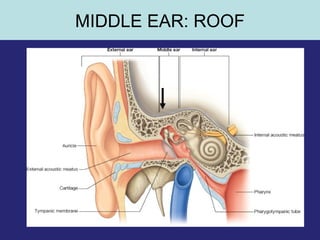
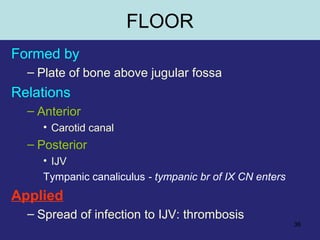
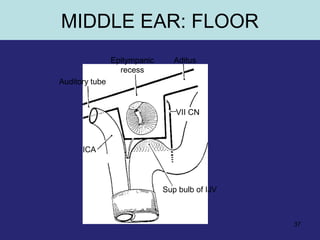
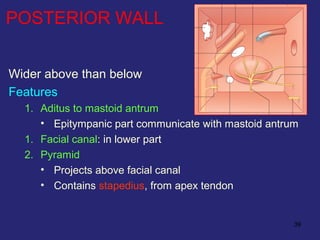
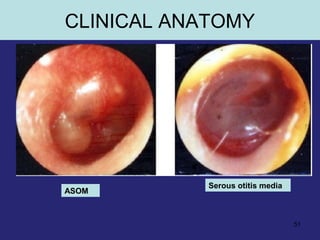
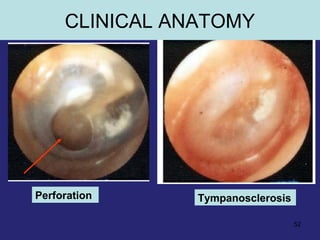
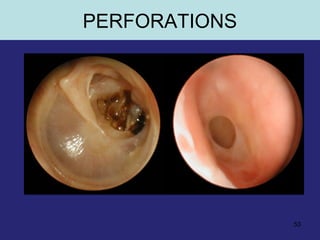
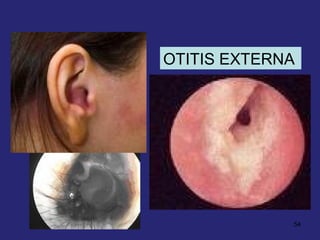
This document provides an overview of the anatomy of the ear in 3 parts:
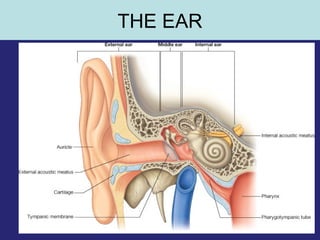
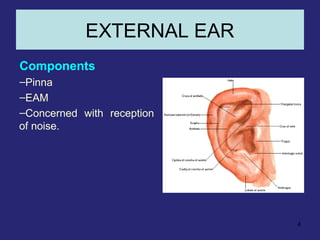
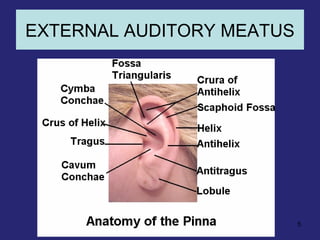
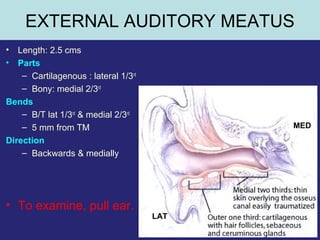
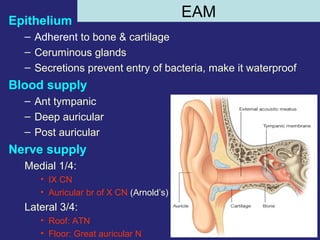
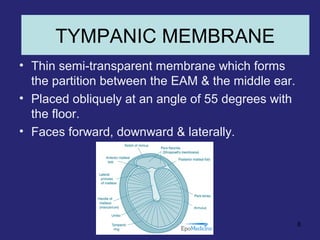
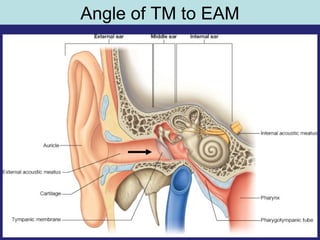
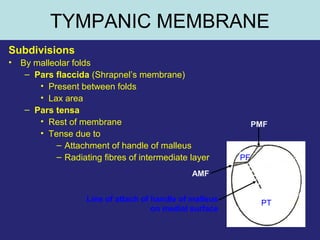
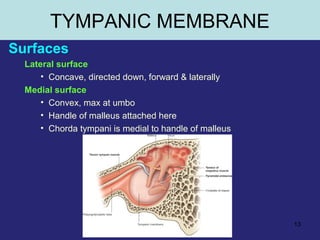
