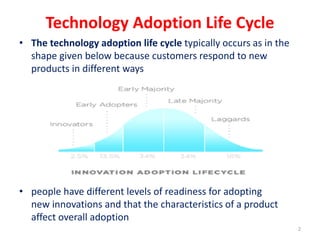
Rogers classified individuals into five groups in the technology adoption life cycle: innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority, and laggards. Innovators are willing to take risks and have the highest social status and financial liquidity. Early adopters have high social status and influence opinions. The early majority adopt after early adopters when more people are using the technology, while the late majority need most people to adopt before doing so and are more doubtful. Laggards are last to adopt and focused on traditions.