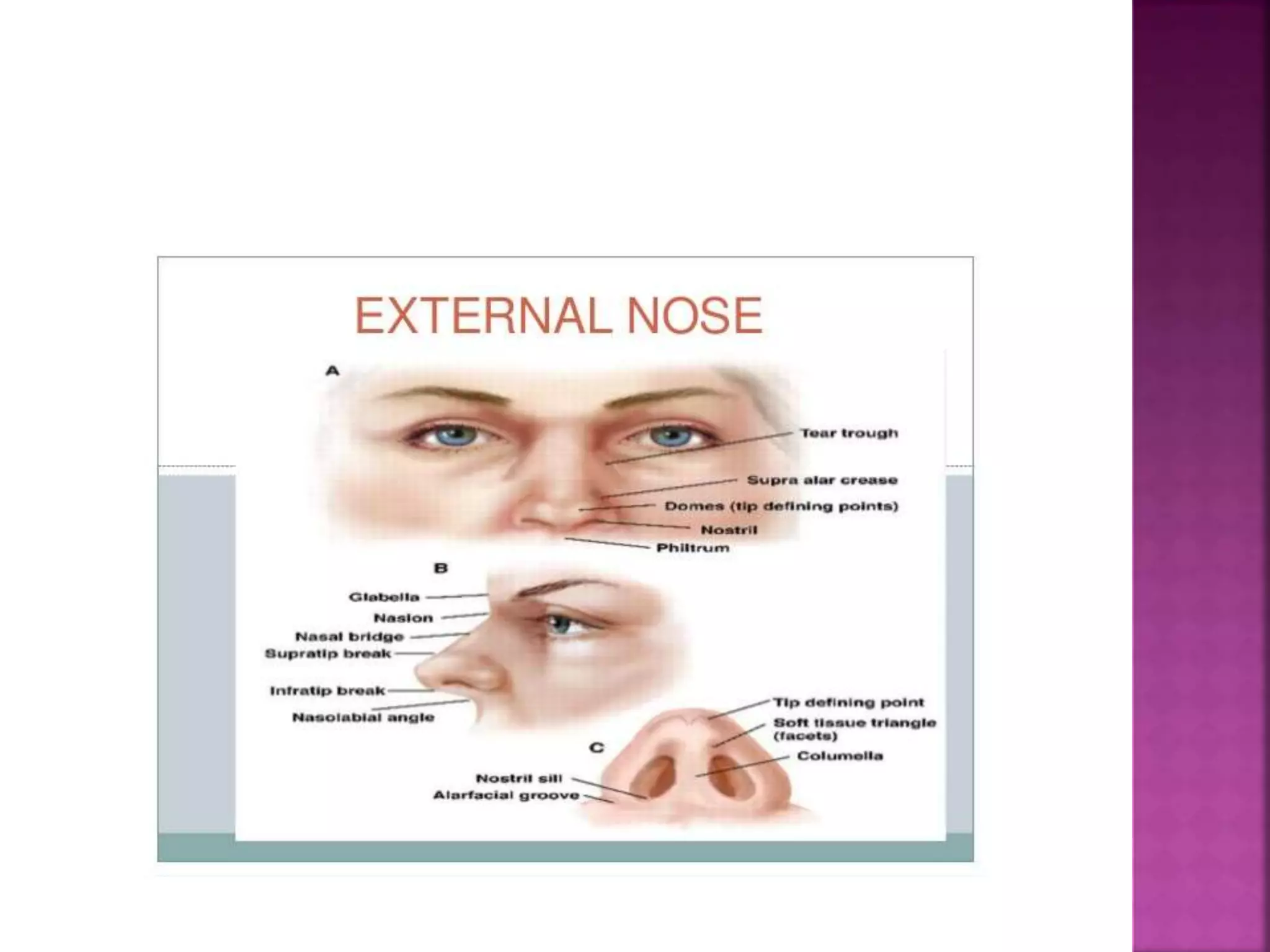
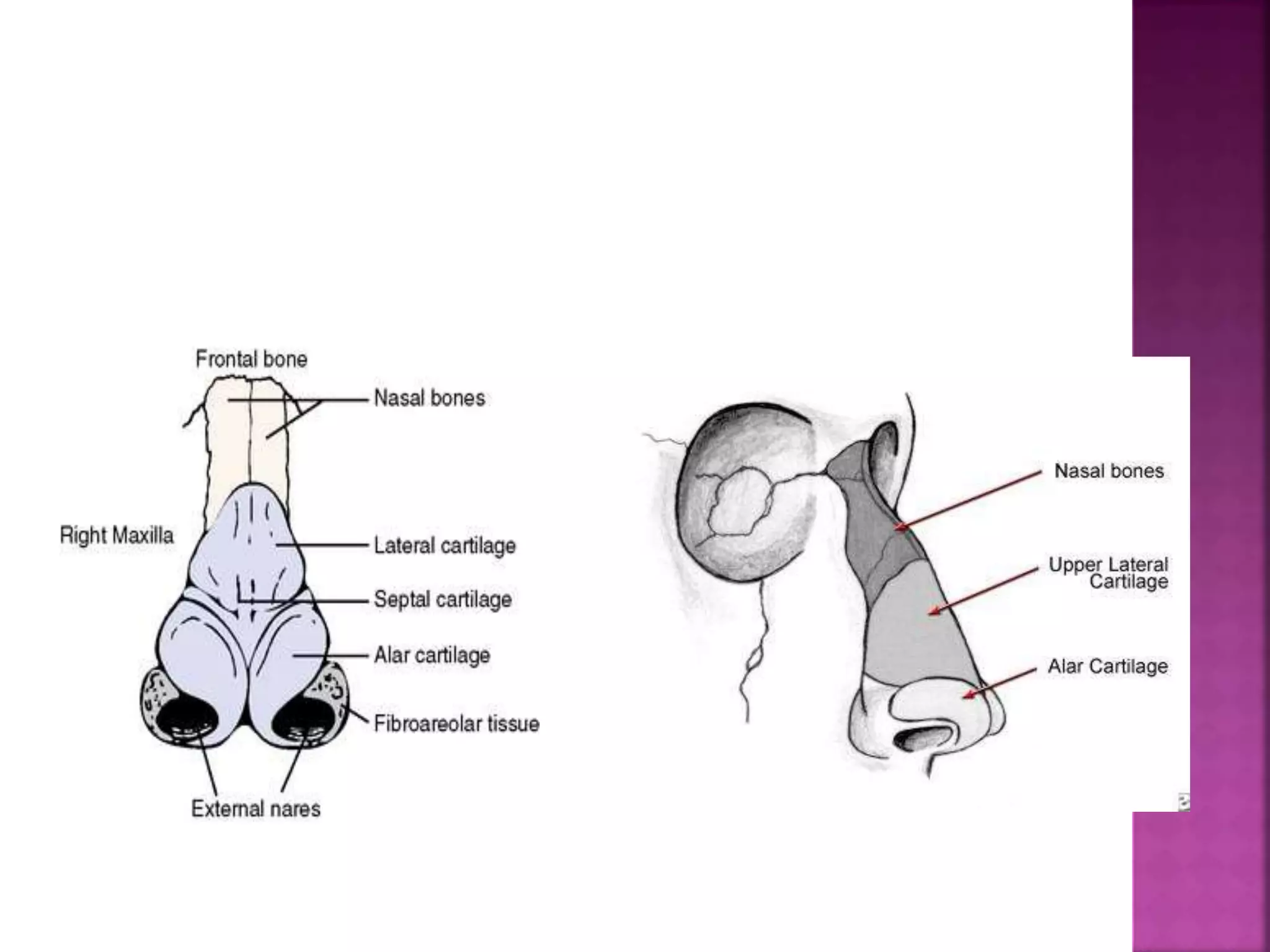
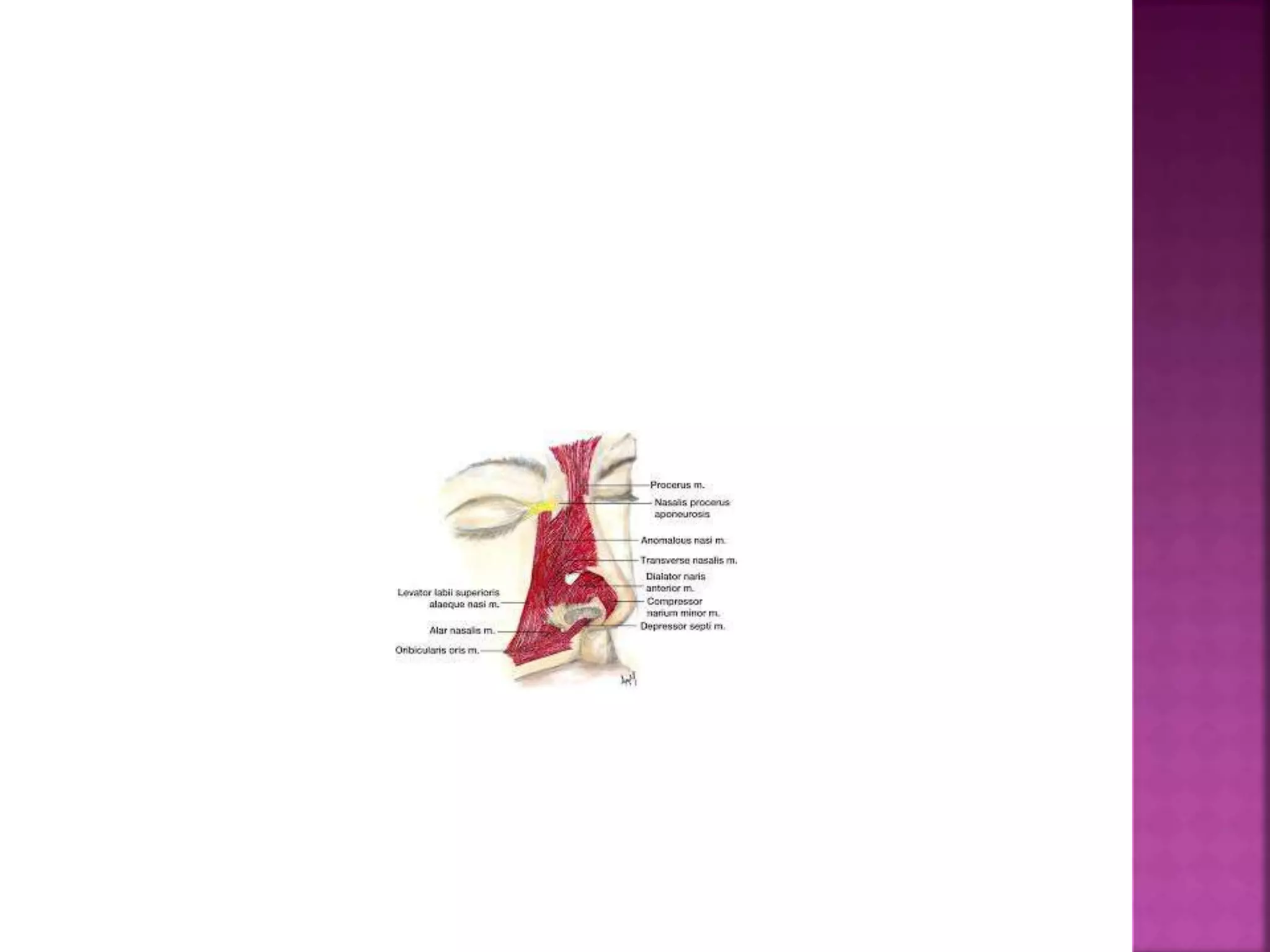