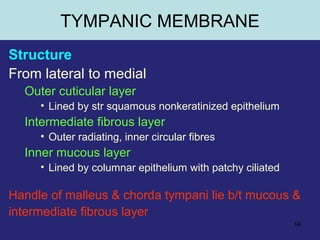
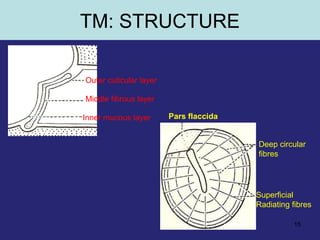
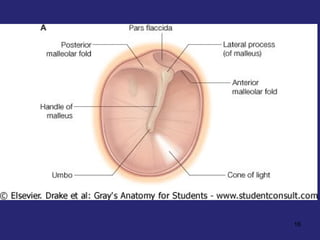
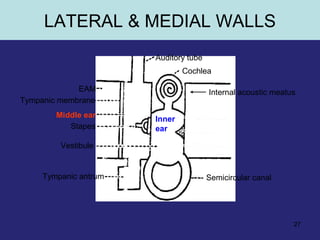
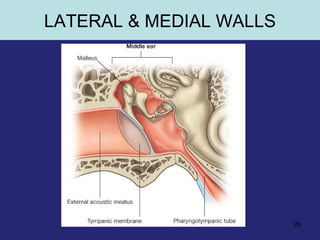
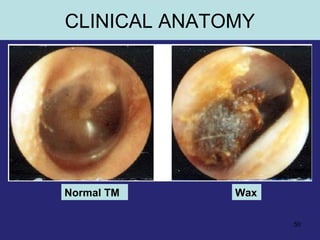
1. The external ear which includes the pinna and external auditory meatus leading to the tympanic membrane.
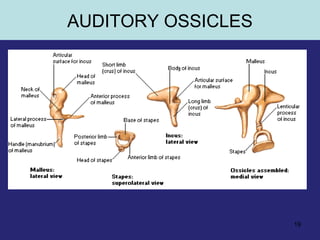
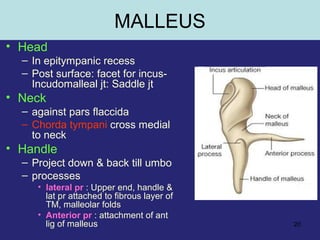
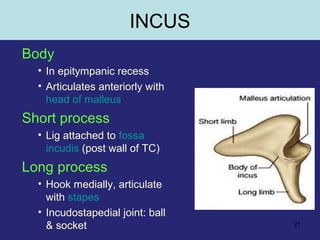
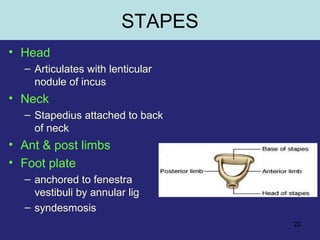
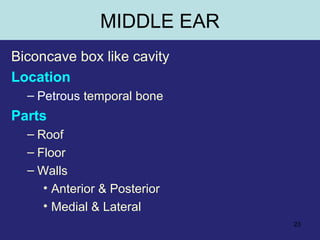
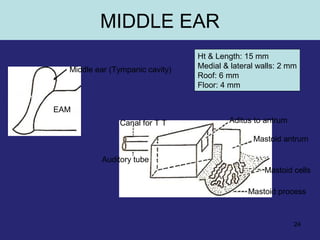
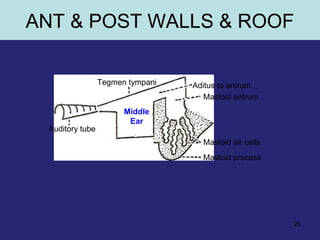
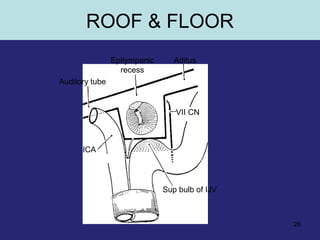
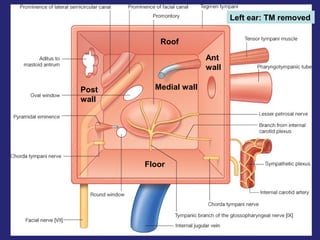
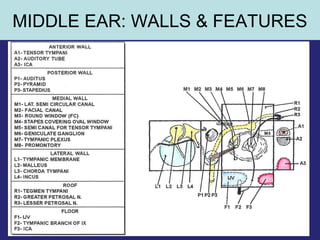
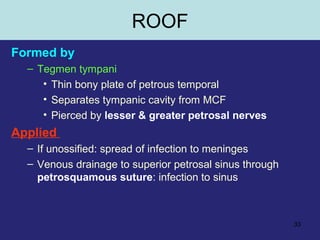
