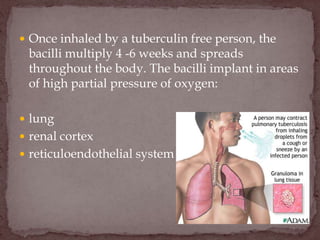
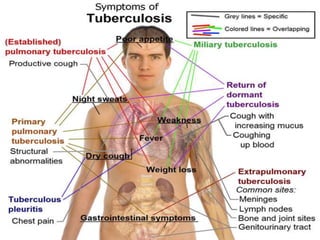
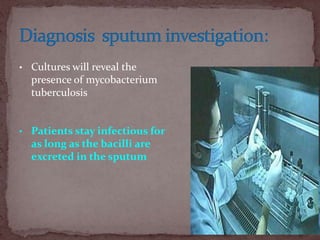
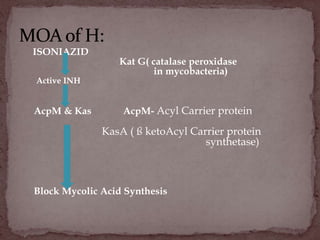
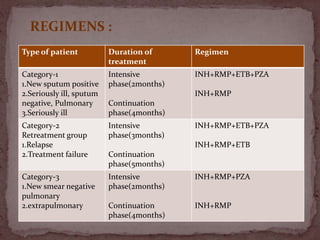
Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious infectious disease primarily caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, affecting mainly the lungs but can spread to other areas. Approximately 1/2 of the global population is infected, with high prevalence in developing countries, and typical symptoms include a chronic cough, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Treatment involves a combination of first-line and second-line drugs, with a focus on standardized, supervised approaches to ensure adherence and curtail drug resistance.