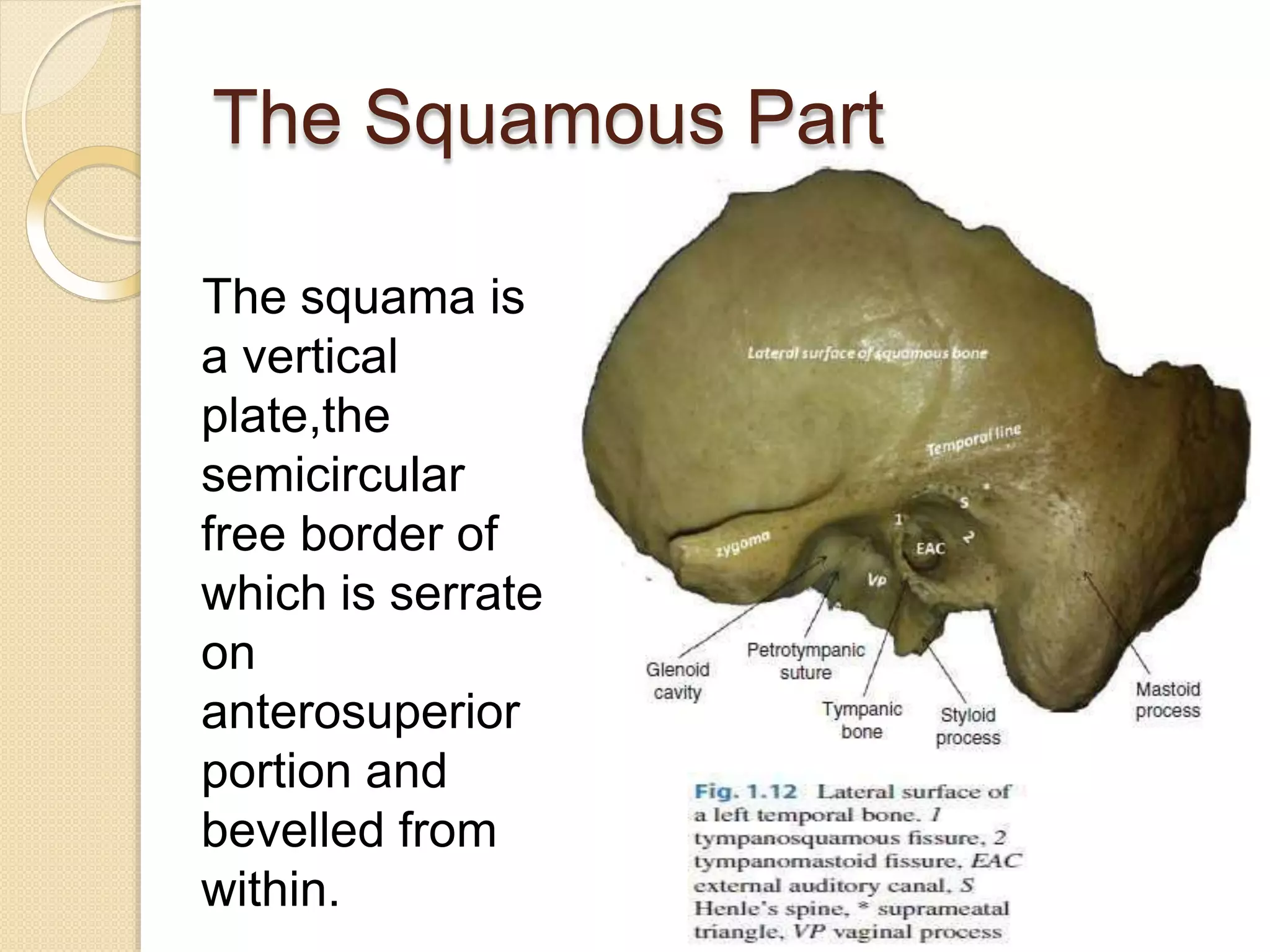
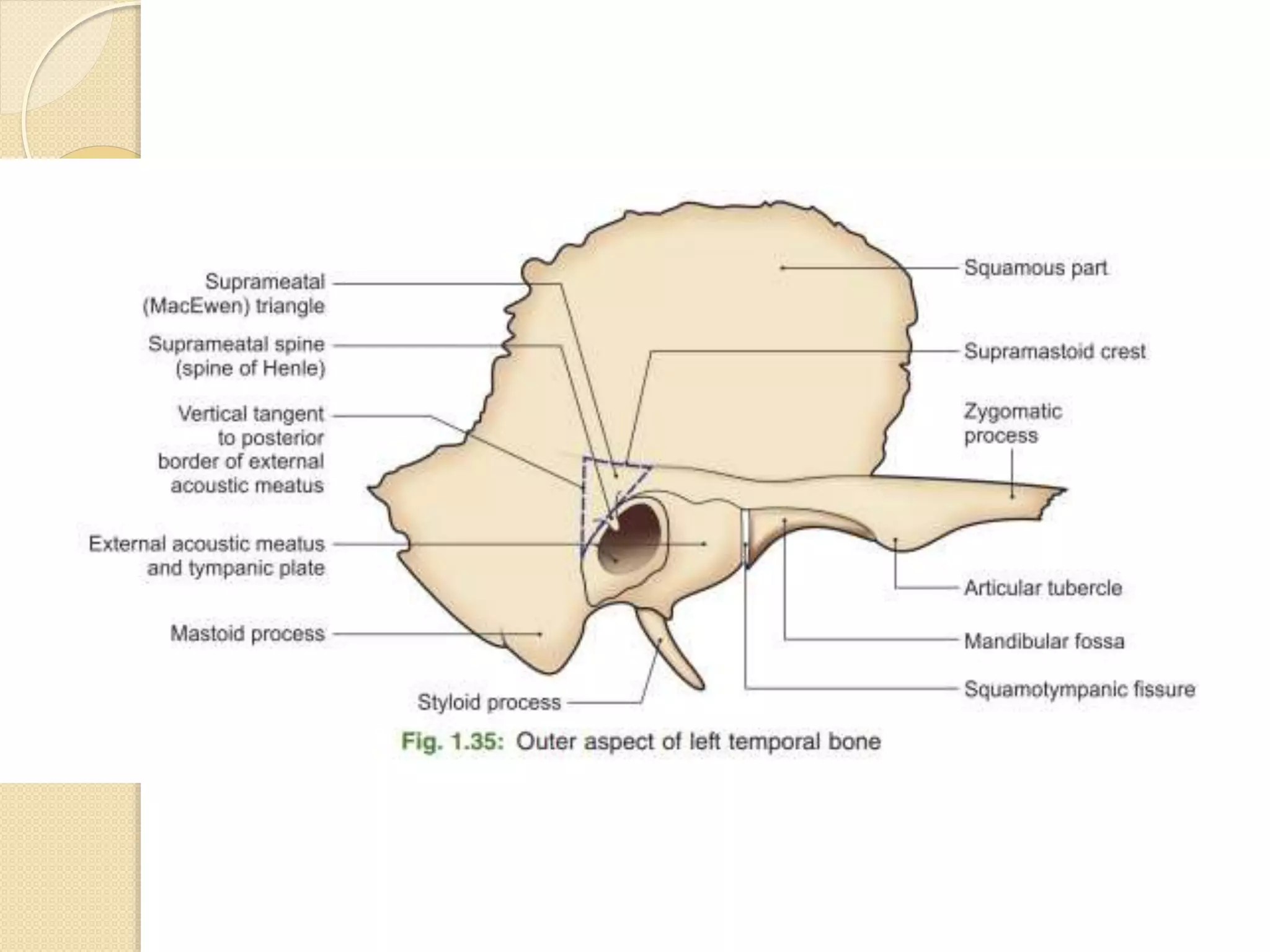
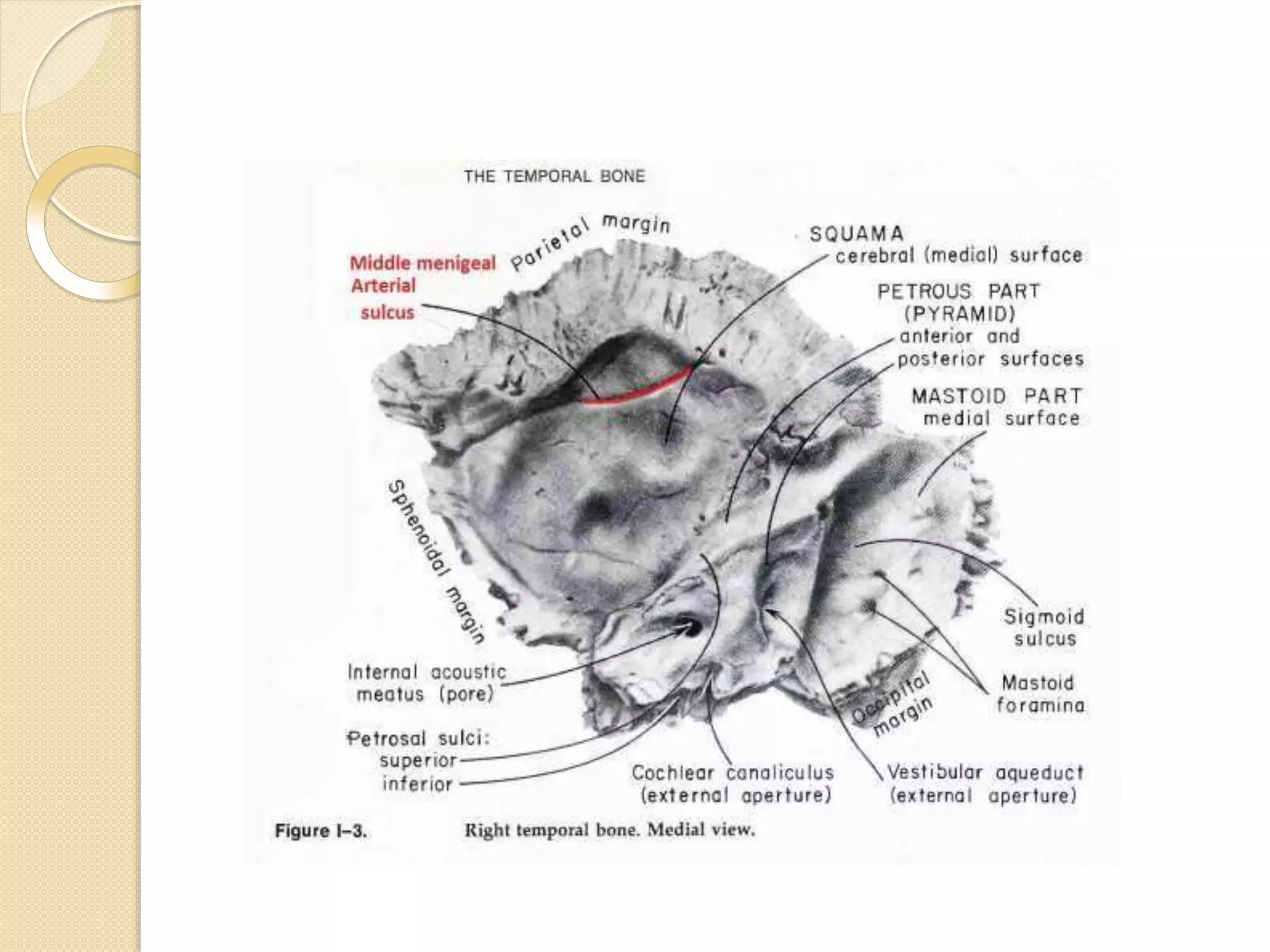
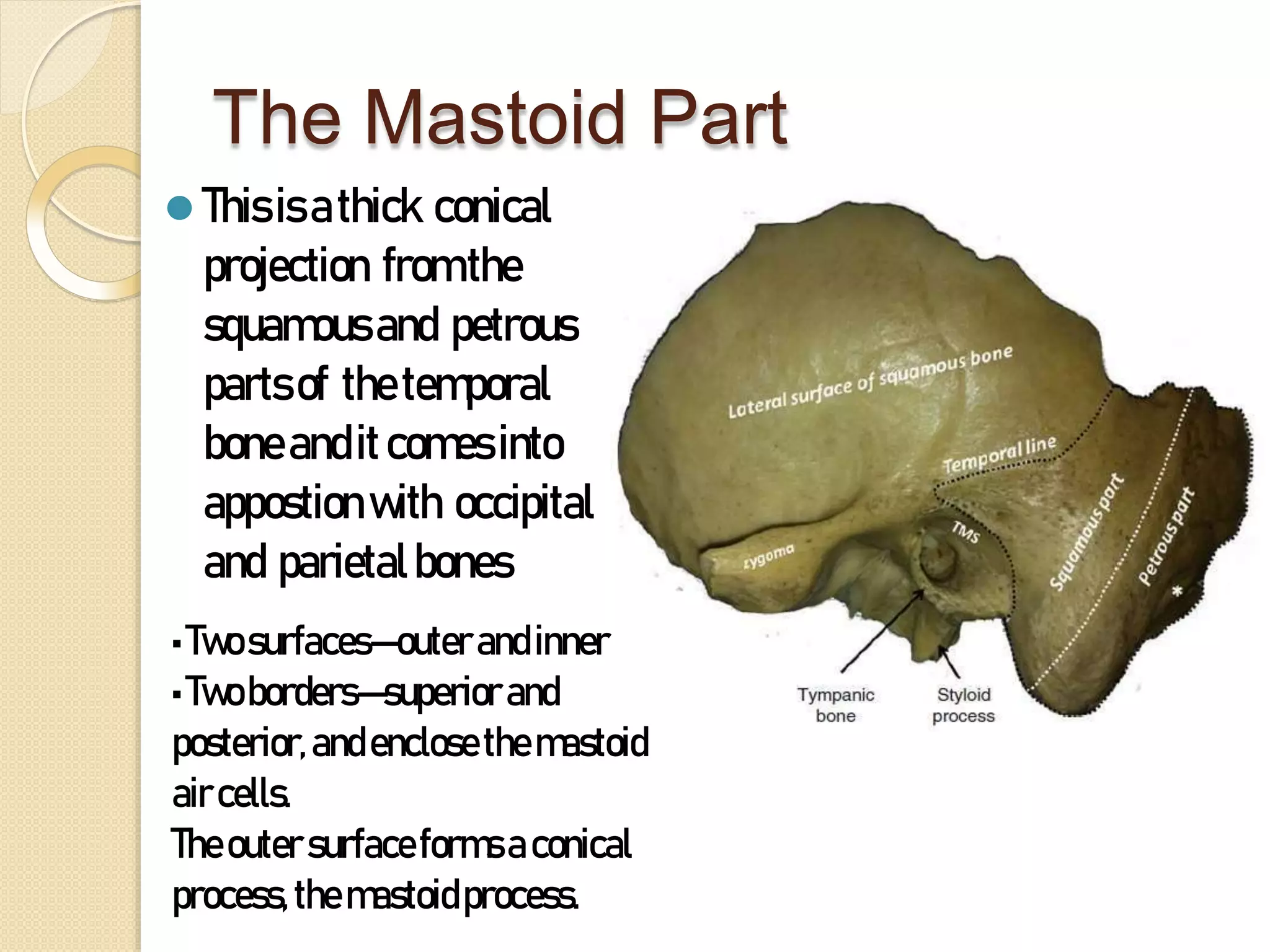
