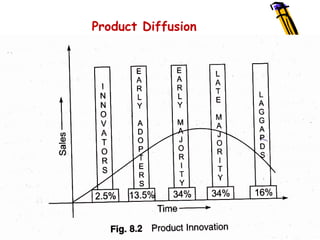
Technology diffusion refers to the spread of new technologies and applications across nations, organizations, industries, and users. It involves the study of how, why, and at what rate new ideas and technologies are adopted. There are several factors that influence the diffusion of technologies within businesses, including the relative advantages over existing technologies, compatibility with existing values, ease of understanding and application, and ability to experiment. Technologies typically diffuse first within innovative organizations, then major competitors, and finally smaller organizations and laggards. The rate of diffusion depends on profitability and investment requirements.