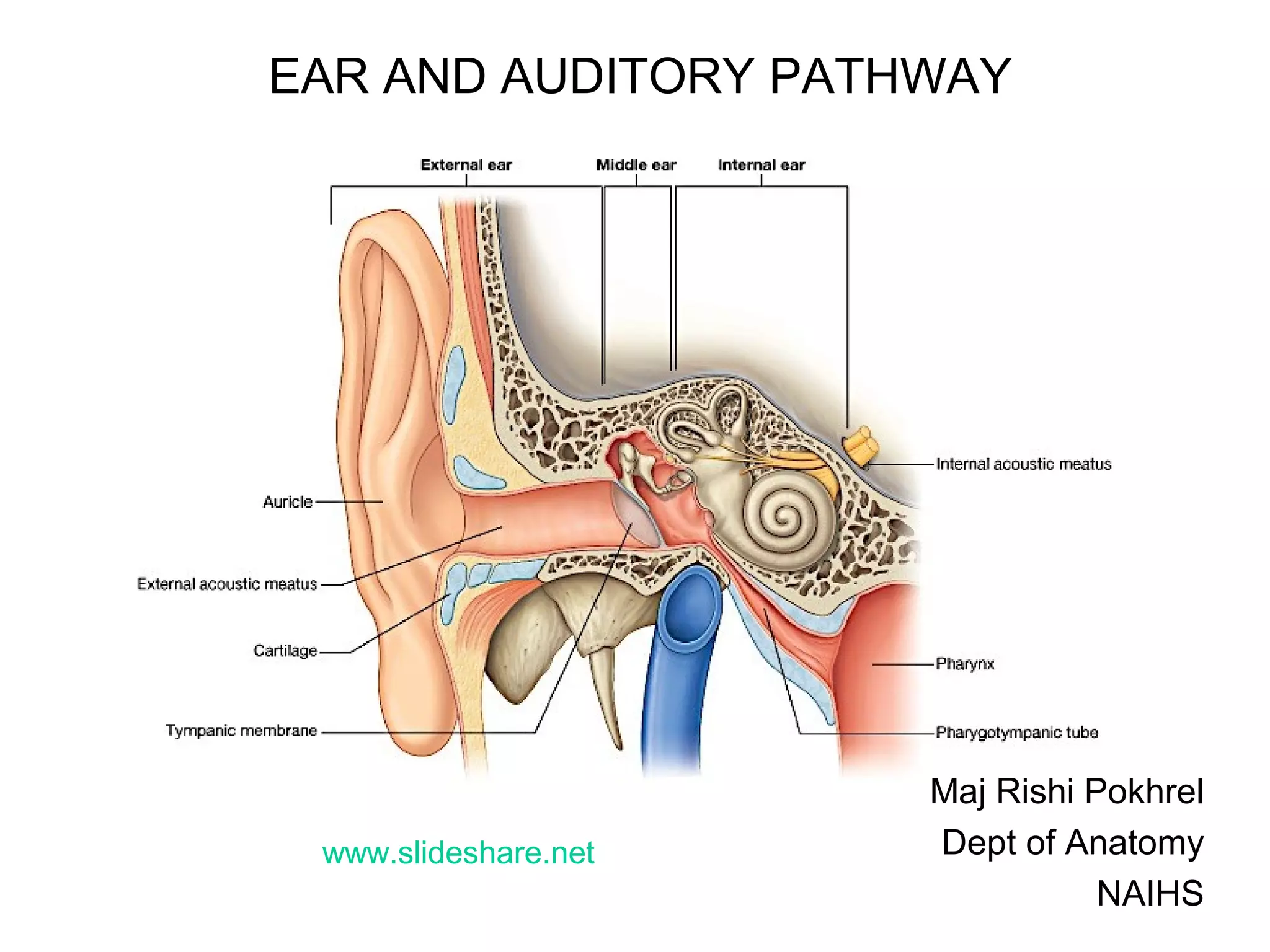
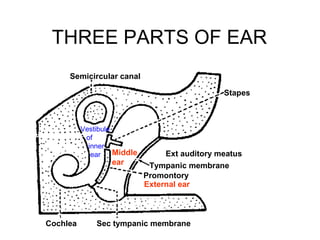
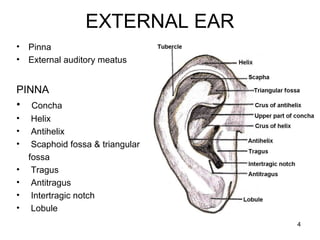
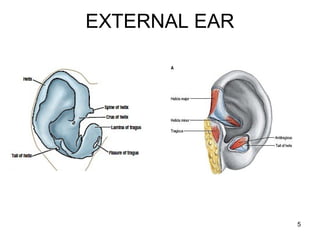
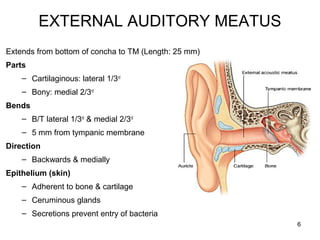
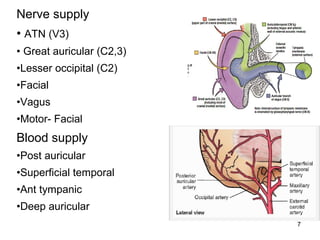
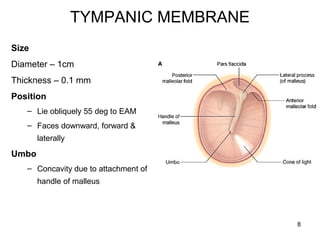
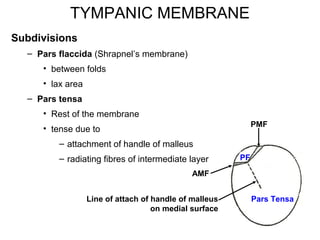
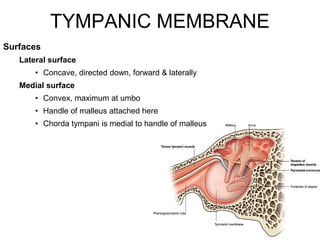
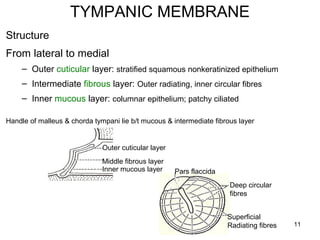
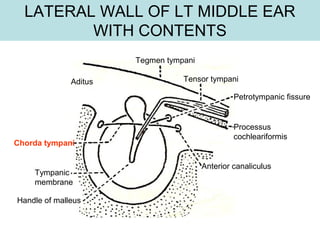
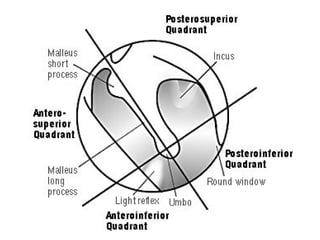
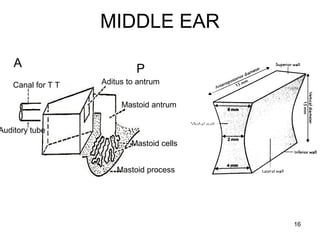
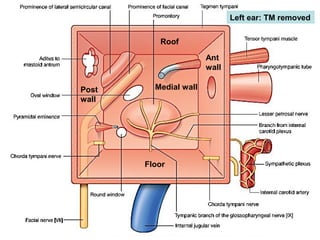
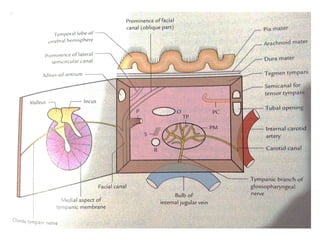