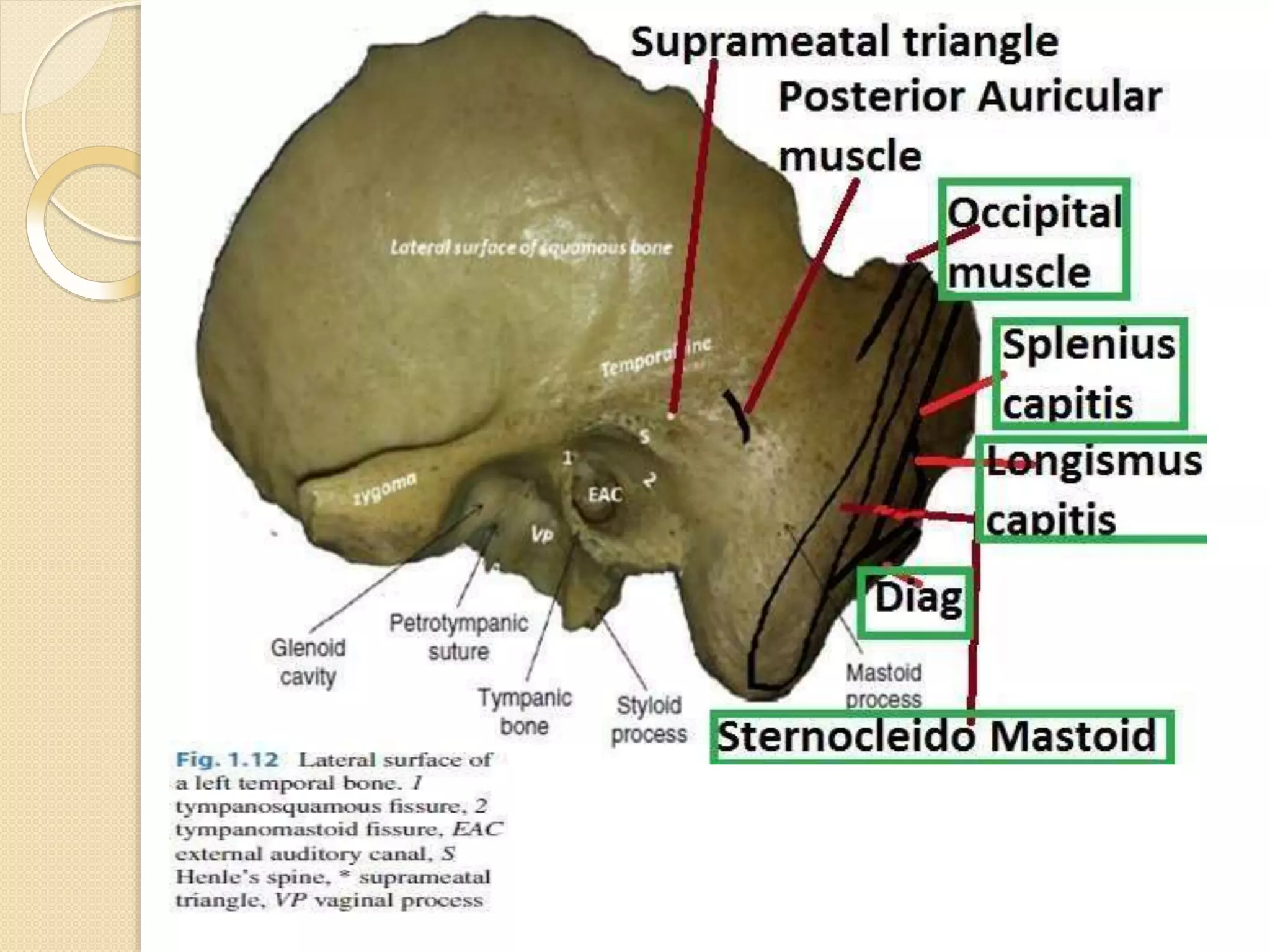
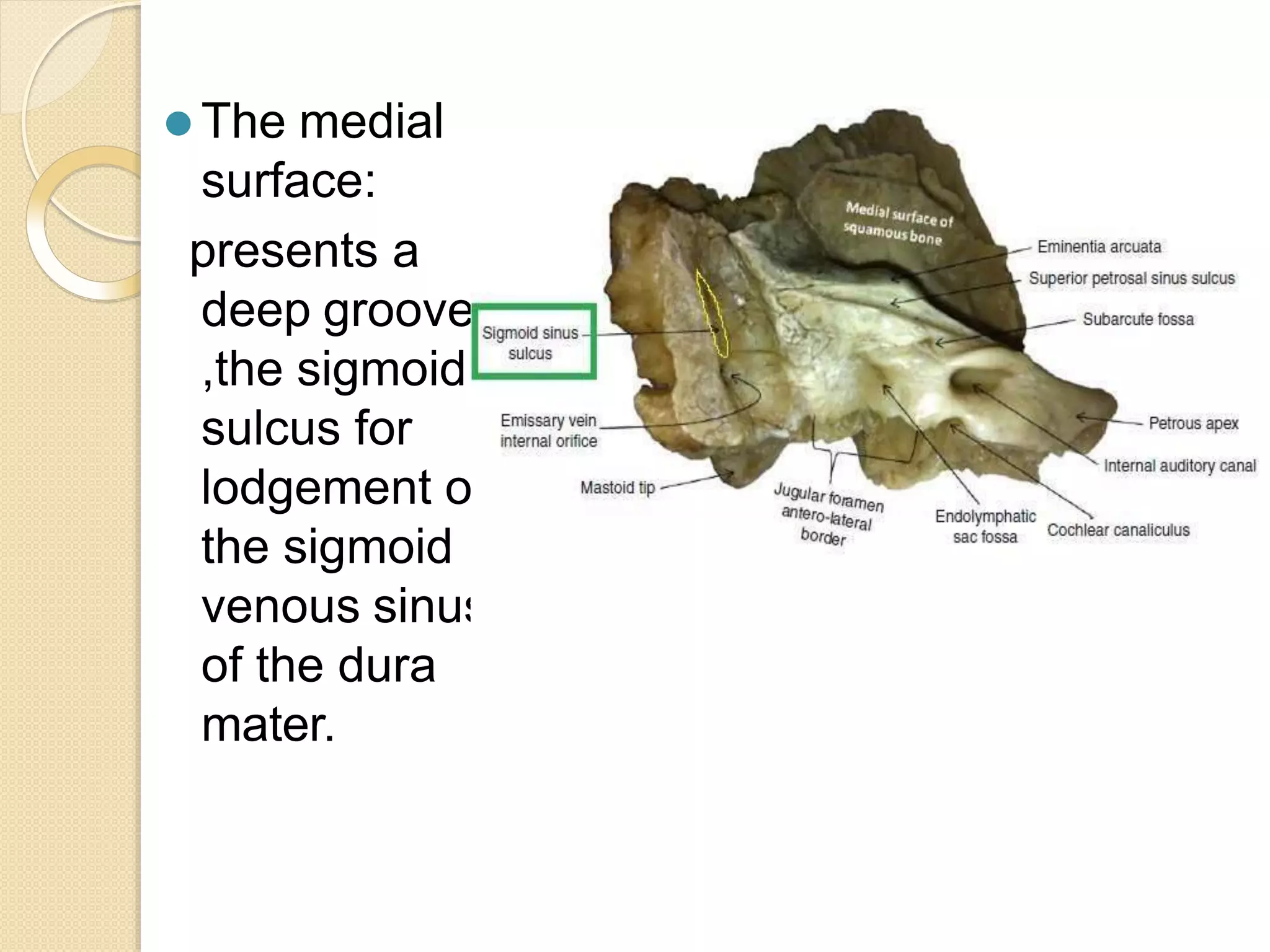
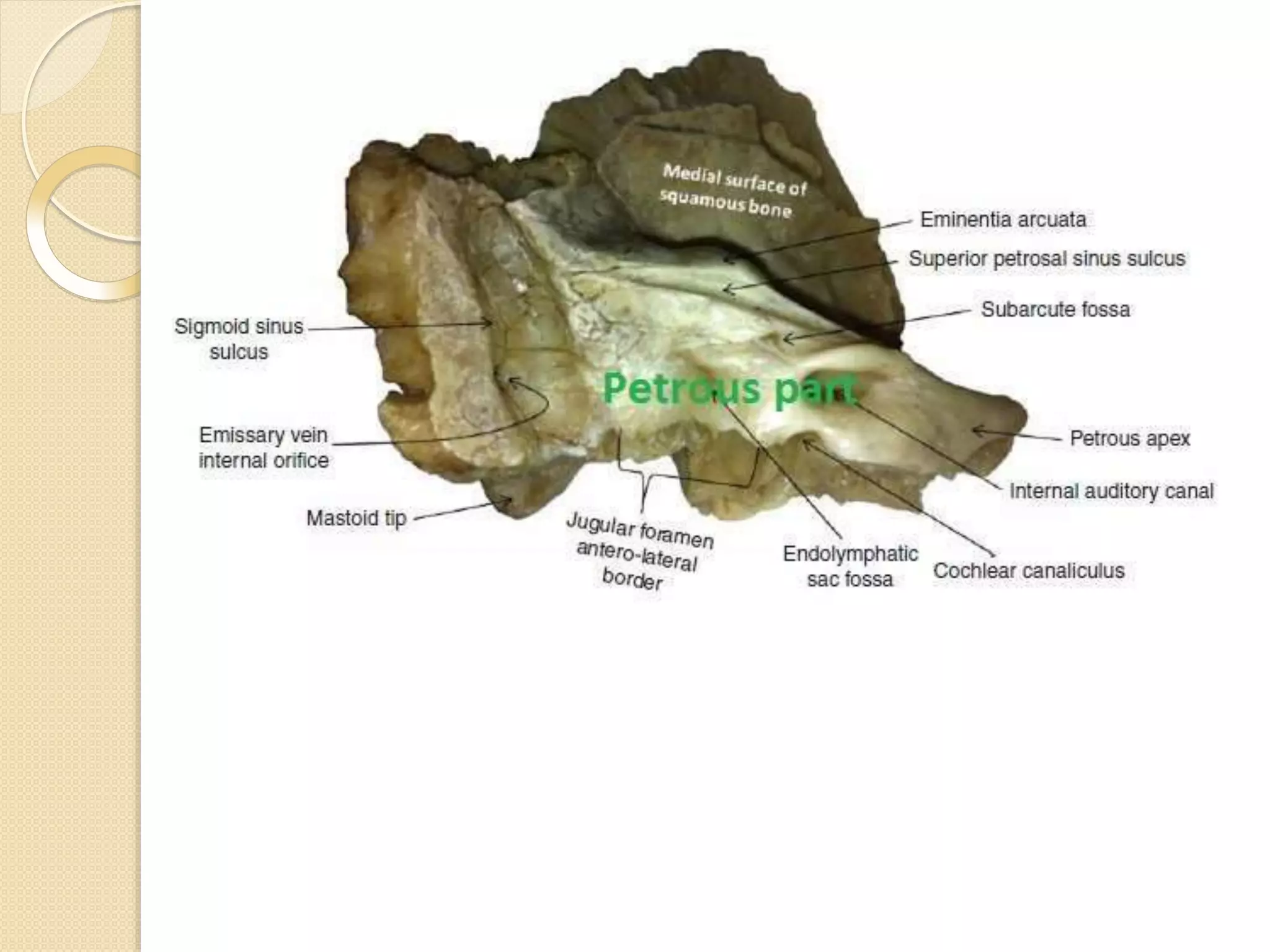
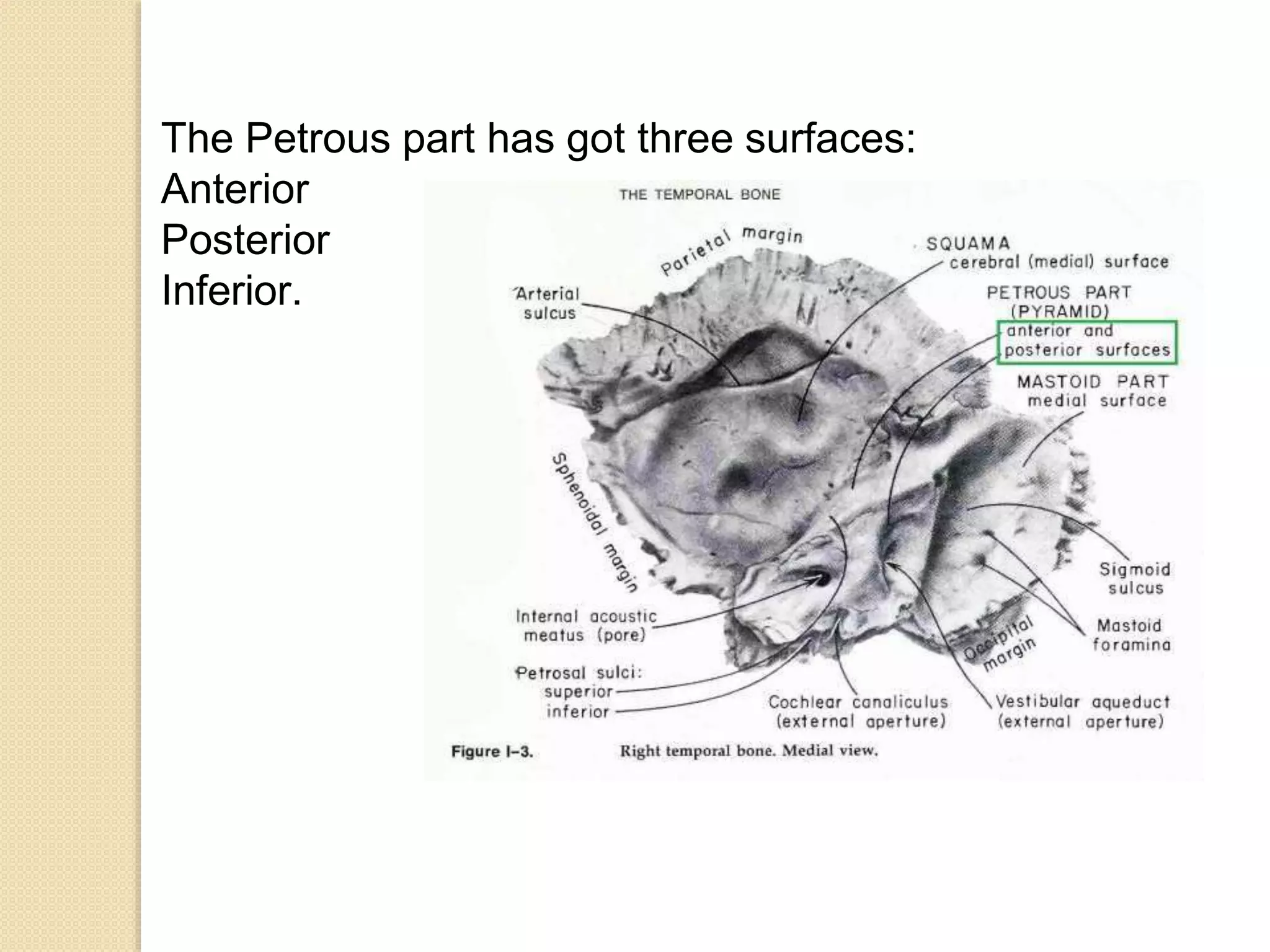
