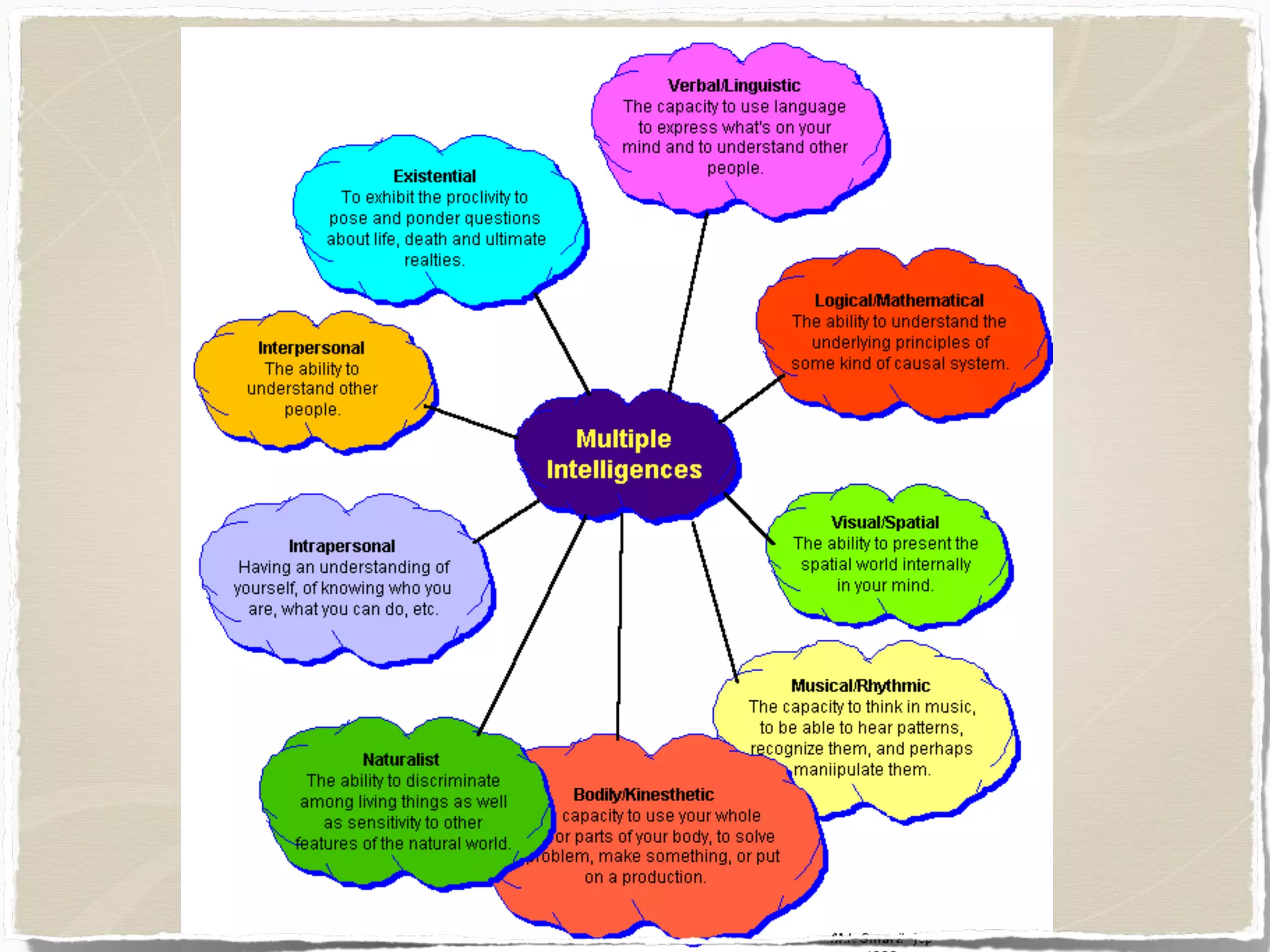
This document discusses key issues in teaching young learners including classroom management, special needs of students, dyslexia, attention deficit disorder, multiple intelligences, tutoring, use of technology, and importance of professional support. It provides strategies for managing behavior, meeting needs of students with dyslexia or ADHD, incorporating multiple intelligences, creating effective tutoring lessons, using technology safely, and joining professional organizations. Professional support organizations can help teachers stay informed on educational developments.