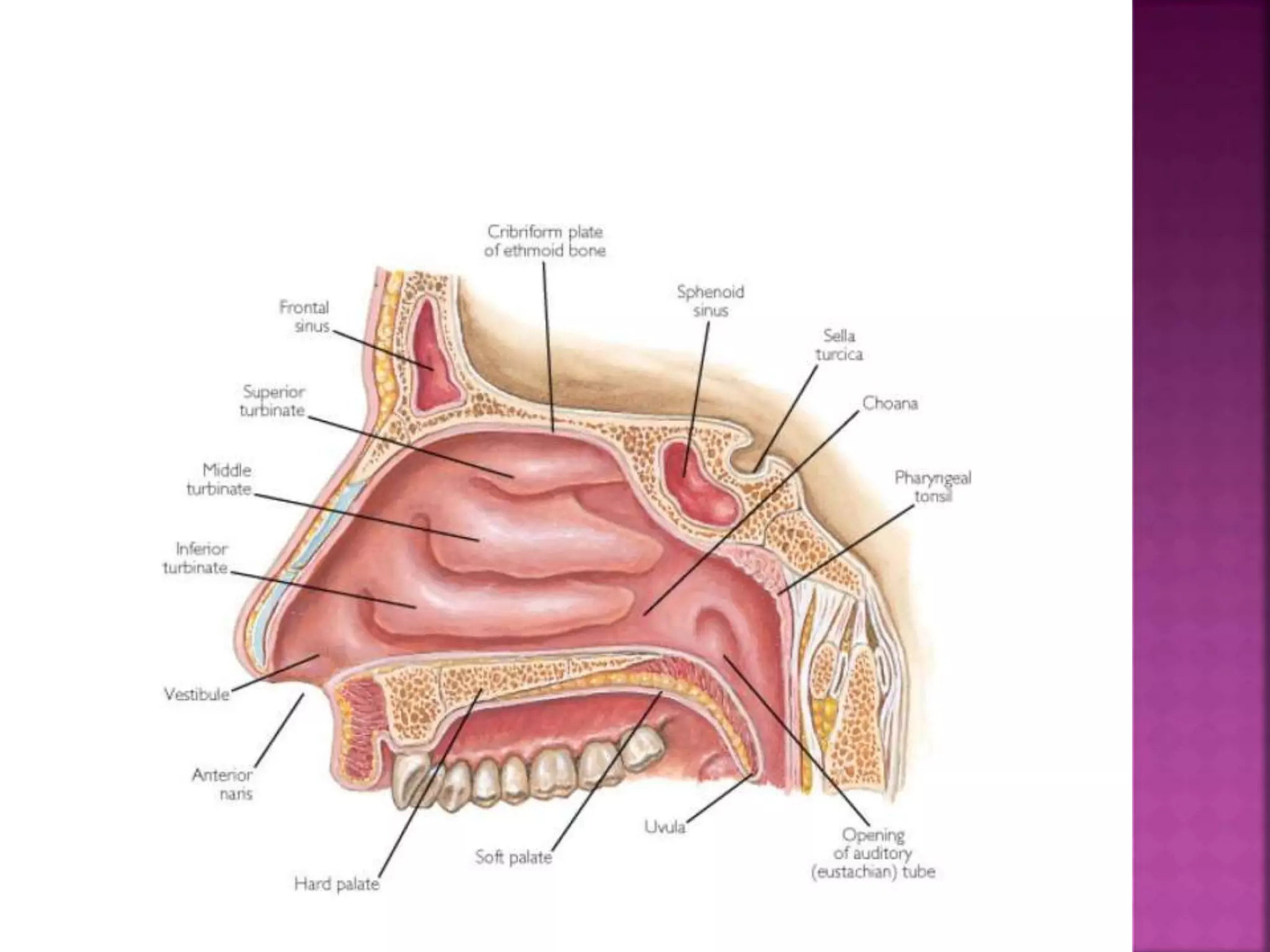
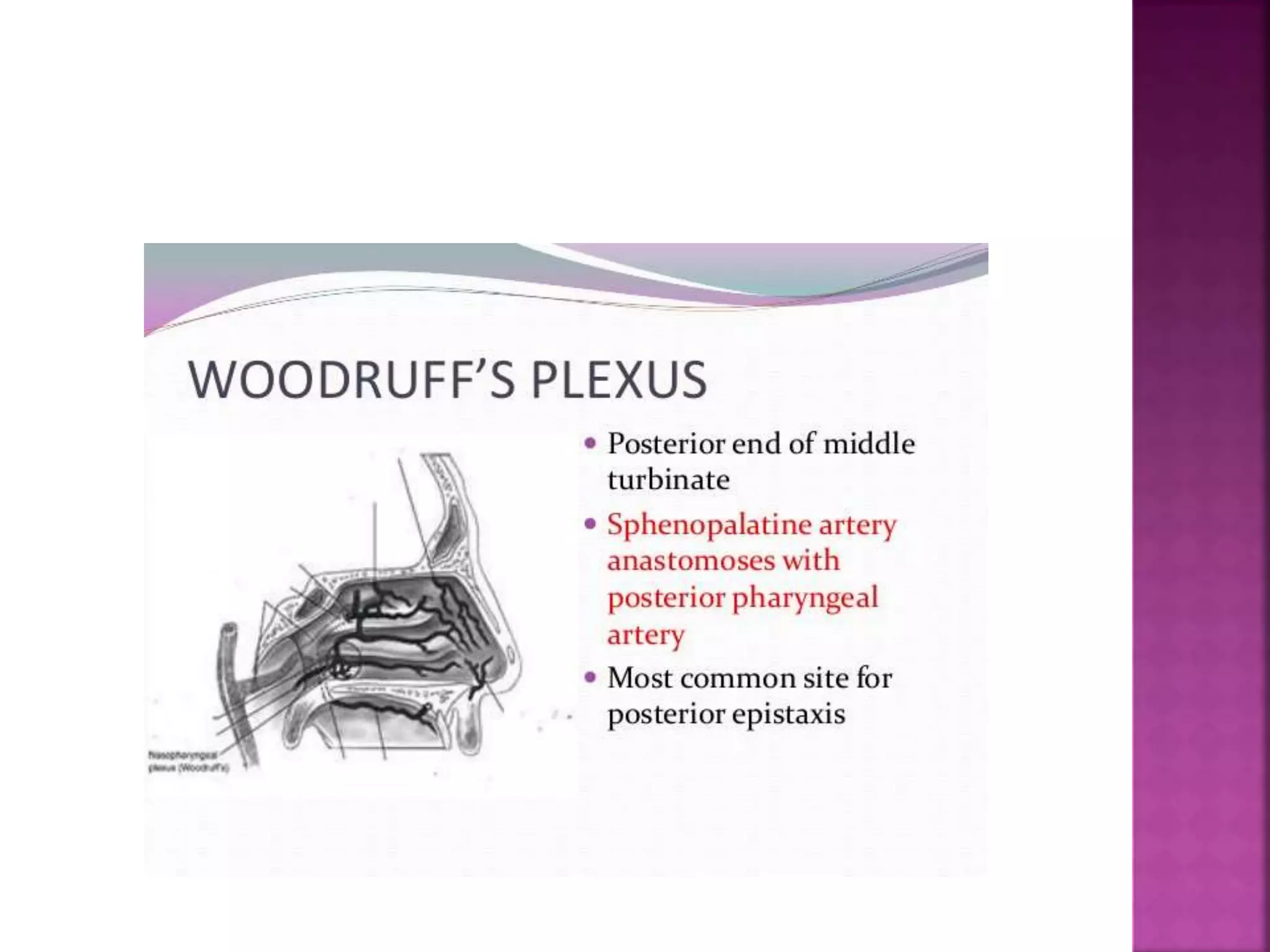
The document describes the anatomy of the nose, including its external structures, internal nasal cavity, blood supply, nerve supply, and lymphatic drainage. It details the bones and cartilages that make up the external nose and nasal septum, and describes the nasal vestibule, nasal cavities, nasal conchae and meatuses within the nasal cavity. It also outlines the skin lining, blood vessels, nerves and lymphatic drainage of the nose.