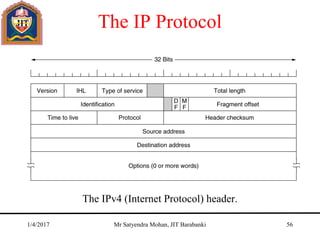
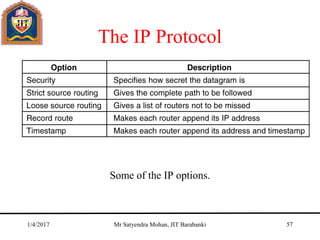
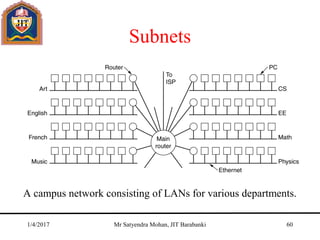
The document outlines key concepts of the network layer, including design issues, routing algorithms, and performance aspects such as congestion control and quality of service. It covers both connectionless and connection-oriented services, along with internetworking principles and protocols such as IP, OSPF, and BGP. The document concludes with design principles and various protocols that ensure efficient network communication.













![References
[1] A. S. Tanenbaum, “Computer Network”, Pearson Education
[2] Forouzen, “Data Communication and Networking”, TMH
1/4/2017 Mr Satyendra Mohan, JIT Barabanki 67](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cn-3-170125173809/85/The-Network-Layer-in-CN-67-320.jpg)
