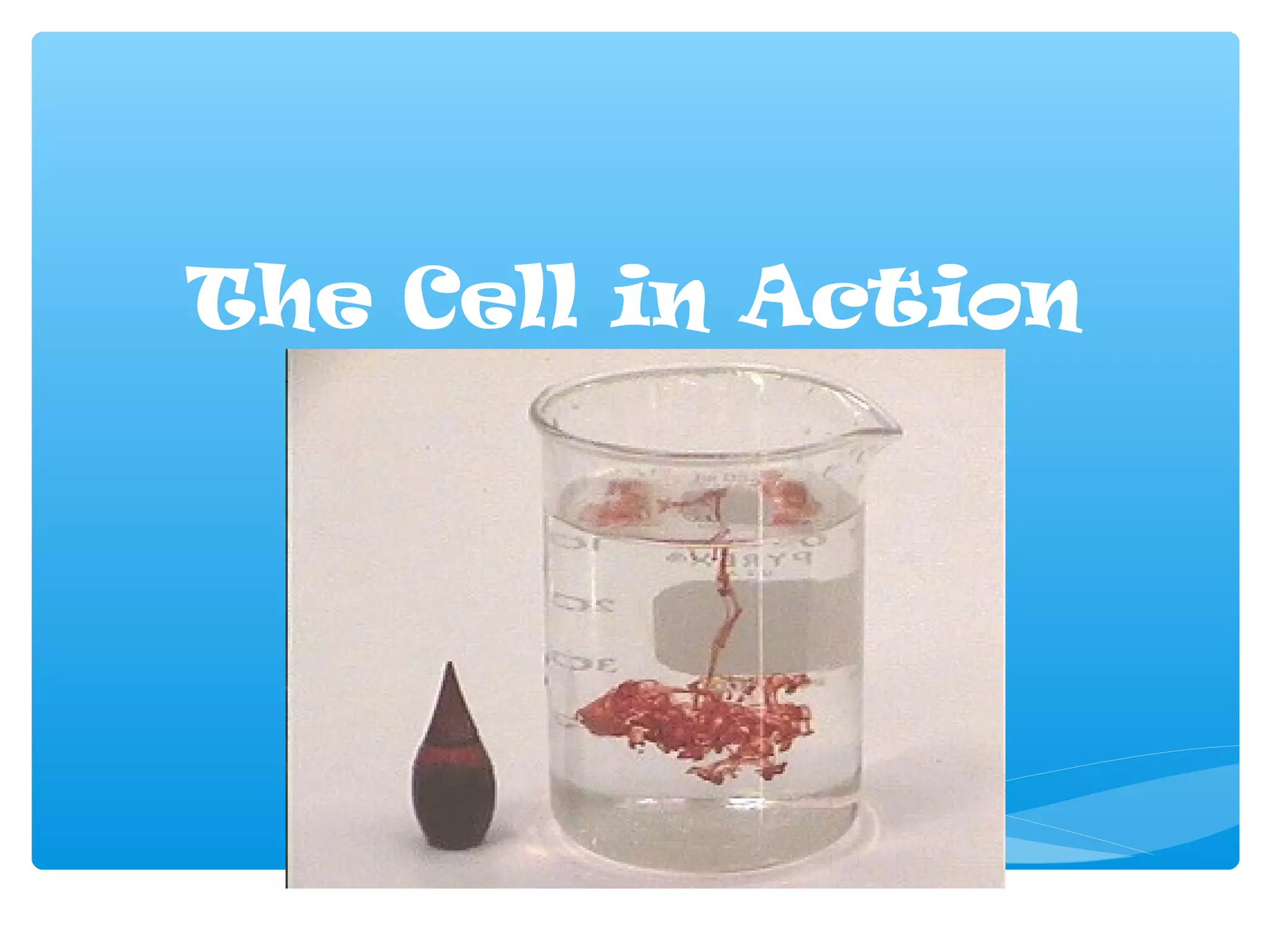
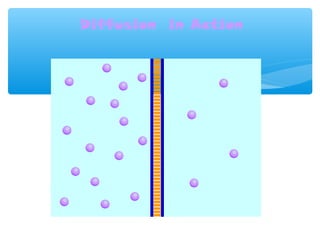
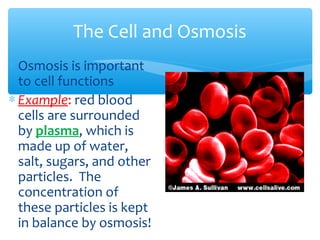
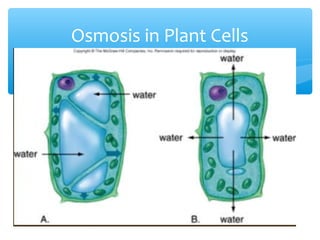
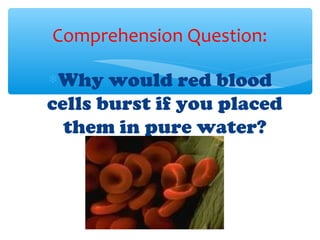
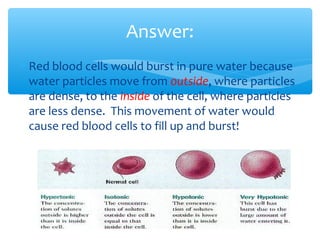
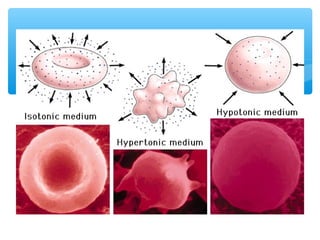
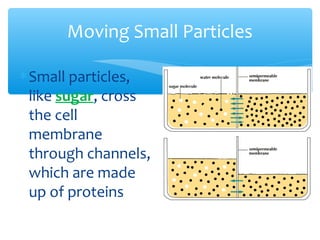
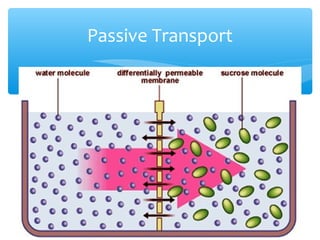
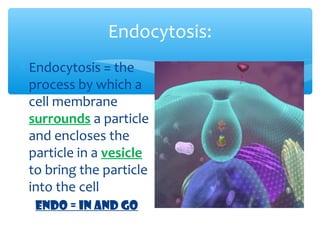
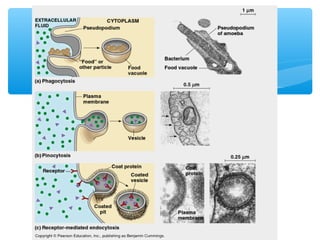
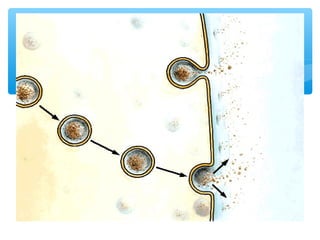
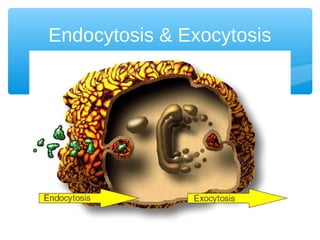
The document discusses various processes that cells use to exchange materials with their environment, including diffusion, osmosis, and active and passive transport. Diffusion is the movement of particles from high to low concentration without energy usage. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane. Passive transport includes osmosis and diffusion, while active transport requires energy and can move particles against a concentration gradient, such as endocytosis and exocytosis.