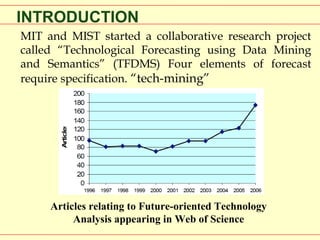
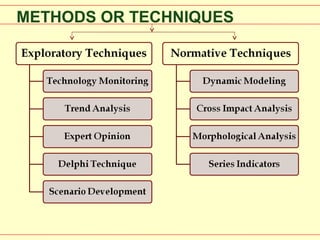
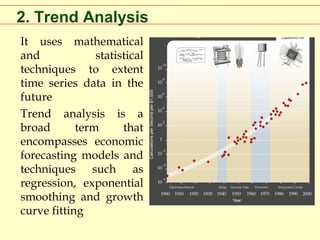
This document discusses methods and techniques for technological forecasting. It begins by introducing a collaborative research project on technological forecasting using data mining and semantics between MIT and MIST. It then lists leading journals in future-oriented technology analysis and technological forecasting. The rest of the document describes both qualitative and quantitative forecasting methods, including exploratory methods like technology monitoring, trend analysis, expert opinion, Delphi technique, and scenario development. It also discusses normative methods such as dynamic modeling, cross impact analysis, morphological analysis, and using series indicators. It concludes by noting no single technique is best and that choosing a technique depends on cost, accuracy, available data, computers, time, and forecast horizon.