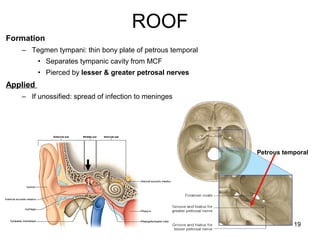
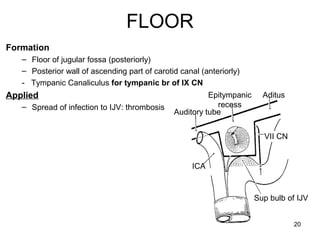
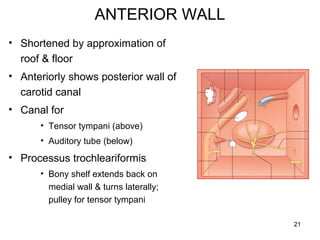
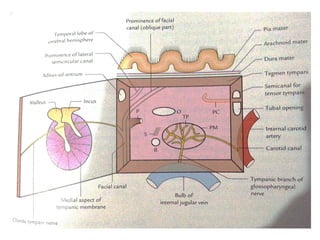
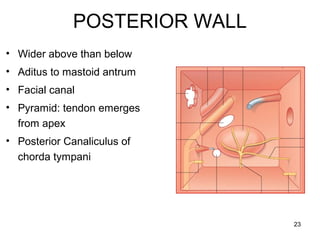
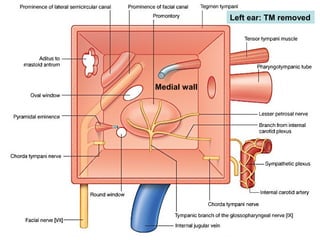
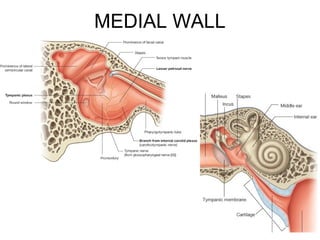
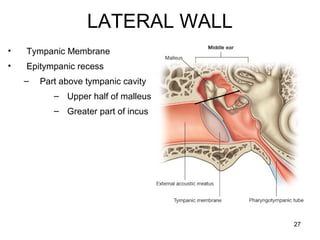
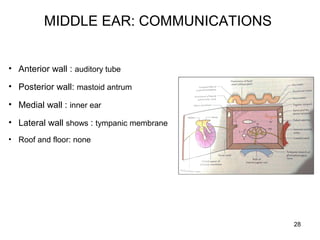
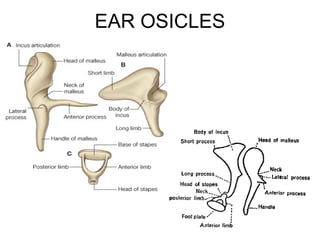
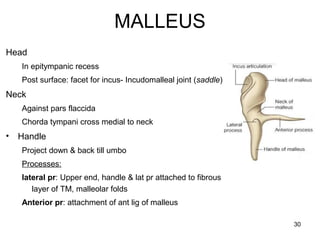
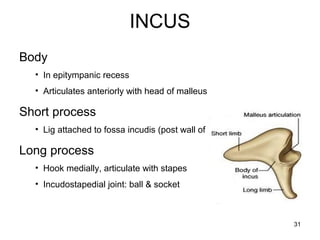
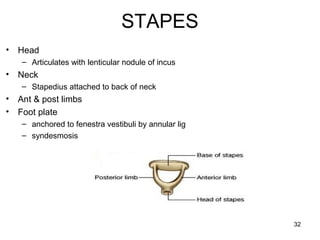
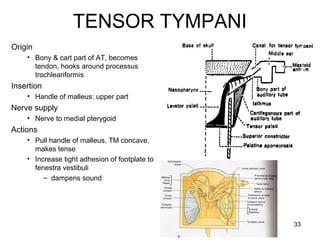
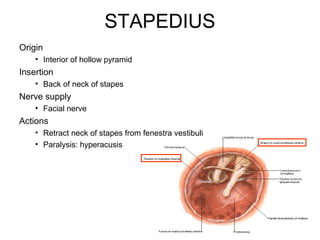
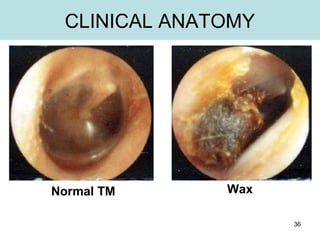
