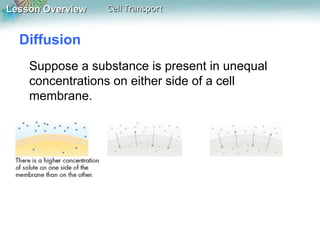
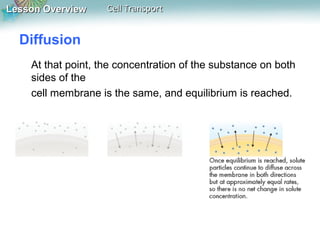
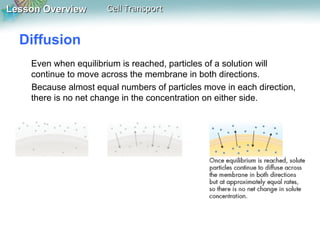
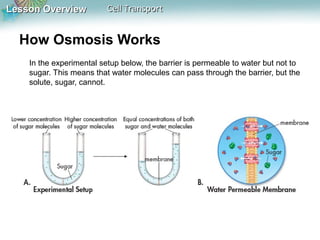
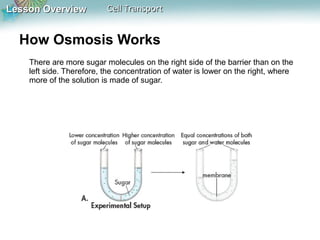
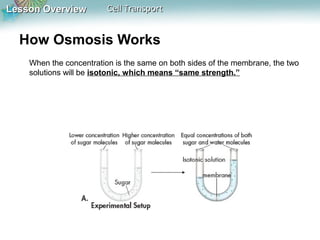
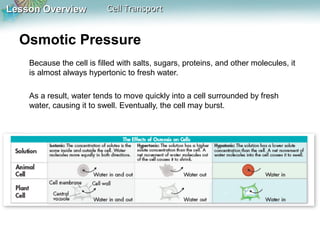
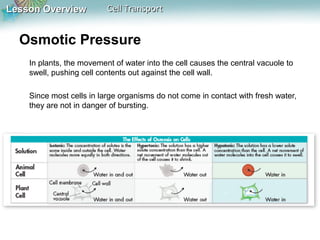
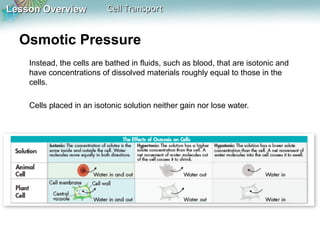
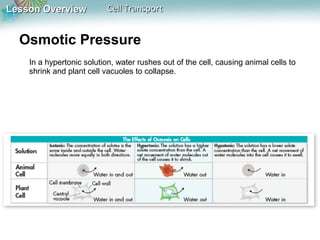
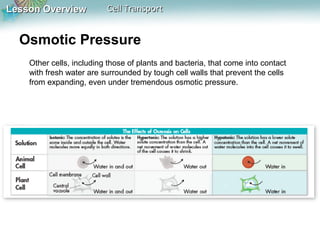
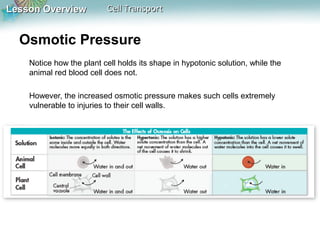
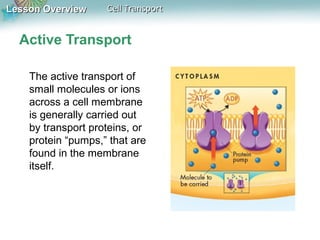
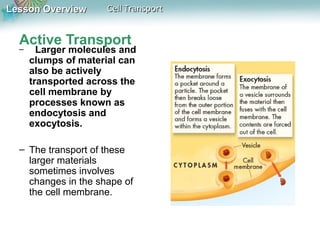
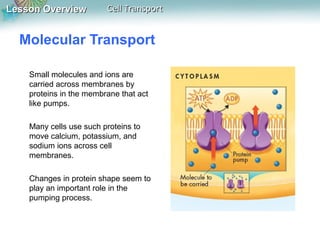
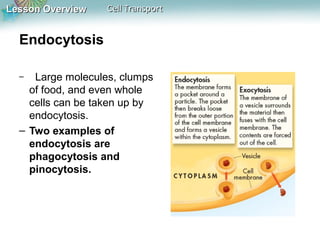
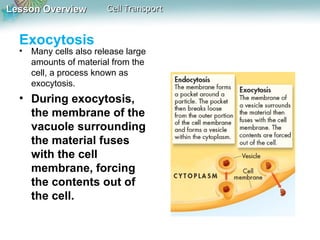
This document discusses different types of cell transport mechanisms, including passive transport through diffusion and facilitated diffusion, as well as active transport. It explains that passive transport involves the movement of materials across membranes without using energy, such as diffusion of substances from high to low concentration areas. Active transport requires energy and moves materials against a concentration gradient using protein pumps and channels. It also describes osmosis as a type of facilitated diffusion and how osmotic pressure impacts cells. Bulk transport of larger particles uses endocytosis to bring materials into cells and exocytosis to expel them.