Embed presentation
Downloaded 24 times



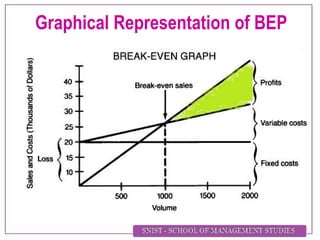

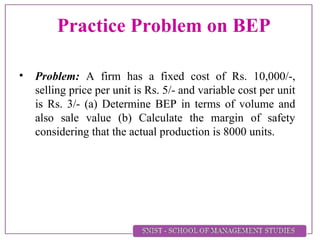



Break Even Analysis refers to analyzing the break-even point (BEP), which is the point at which total revenue equals total cost, resulting in no profit or loss. The BEP denotes the minimum production volume needed to avoid losses. Determinants of BEP include selling price, contribution margin, contribution margin ratio, fixed costs, and variable costs per unit. Examples then demonstrate calculating BEP in terms of units and sales value, margin of safety, and production needed to achieve a specified profit level.







