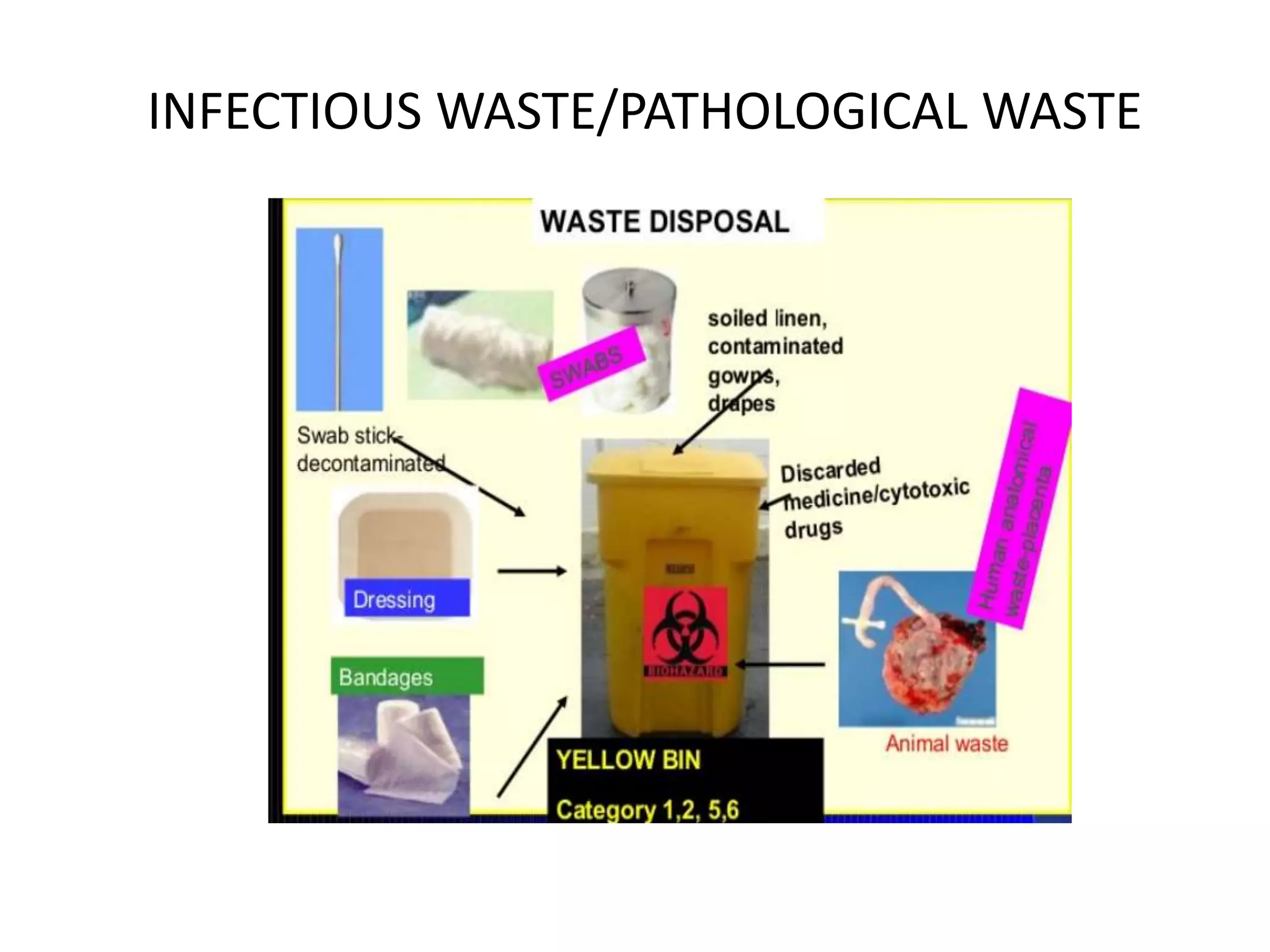
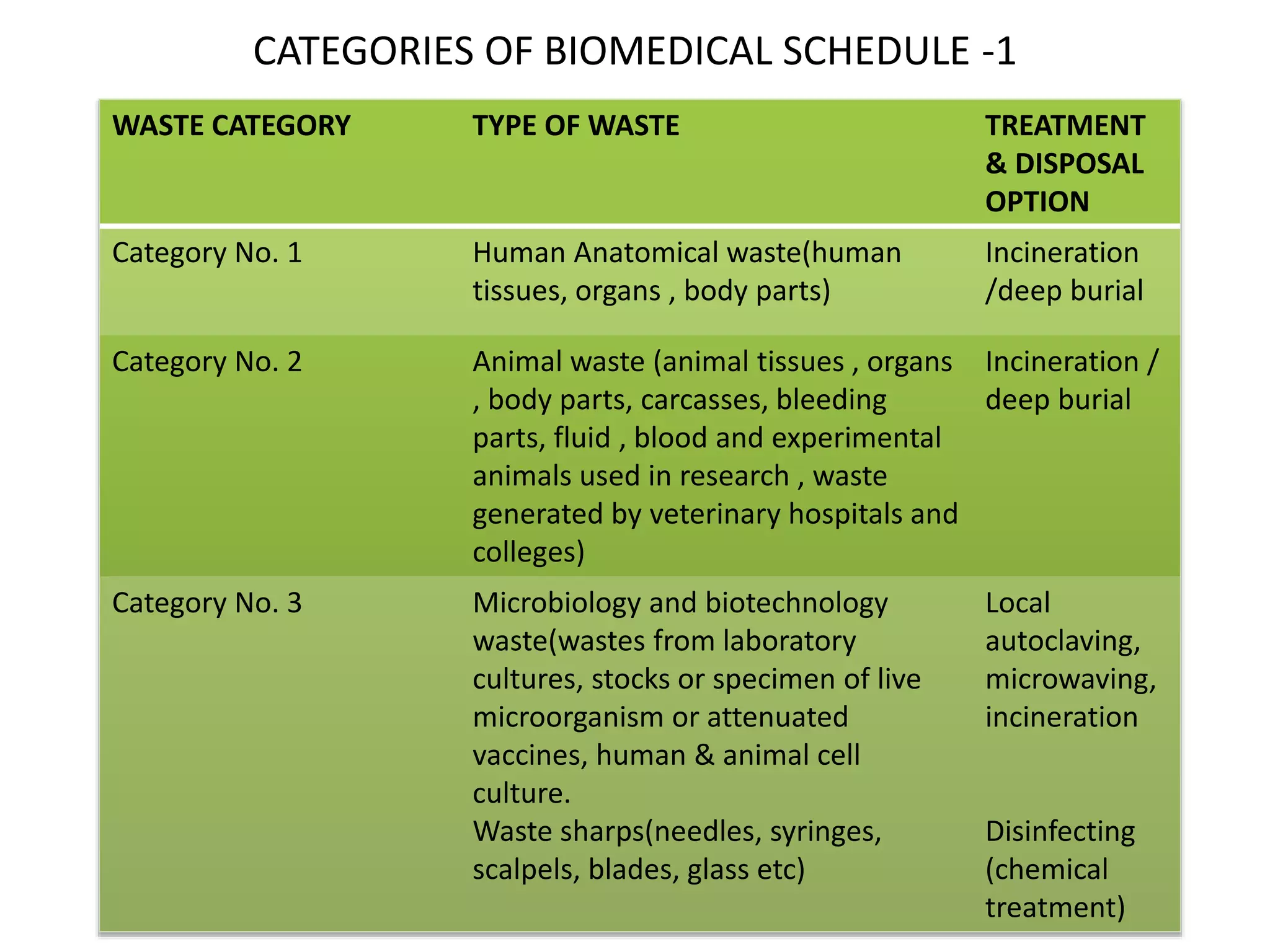
Hospital waste is categorized as hazardous or non-hazardous. Hazardous waste includes infectious waste like human tissues, sharps that can transmit disease, and expired pharmaceuticals. Proper management of hospital waste involves segregating, collecting, storing, transporting, and treating waste. Common treatment methods are incineration, chemical disinfection, and autoclaving to reduce pathogens before waste is disposed of safely. Proper hospital waste management is important to protect staff, patients, and the environment from disease and contamination.