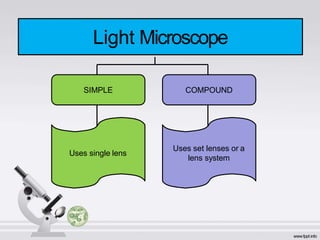
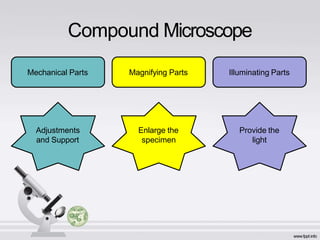
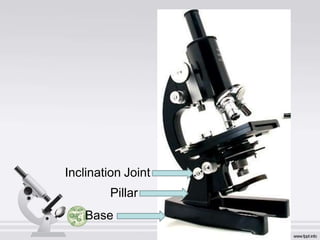
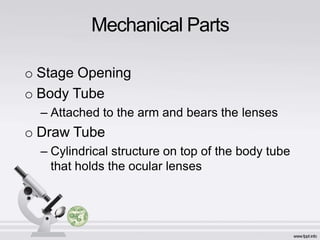
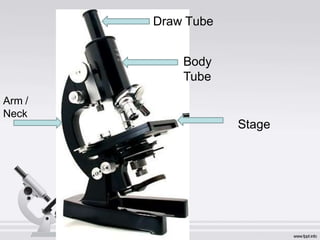
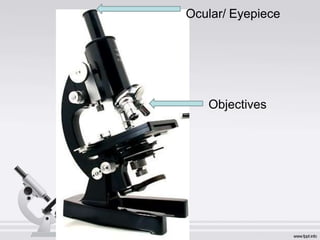
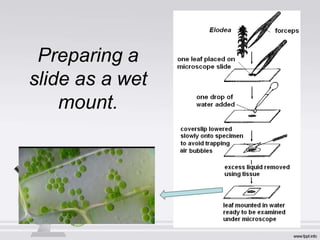
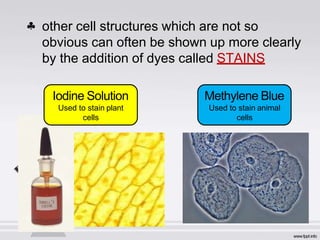
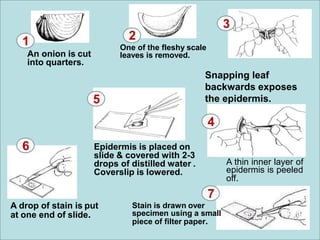
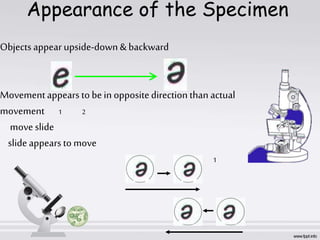
The document describes the parts and functions of a compound microscope. It explains that a microscope is used to magnify small objects and see details not visible to the naked eye. The main parts are the mechanical components that support and adjust the microscope, as well as the magnifying and illuminating parts. The magnifying parts include objective lenses of different magnifications and an eyepiece, while the illuminating parts provide lighting. Proper use and care of the microscope is also outlined.