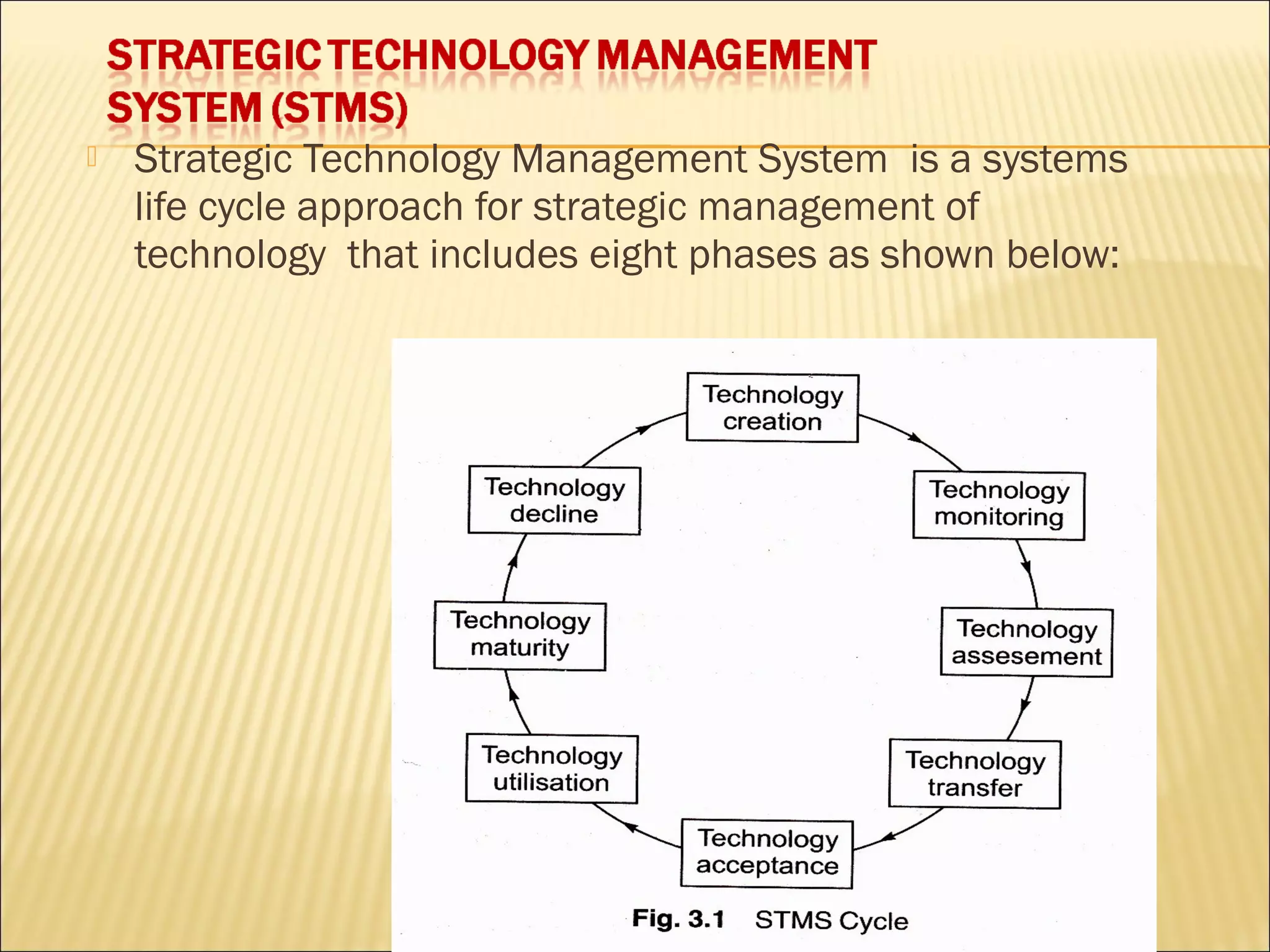
Technology management (MOT) involves the development, planning, implementation, and assessment of technological capabilities to achieve organizational strategic objectives. At the national level, MOT aims to ensure competitive technological advantage, while at the enterprise level, it focuses on gaining and maintaining a strong technological position to support competitive strategies. Key tasks of MOT at the enterprise level include technology planning, R&D management, and innovation management. Strategic management of technology (SMOT) adopts a long-term perspective and impacts all organizational levels and functions. An effective strategic technology management system (STMS) follows an eight-phase systems life cycle approach for strategic MOT.