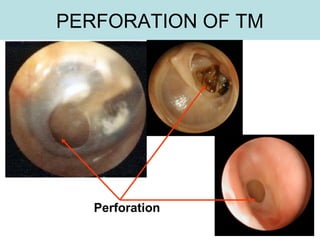
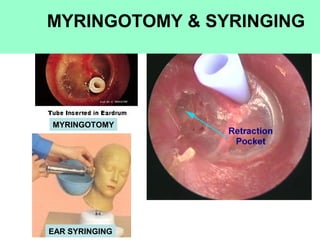
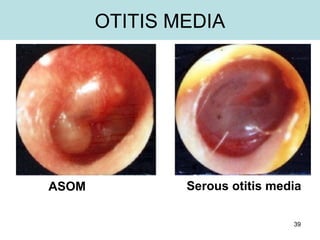
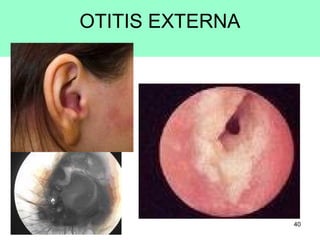
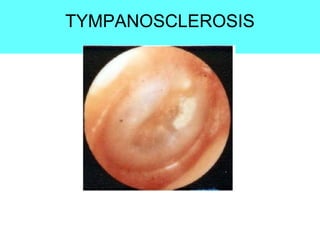
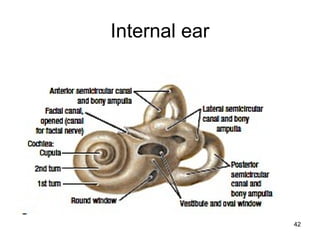
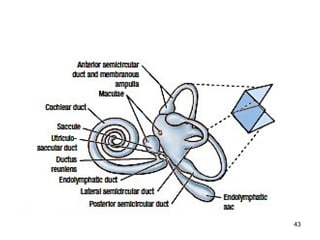
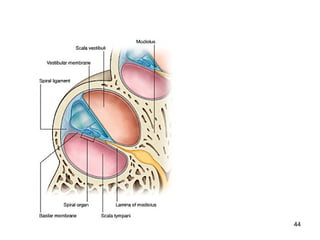
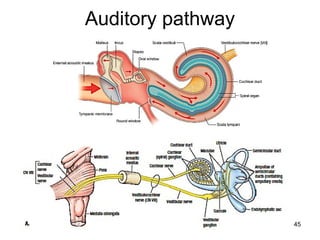
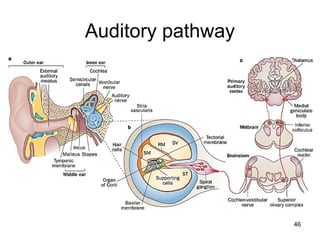
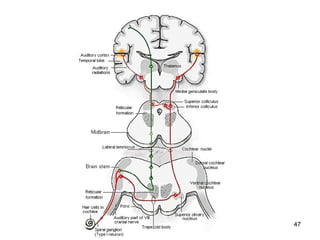
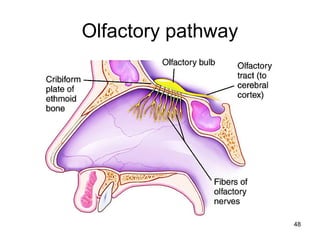
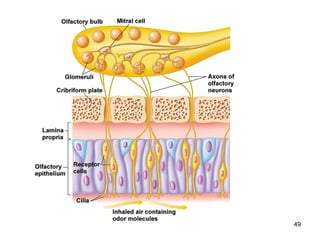
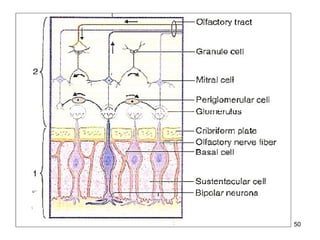
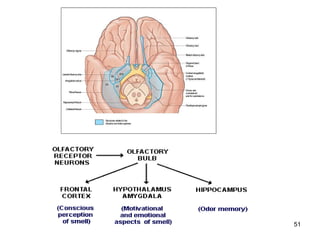
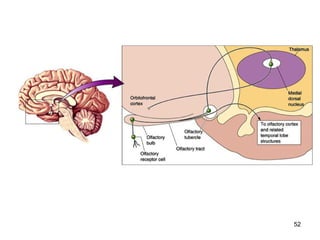
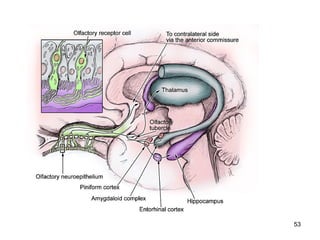
The document provides information on the anatomy of the ear and auditory pathway. It discusses the three parts of the ear - external ear, middle ear, and inner ear. The external ear includes the pinna and external auditory meatus. The middle ear contains the tympanic membrane, three ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes), and two small muscles (tensor tympani and stapedius). The inner ear is made up of the cochlea and vestibular system. The auditory pathway transmits signals from the inner ear to the brainstem and auditory cortex.