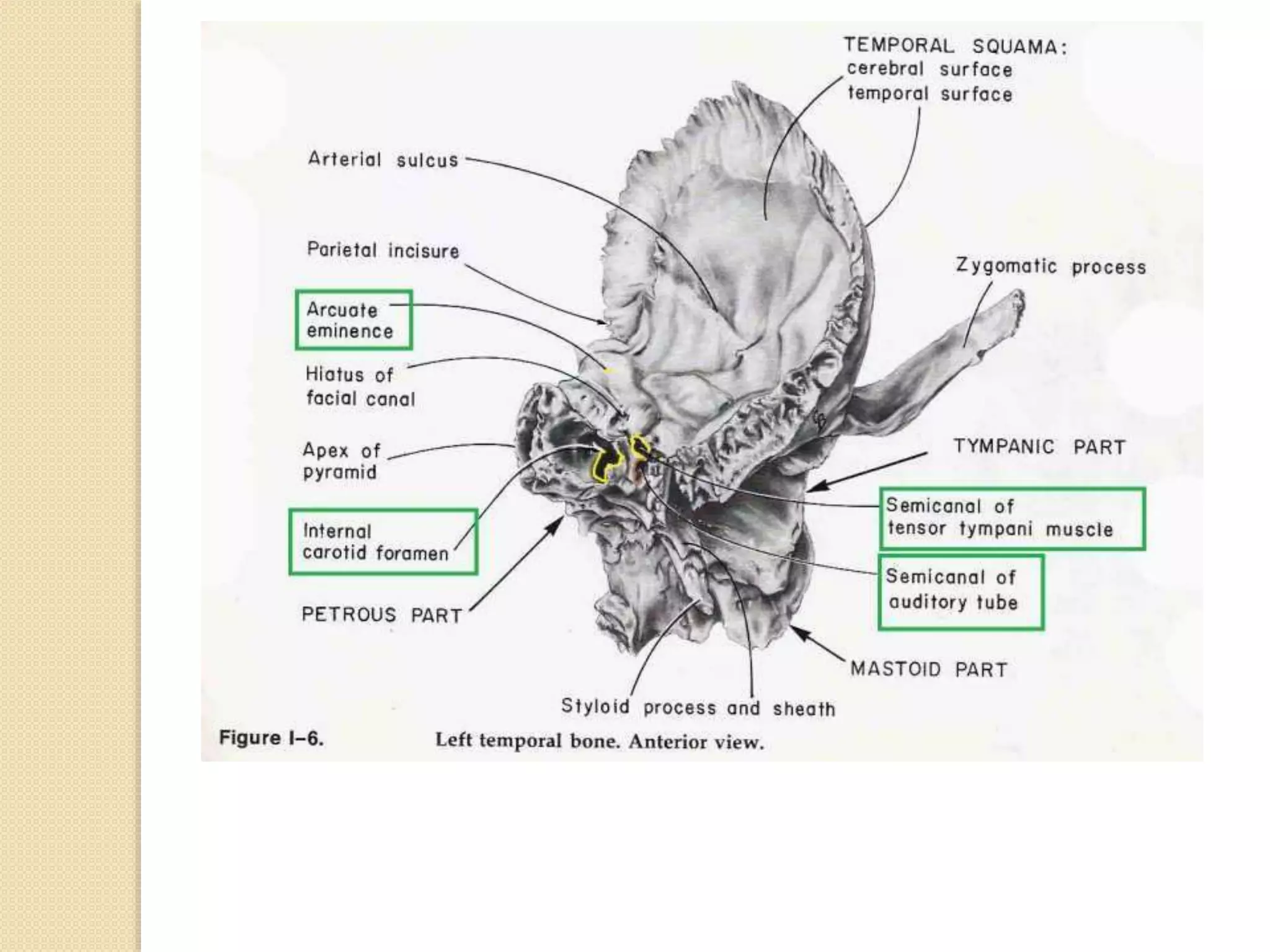
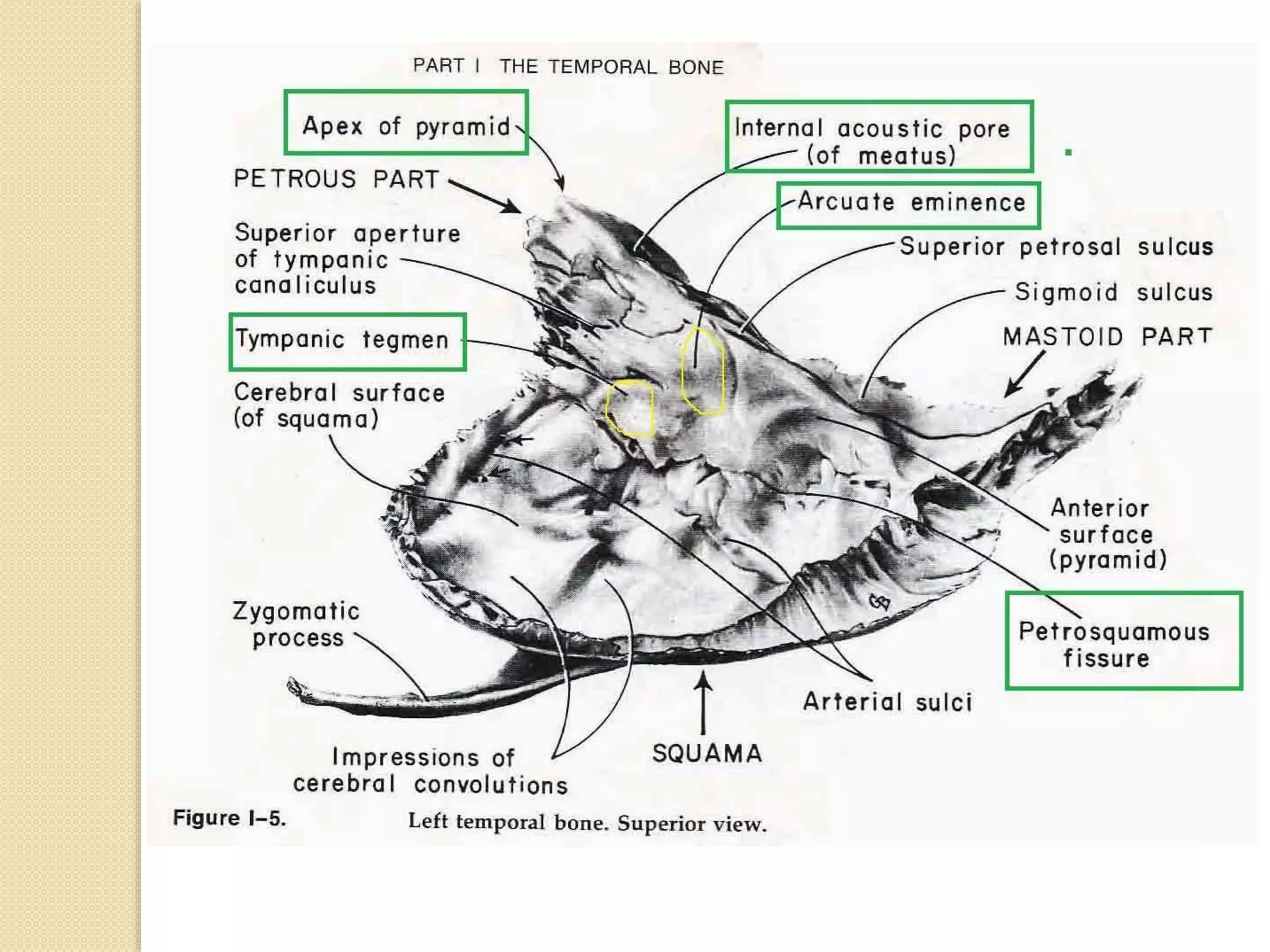
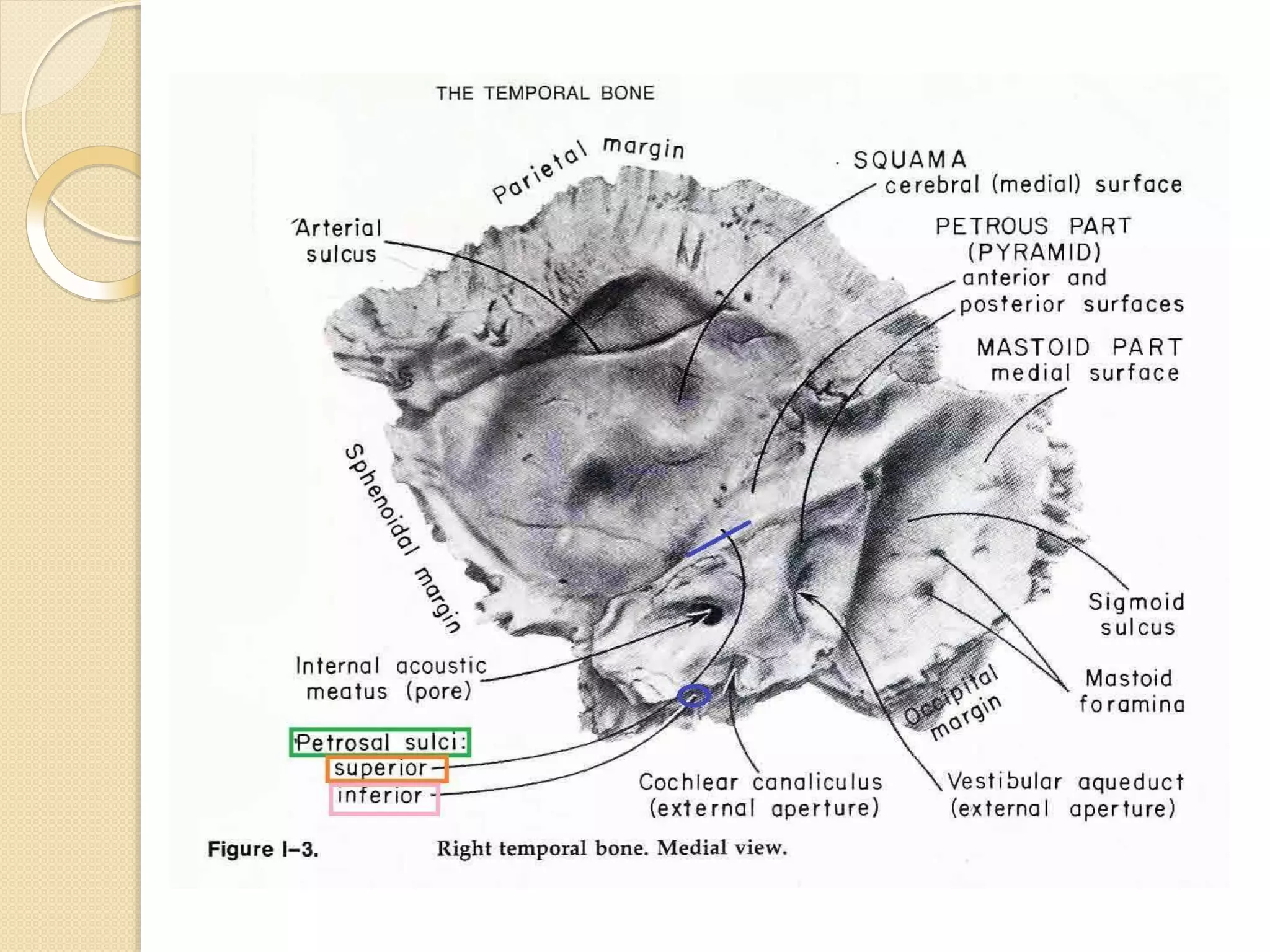
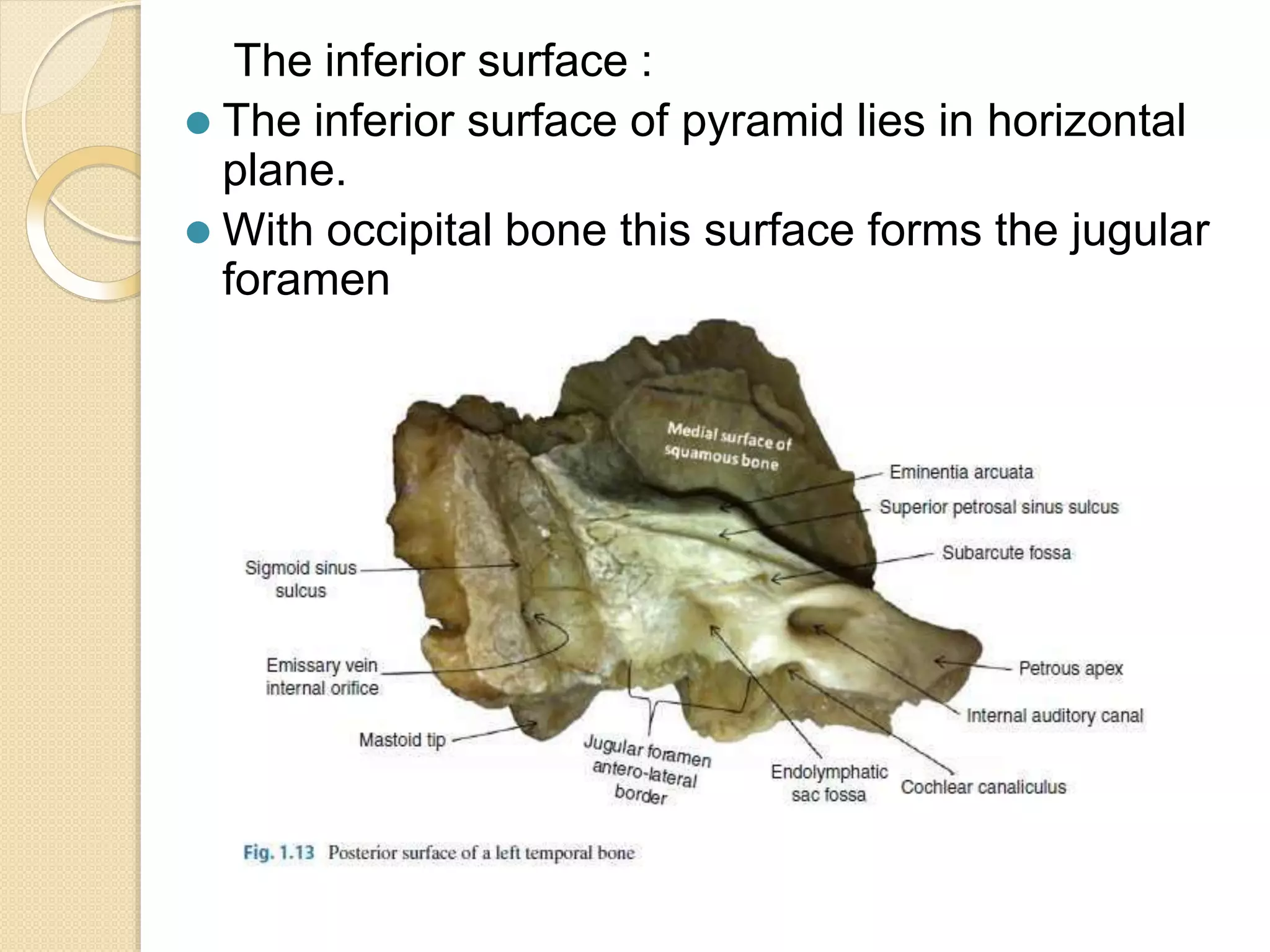
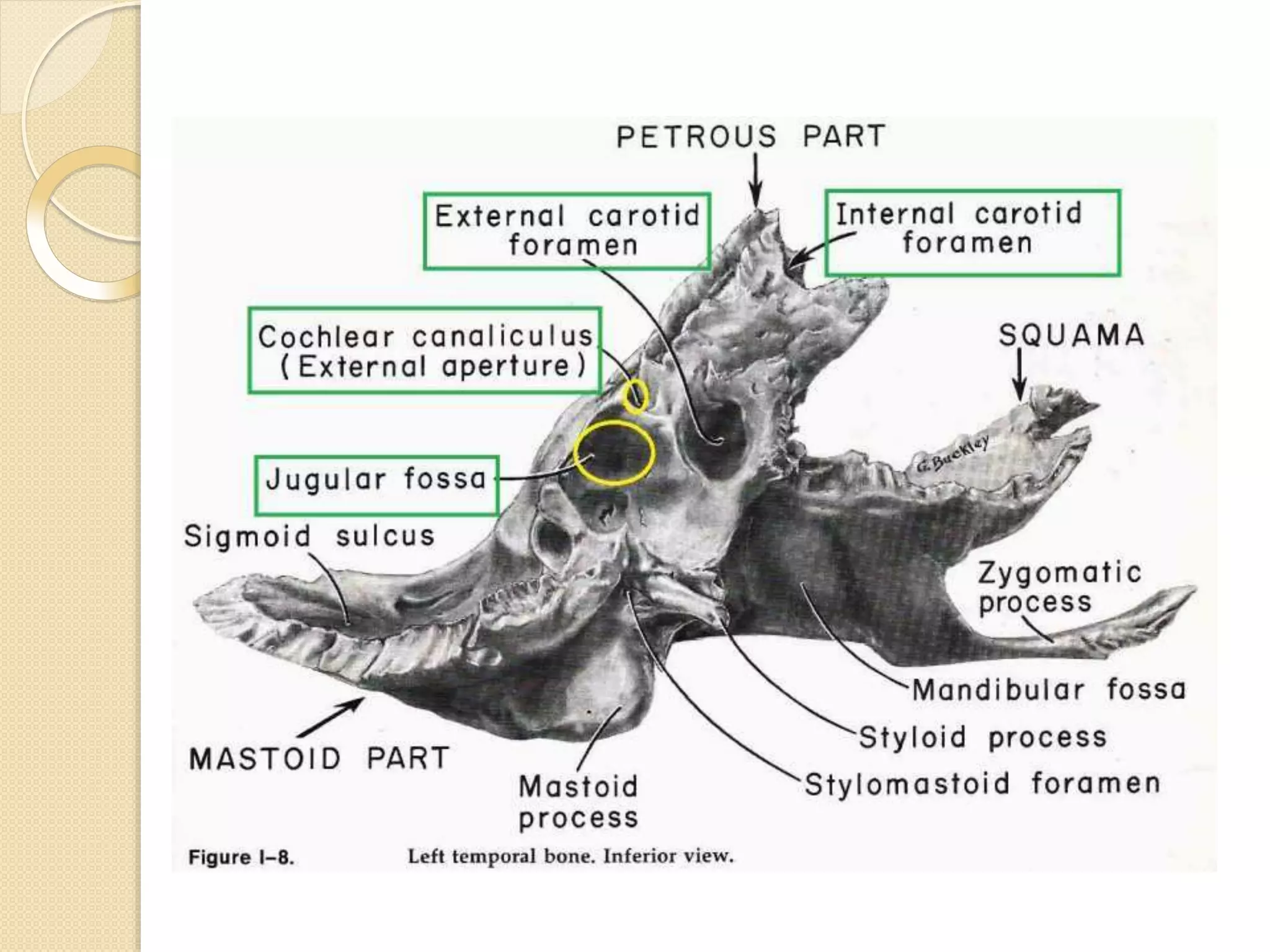
