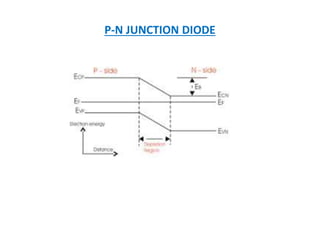
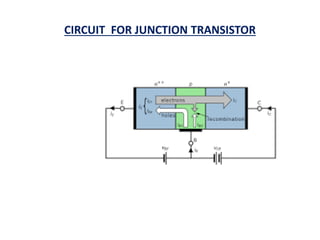
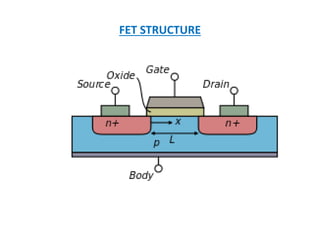
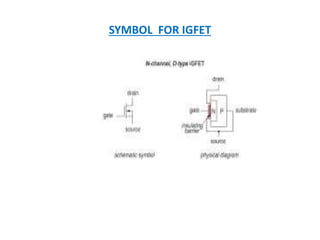
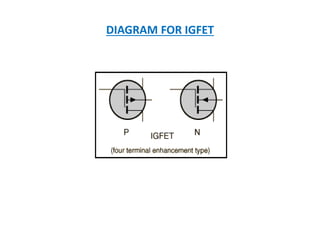
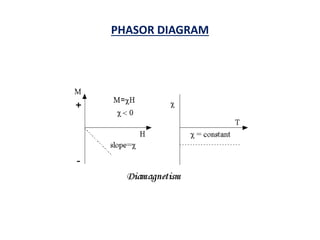
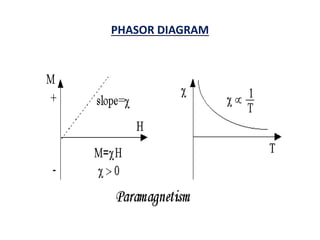
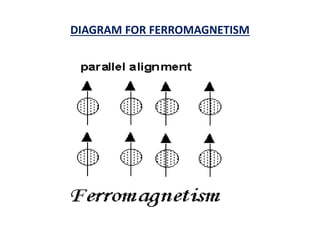
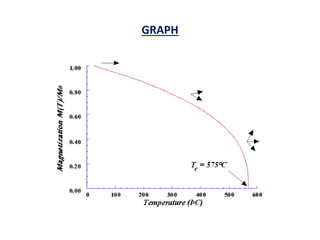
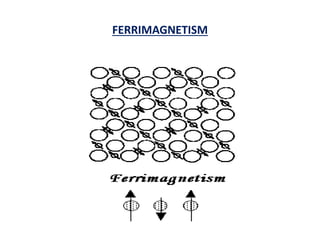
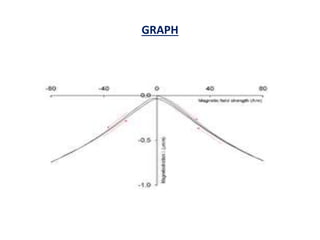
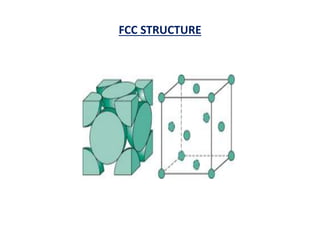
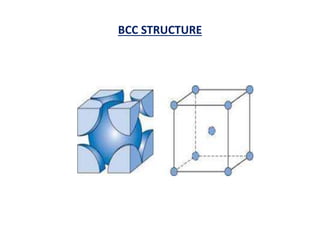
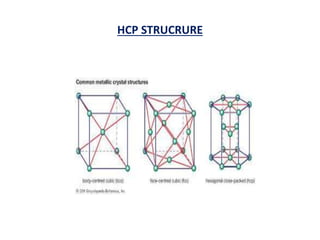
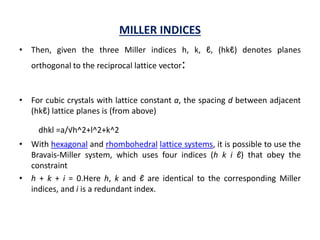
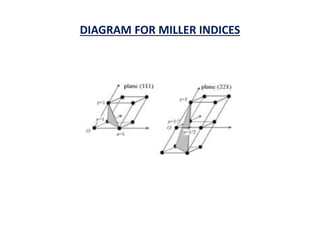
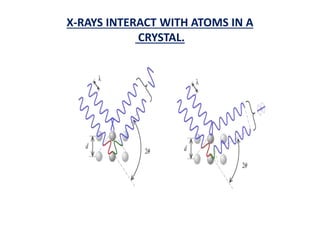
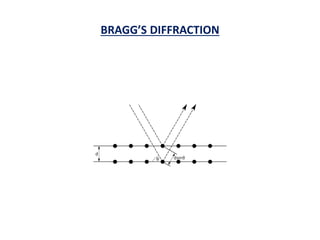
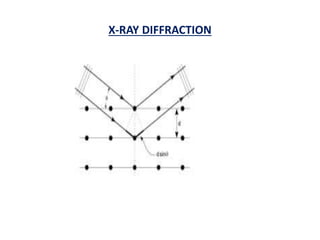
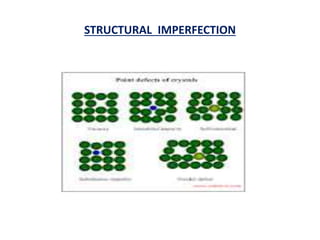
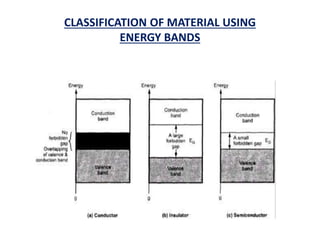
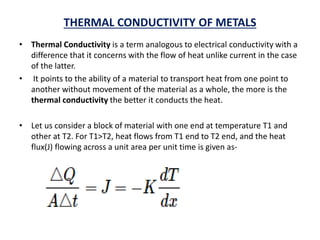
This document discusses the crystal structure of materials and different types of bonds in solids. It describes metallic, ionic, covalent, and network solids. Metallic solids are held together by delocalized electrons forming a 'electron soup'. Ionic bonds occur through electron transfer between metals and non-metals. Covalent bonds involve electron sharing. Network solids form extensive 1D, 2D or 3D networks through covalent bonds. The properties of these materials depend on the type of bonding. The document also discusses crystal structure, unit cells, packing factors, Miller indices, Bragg's law and uses of X-ray crystallography.



































![HEAT DEVELOPED IN CURRENT CARRYING
CONDUCTOR
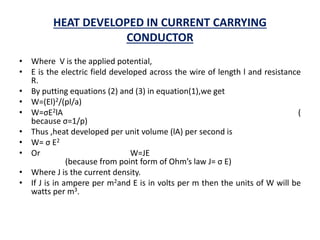
• According to Joule’s law, the heat developed in a conducting wire is given
by I2 R,
• Where I is current flowing through the wire having resistance R.
• If p is the electrical resistivity of wire,
• L is the length of wire and
• A is the area of cross section of wire
• Then, Heat developed W=I2R
• Or W=v2/R 1)
• [because V=IR ( from OHM’s law)]
• As V=El (2)
• And R=pl/a (3)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/materialscienceeeem-170105085525/85/Material-science-eeem-48-320.jpg)