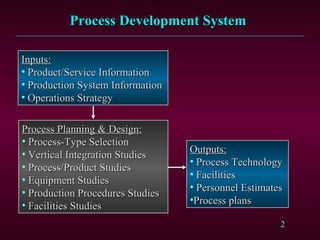
The document discusses process development, which involves planning and designing production processes based on inputs like product information, production systems, and operations strategies. Key factors that affect process development include the nature of product demand, degree of vertical integration, production flexibility, degree of automation, and product quality needs. The document outlines different types of process designs like product-focused, process-focused, and group technology approaches. It also discusses considerations around process reengineering.