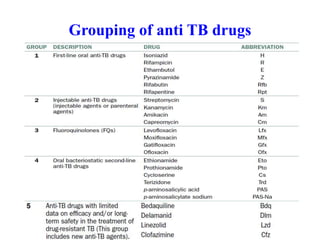
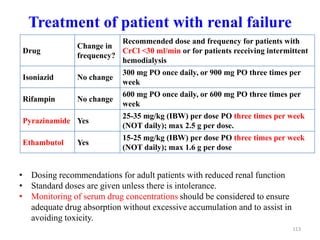
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It typically affects the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body. There are several drug regimens used to treat TB, with the primary first-line drugs being isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, ethambutol, and streptomycin. Treatment must continue for a sufficient time, such as 6-9 months, to fully cure the infection and prevent relapse or development of drug resistance. Second-line drugs are used for cases of drug-resistant TB or in cases where patients cannot tolerate first-line drugs. The goals of TB treatment are to cure the patient, prevent death, prevent relapse



























![50
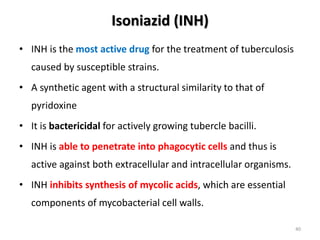
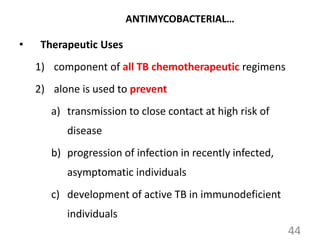
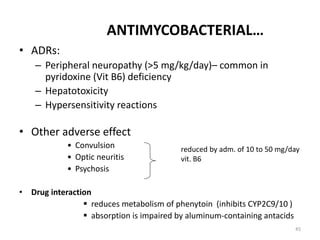
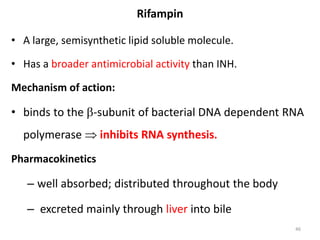
ANTIMYCOBACTERIAL…
3. Imparts a harmless red-orange color:
– to urine, feces, saliva, sweat, tears, and contact
lenses.
– Patients should be advised of such discoloration of
body fluids.
Drug interaction
– is a strong microsomal enzyme inducer; enhances its own
metabolism as well as other drugs [warfarin, Steroids, HIV
protease inhibitors , NNRTIs, & ketoconazole]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13-240408223004-fd94392b/85/13-Tuberculosis-management-37-320.jpg)


















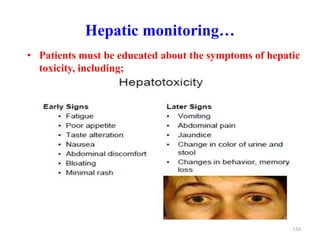
![Hepatic monitoring
• Obtain baseline liver function tests (LFTs)
a. serum transaminase enzymes
– (AST) [normal 0-40 u/l]
– (ALT) [normal 0-40 u/l]
b. alkaline phosphatase [normal 25-115 u/l]
c. Total bilirubin [normal 0.2-1.5 mg/dl]
• Repeated monthly hepatic enzyme measurements in the
following settings:
– Abnormal baseline results
– A drug reaction is suspected
– Liver disease (eg, hepatitis B or C, alcohol abuse)
– Pregnancy and the first three months postpartum
– Combination therapy including pyrazinamide in continuation
phase
115](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13-240408223004-fd94392b/85/13-Tuberculosis-management-67-320.jpg)