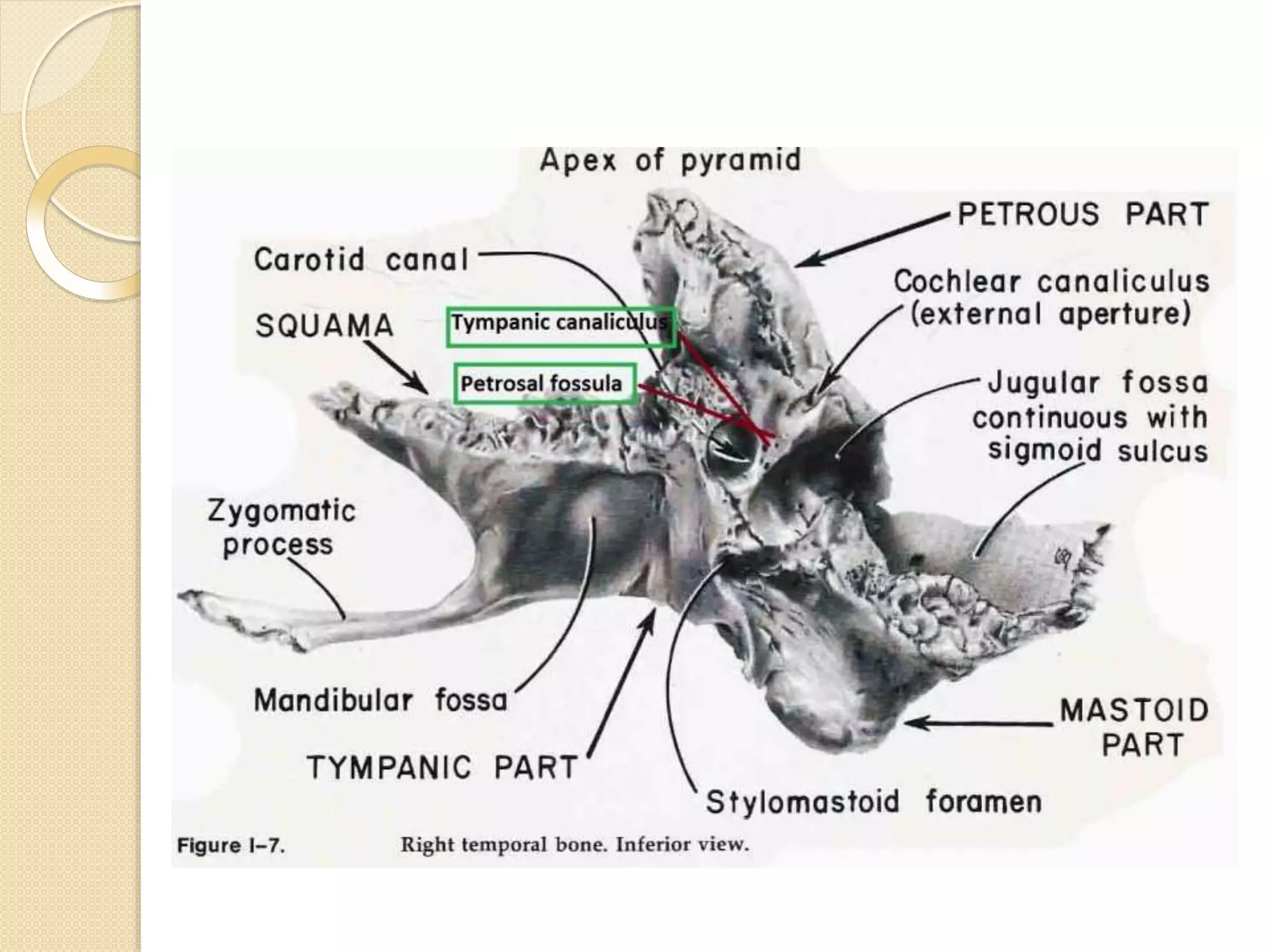
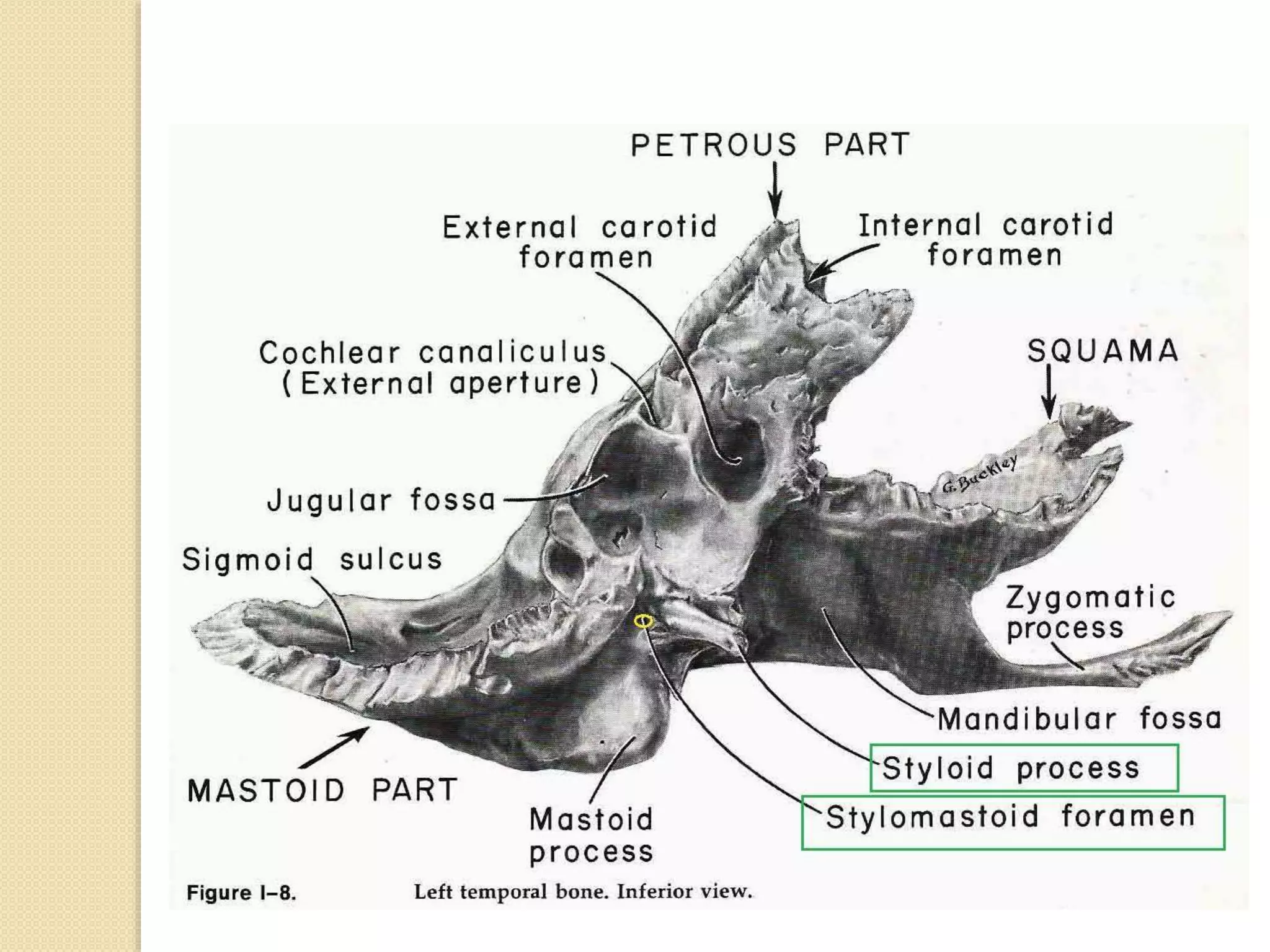
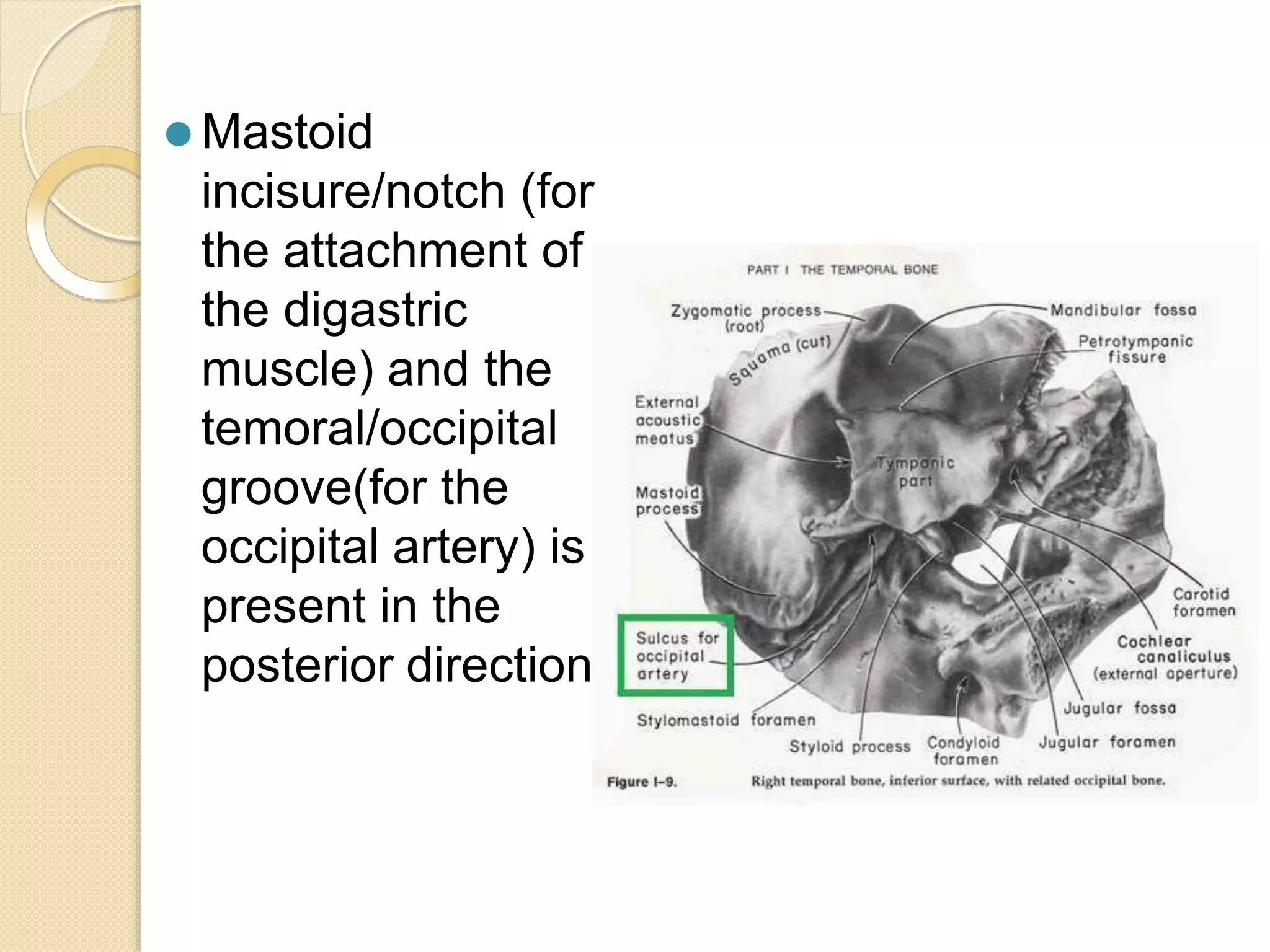
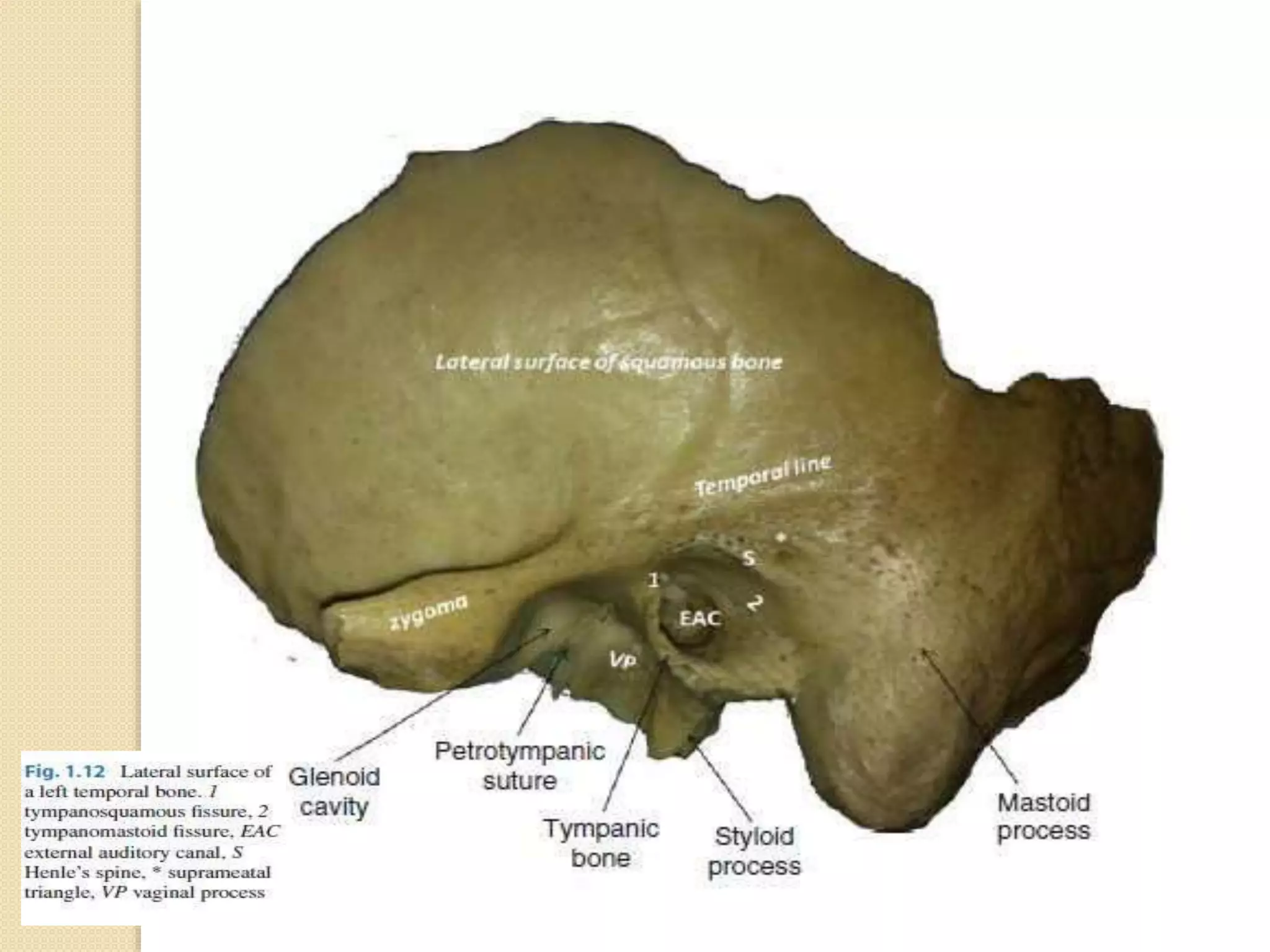
