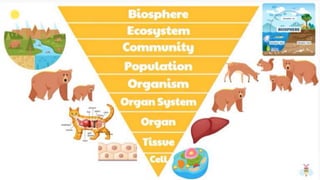
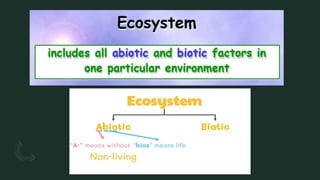
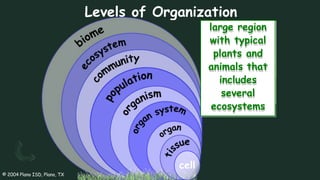
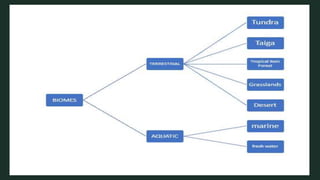
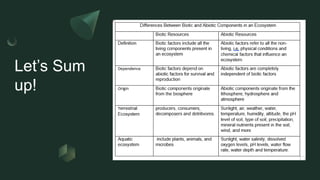
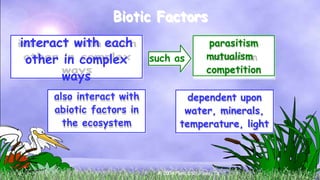
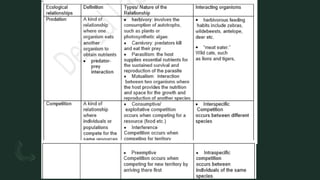
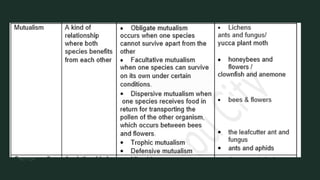
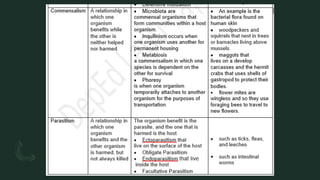
The document discusses how organisms interact with biotic and abiotic factors in their environment. It defines ecology as the study of these interactions and relationships. It explains that abiotic factors are non-living physical and chemical conditions like temperature, water, and sunlight. Biotic factors are the living organisms an ecosystem, including animals, plants, and other organisms. The document provides examples of different ecological relationships like predation, competition, and mutualism.