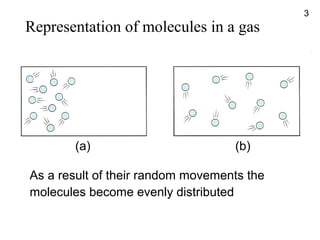
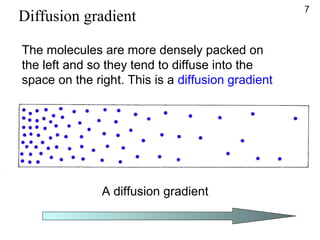
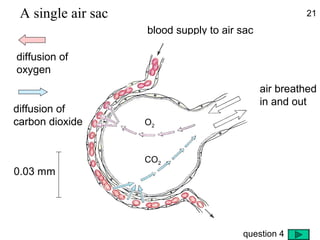
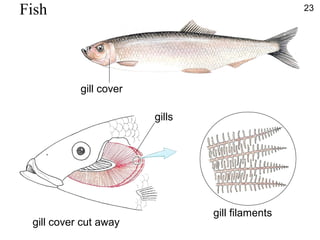
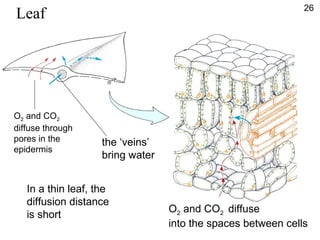
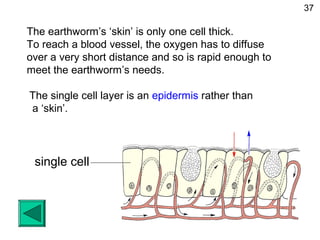
- Molecules move freely in gases and liquids which allows substances to diffuse and become evenly distributed.
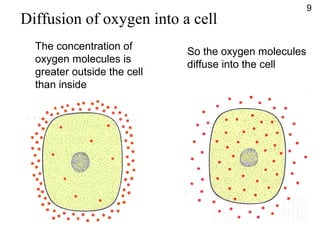
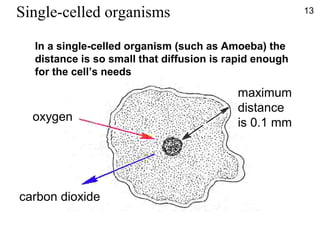
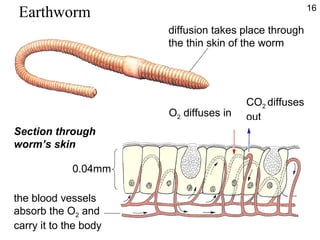
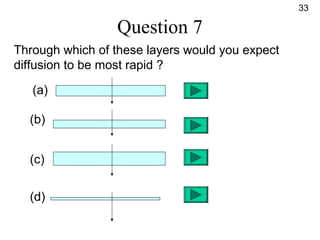
- Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration and allows substances like oxygen to enter cells.
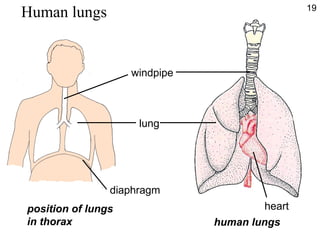
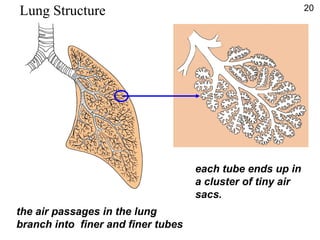
- While diffusion works for single-celled organisms and transporting oxygen in the human body, it is too slow for large organisms so systems like blood circulation evolved.