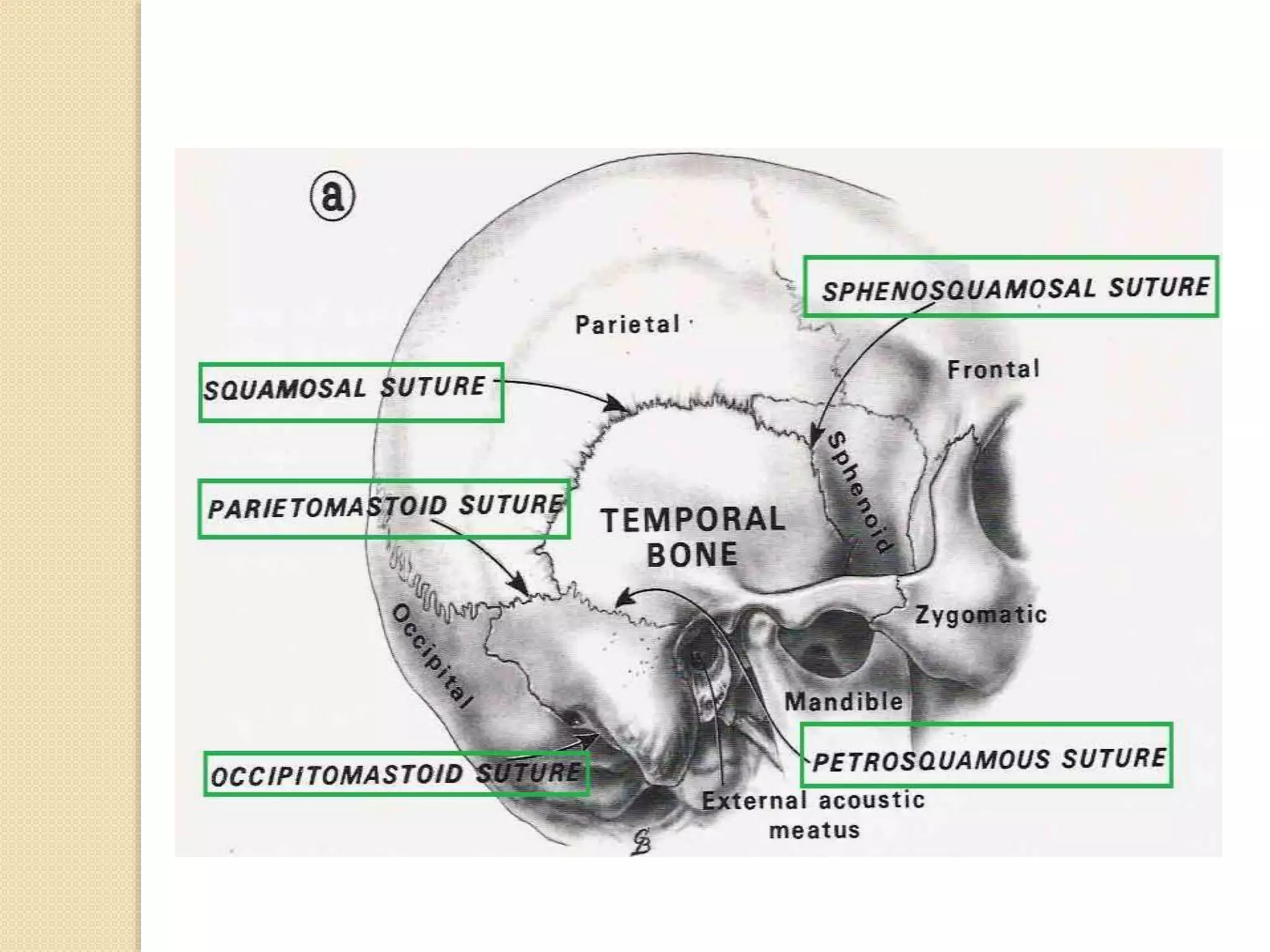
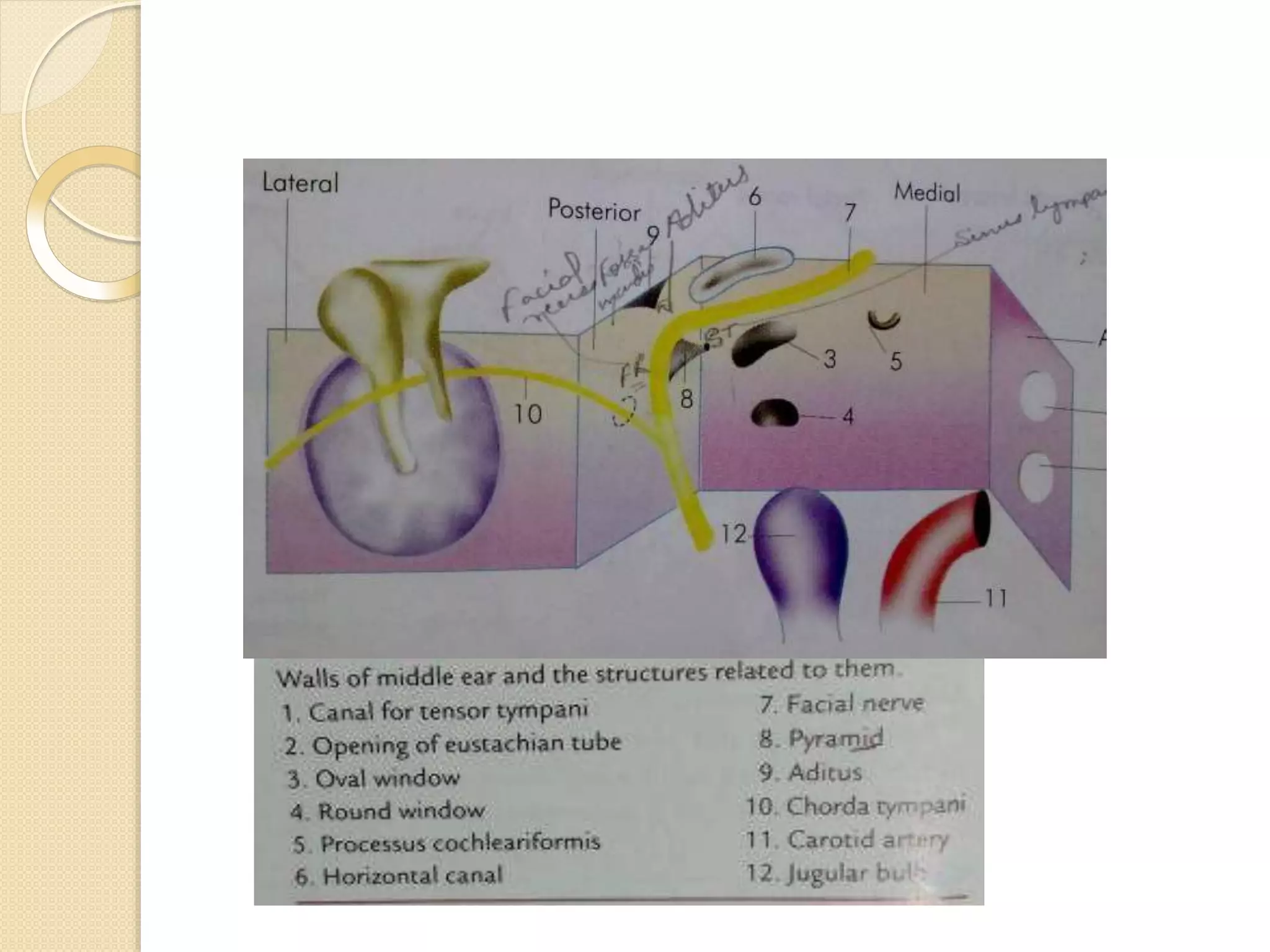
The temporal bone contributes to the base and lateral wall of the skull. It is divisible into four parts - squamous, mastoid, petrous, and tympanic. The squamous part forms the temporal fossa and articulates with other bones. The mastoid part projects backward and houses air cells. The petrous part is pyramid-shaped and contains structures like the internal acoustic meatus. The tympanic part forms parts of the external acoustic meatus and tympanic cavity. The temporal bone articulates with surrounding bones and contains numerous structures important for hearing and cranial nerve transmission.