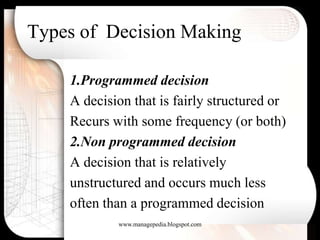
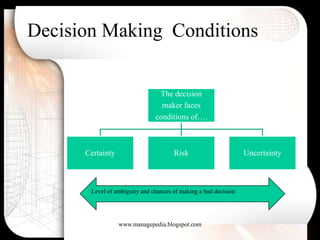
Strategic decisions are made by top management, are future-oriented, require significant resources, and have long-term impacts on an organization. They are difficult to define, rarely have a single best solution, and involve trade-offs. Managers use both rational and behavioral models in decision-making. The rational model assumes complete information and logical evaluation of alternatives, while the behavioral model recognizes limitations in information, bounded rationality, satisficing, intuition and escalation of commitment.