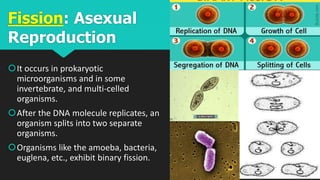
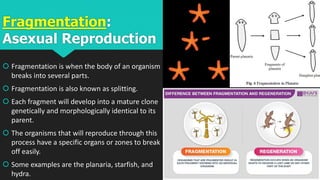
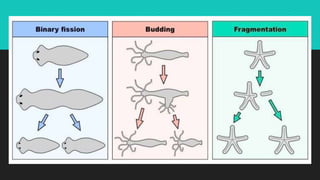
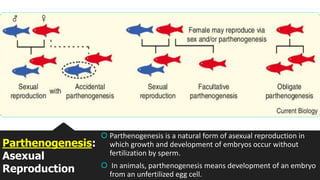
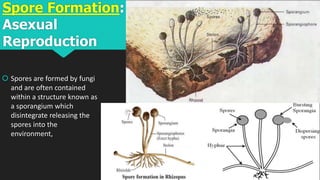
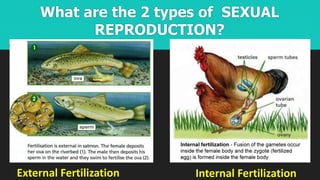
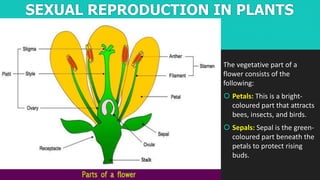
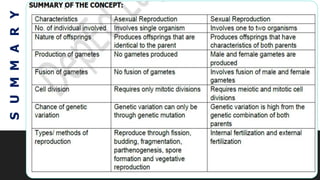
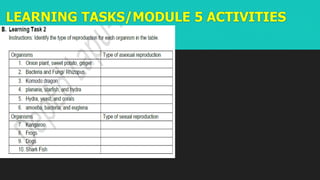
This document discusses and compares asexual and sexual reproduction. It defines reproduction as the process by which living organisms form new individuals of the same kind. The two main types of reproduction are then explained as asexual reproduction, where offspring are genetically identical to the parent, and sexual reproduction, which involves the fusion of egg and sperm cells. Examples of asexual reproduction methods like binary fission, budding, fragmentation, and spore formation are provided. For sexual reproduction, the document describes the process in plants including the male and female reproductive organs of flowers and how fertilization occurs both internally and externally in different species. Learning tasks at the end instruct students to complete related activities on the Edmodo online platform.