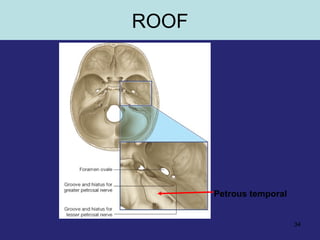
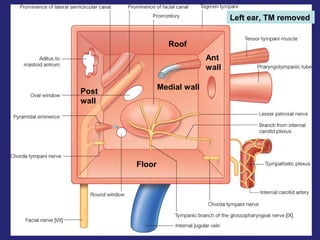
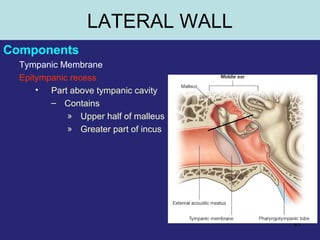
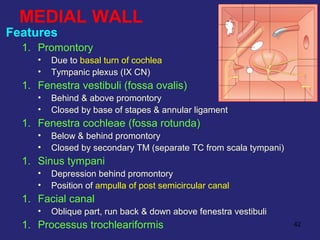
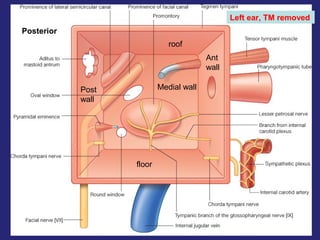
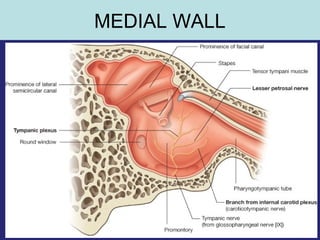
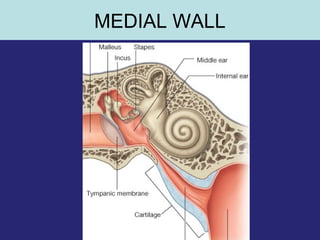
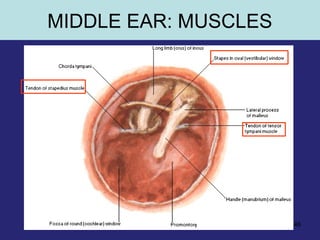
2. The middle ear which is an air filled cavity containing the 3 ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) that transmit sound vibrations from the tympanic membrane to the inner ear.
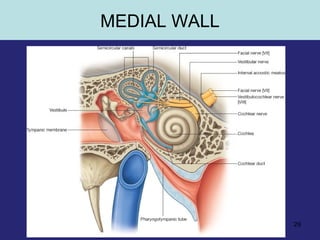
3. The inner ear which contains the bony and fluid filled labyrinth involved in hearing and balance. Each section describes the structures and their functions. Clinical correlations regarding common ear diseases are also discussed.